![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
how many vertebrae are in each level of the spinal cord? how do the spinal nerve roots numbers compare to the vertebrae number? |
C - 7 bones but 8 nerve roots. T - 12. L - 5. S - 5 fused. Coccyx - 3-5. spinal nerves in cervical region are named for bone BELOW because there are 8 nerves and 7 bones. All other segments are named for bone above. C5 nerve is ABOVE C5 bone. T5 nerve is BELOW T5 bone. |
|
|
what surface landmarks correspond to spinal column levels? |
Prominent SP = C7 Inf border of scapula with hands by side = T7 intercristine line = L4 |
|
|
outline the major ligaments of the spinal column: what ligaments do you cross doing an epidural? |
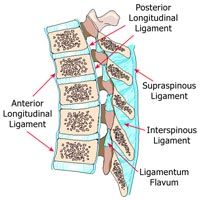
ant & post longitudinal are on each side of vertebral body. supra spinous, interspnous and ligamentum flavum are crossed by needle. |
|
|
what are the major difference in anatomy of the thoracic vs lumbar region? |
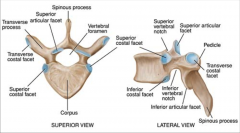
SP: T is more vertical with tip overlying vertebral body below. L is shorter/horizontal. TP: T is longer, L more stubby Articular facet joints: the joints b/w 2 vertebral bodies. T are vertical to allow rotation, lumber horizontal for flex/ext. Canal: T is rounder & smaller. L pyramid shaped, bigger. Epidural space: |
|
|
where are the major vessels in the spinal column situated? Are they at risk with epidural needle? |
longitudinal arterial system (ant and post arteries) are in the dural sac and should not be hit by epidural. The segmental arterial system comes in at each level with the spinal nerve roots that run through epidural space...they are not in the posterior epidural space so shouldn't be hit. extra dural venous plexus is in the epidural space...most of it is anterior to the dural sac but some is posterior and can be hit by needle |
|
|
What is the dural sac? where does it run to? what are the layers of it and where do those layers sit? |
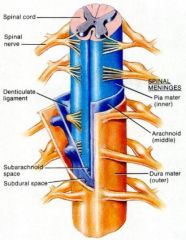
The dural sac is everything the dura envelops, runs down to S2: Dura is outer layer, Arachnoid inside this adjoining it. CSF sits between arachnoid and pia. Pia coats the spinal column which floats in dural sac. dura (& its layers) covers the spinal nerve roots as they exit. |
|
|
what is the epidural space? what are its borders? |
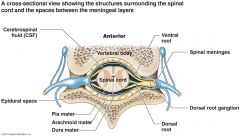
epidural space is outside the dura. i.e. if you go to far its a "dural tap" Borders: ant=verterbral body/post longitudinal ligament Post= ligamentum flavum/verterbral arch. NOTE - the dura IS NOT the anterior border of the epidural space as the epidural space wraps circular around it to vertebral body. |
|
|
what is contained in the epidural space? |
Dural sac and its spinal column spinal nerve roots fat extra dural venous plexus. spinal arteries (travel along nerve roots to spinal cord) lymphatics |
|
|
what are the key points about the epidural venous system? |
valveless and continues with pelvic veins and intracranial veins (issue if feed cath into vein - can inject LA into cranium) drain into azygous vein to IVC, as they are Valveless=subject to intra abdominal pressure (> in preg/abdo mass). Larger venous system in thoracic than lumbar region. |

