![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Turner syndrome manifestations
|
-primary amenorrhea, high arched palate, and widely spaced nipples are characteristic manifestations of Turner syndrome
-an additional characteristic finding is OVARIAN DYSGENESIS, which manifests as "streak gonads" |
|
|
Bartonella henselae
|
-Bartonella henselae causes cat-scratch disease --> fever/lymphadenopathy (self-limited)
-organism resides in oral cavity of cats – transmitted to humans by cat scratches and bites -Bartonella henselae can also cause bacillary angiomatosis (BA) in immunocompromised patients, with red-purple papular skin lesions. --these vascular proliferations may also be found within the viscera --bacillary angiomatosis can be fatal if left untreated -Lastly, Bartonella henselae can cause culture-negative endocarditis |
|
|
Toxic shock syndrome
|
-toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is caused by Staphylococcus aureus
-patients present with fever, vomiting diarrhea, desquamation, and hypotension |
|
|
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
|
-hemolytic uremic syndrome is triad of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and renal insufficiency CAUSED BY E.COLI O157:H7
|
|
|
Malignant otitis externa
|
-pseudomonas aeruginosa can cause malignant otitis externa in individuals using contaminated pools and hot tubs
|
|
|
Reactive arthritis
|
-reactive arthritis is a type of HLA-B27-positive reactive arthritis classically accompanied by urethritis and conjunctivitis
-reactive arthritis is associated with Chlamydia, Shigella, Salmonella, Yersinia, and Campylobacter infections |
|
|
Condylomata acuminata
|
-condylomata acuminata = genital warts
--caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), type 6 and 11 --condylomata acuminata presents as soft, tan, cauliflower-like masses on penis, vulva, and peri-anal areas |
|
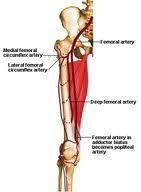
Femoral neck fracture
|
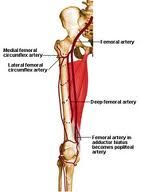
-a femoral neck fracture can damage the blood supply to the femoral head and neck
--most common with displaced fractures --the MEDIAL FEMORAL CIRCUMFLEX ARTERY provides majority of blood supply to femoral head and neck --injury to this vessel can cause avascular necrosis of the femoral head |
|
|
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
|
-AR disorder of neutrophil phagosome-lysosome fusion
-results in neurologic abnormalities, PARTIAL ALBINISM, and an immunodeficiency caused by defective neutrophil function -Ched – head problems (neurologic) -Hi-gosh you're white (albinism) |
|
|
GI embryo
|
-abnormal rotation and fixation of midgut early during fetal life results in intestinal malrotation
-two main manifestations of this condition are intestinal obstruction (due to compression by the adhesive bands) and midgut volvulus (intestinal ischemia due to twisting of vessels). |
|
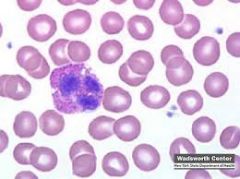
Eosinophils
|
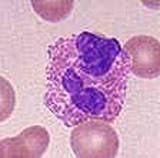
-late phase of an atopic asthma attack involves mucosal infiltration by eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils
-eosinphils have biloped nuclei, and are backed with large eosinophilic (pink) granules of relatively uniform size -eosinophils also release MAJOR BASIC PROTEIN, a potent ANTI-HELMINTHIC toxin capable of damaging human epithelial and endothelial cells. -vs. neutrophils tend to have multilobed (more than 3) nuclei and stain relatively pale -vs. basophils contain granules that stain dark blue, are irregularly sized, and usually obscure the nucleus. |
|
|
Blood transfusion and calcium chelation
|
-normal serum calcium level is 8.4-10.2 mg/dL
-patients who receive equivalent of more than one body blood volume (5-6 liters) of whole blood transfusions or packed red cells over period of 24 hours may develop elevated plasma levels of CITRATE (a substance added to stored blood). -citrate chelates calcium and magnesium, and may reduce their plasma levels, causing paresthesias |
|
|
Normal sorbitol metabolism
|
-aldose reductase converts glucose into sorbitol, which is further metabolized into FRUCTOSE by sorbitol dehydrogenase
-this pathway is most active in the seminal vesicles, because sperm use fructose as their primary energy source -other tissues that have sorbitol dehydrogenase activity include retina, renal papilla, and Schwann cells, but these have much less sorbitol dehydrogenase activity - |
|
|
Sorbitol dehydrogenase in the lens
|
-human lens has significant levels of sorbitol dehydrogenase, which allows for production of fructose
-however, this enzyme has much lower Vmax in sorbitol-to-fructose direction than in reverse direction -when glucose levels are low, the limited forward activity of this enzyme is sufficient to convert enough sorbitorl into fructose to prevent sorbitol accumulation --but long-standing hyperglycemia can lead to production of excessive amounts of sorbitol that is trapped in cells --this leads to increased osmotic pressure, facilitating influx of water into lens cells, causing lens degeneration --> lens opacification and cataract formation |
|
|
Lipoic acid
|
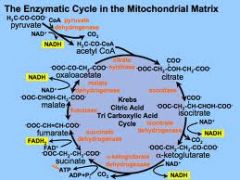
-lipoic acid is a cofactor for several mitochondrial enzymes
--pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH –deficiency results in lactic acidosis) --PDH converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA, which can enter the Krebs cycle and be made into citrate by citrate synthase (first step) --branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase (deficiency results in maple syrup urine disease) --alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase |
|
|
Positive and negative predictive values
|
-these depend on disease prevalence in population
-vs. sensitivity and specificity of a test do not depend on prevalence of disease in population |

