![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Element 1 |
Hydrogen (H) 1 gas |
|
|
Element 2 |
Heluim (He) 4 gas |
|
|
Element 3 |
Lithium (Li) 7 solid |
|
|
Element 4 |
Beryllium (Be) 9 solid |
|
|
Element 5 |
Boron (B) 11 solid |
|
|
Element 6 |
Carbon (C) 12 solid |
|
|
Element 7 |
Nitrogen (Ni) 14 gas |
|
|
Element 8 |
Oxygen (O) 16 gas |
|
|
Element 9 |
Fluorine (F) 19 gas |
|
|
Element 10 |
Neon (Ne) 20 gas |
|
|
Element 11 |
Sodium (Na) 23 solid |
|
|
Element 12 |
Magnesium (Mg) 24 solid |
|
|
Element 13 |
Aluminum (Al) 27 solid |
|
|
Element 14 |
Silicon (Si) 28 solid |
|
|
Element 15 |
Phosphorus (P) 31 solid |
|
|
Element 16 |
Sulfur (S) 32 solid |
|
|
Element 17 |
Chlorine (Cl) 35 gas |
|
|
Element 18 |
Argon (Ar) 40 gas |
|
|
Element 19 |
Potassium (K) 39 solid |
|
|
Element 20 |
Calcium (Ca) 40 solid |
|
|
molecule |
-a molecule is a unit of two or more atoms (of the same or different elements) that are bonded together
|
|
|
molecule element |
-is a molecule consisting of atoms of the same element
|
|
|
7 diatomic molecules |
H2,N2,02,F2,Cl2,Br2,I2 (these elements naturally exist as two atoms bonded together) |
|
|
molecule compound |
-a molecule consisting of 2 or more different elements ex. water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), salt (NaCl) |
|
|
ionic bond |
-between a metal and a non-metal -non-metal takes electrons from the metal -metal becomes a positive ion, non-metal becomes a negative ion -metal always gives,non-metal always takes
|
|
|
covalent |
-occurs between two non-metals -the two atoms share electrons to complete their valence shell |
|
|
ion |
-charged version of an atom |
|
|
ionic compounds |
-are formed when cations and anions bond together due to opposite charge *cations:a positively charged ion cause by the loss of electrons *anions: a negatively charged ion caused by the gain of electrons |
|
|
Metals x Metals |
-mixed metals create alloys *not bonded *solutions
|
|
|
Metal x Non-metals |
-results in formation of ions when joined leading to an ionic bond -cations and anions created -cations and anions attracted to each other due to opposite charge, ionic bond created
|
|
|
Naming rule 1 (Metal x Non-metal) |
-when a metal bonds to a non-metal, the name of the metal comes first and non-metal comes second, with the ending "ide" ex.salt-NaCl- Soduim chloride |
|
|
Non-metal x Non-metal |
-bond through the sharing of electrons resulting in a covalent bond
|
|
|
Naming rule 2 (Non-metal x Non-metal) |
-use the names in order,second non-metal had "ide" on the end -Latin prefixes (1=mono,2=di,3=tri,4=tetra) ex.CO2- Carbon dioxide *never start the first with mono |
|
|
Bonding Behaviors |
-atoms bond to create stability -noble gases are the most stable due to full valence shells -elements behave in a way that will get their valence shells full, this is done by gaining,losing or sharing electrons |
|
|
Alkali Metals |
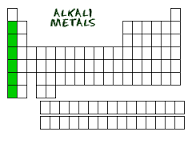
-group 1 *hydrogen not included -soft,shiny,silvery metals, highly reactive,low density (floats) -includes Li,Na,K and ect.. |
|
|
Alkaline Earth Metals |
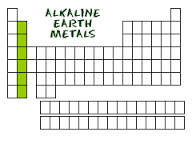
-group 2 -soft and shiny but not soft -burn with bright colorful flames,ideal for fireworks -includes Be,Mg,C ect.. -usually found in compounds |
|
|
Halogens |
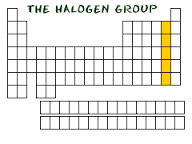
-group 17 -includes Fl,Cl,I -very reactive, hard to find in elemental form -react well with Alkali metals -poisonous effect ex. I w/h achohol used to clean cuts |
|
|
Noble Gases |
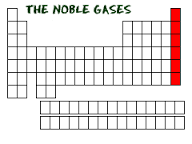
-group 18, colorless,odorless,tasteless, glow brightly w/h electrical currents -generally non-toxic (not Radon) argon=blue,krypton=pink,xenon=purple,neon=red |

