![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
156 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Parietal lobe |
Sensation of touch Vibration, Temperature Spatial and visual preception Interprets lenquage, receives information about hearing, vision, motor, sensory, memory AGNOSIA, AGRAPHIA, ALEXIA, APROXIA |
|
|
|
Color of matter in the brain |
Gray - outside White - inside |
|
|
|
Hippocampus |
Temporal lobe, memory, sends memories to cerebral hemisphere for storage, and RETRIEVES MEMORIES when needed |
|
|
|
Basal ganglia |
Part of the Cerebrum Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, Tourett’s syndromes, ADD, OCD, Addictions |
|
|
|
Amyglada, Almond shaped |
Emotional and Social processing. Fear, pleasure, arousal, processing of memory, formation of emotional memories. |
|
|
|
Thalamus |
It receives information from the cerebellum, basal ganglia, and all sensory pathways except for the olfactory tract, it goes to cerebral cortex. Damage - thalamic pain syndrome,contralateral side. |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Autonomic NC, hormone regulation. Temperature, hunger, sex, sleeping |
|
|
|
Epithalamus |
Pineal gland, secrets melatonin, circadian rythms |
|
|
|
Subthalamus |
Located between thalamus and hypothalamus. Regulates movement produced by skeletal muscles. Associated with Basal ganglia, Substantia niagra |
|
|
|
Midbrain |
Connects forebrain to the hindbrain. Reflex center for visual, auditory, and tactile responses |
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
Coordination, balance , posture. Located below the occipital lobe. Damage produce ipsilateral impairment. |
|
|
|
Ponds |
Respiratory rate, orientation of the head, cranial nerves 5 through 8 |
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata ( myelencephalon) |
Respiration/ Heart rate Vomiting, coughing, sneezing. Damage producing contralateral impairment Cranial nerves 8 to 12 |
|
|
|
Brainstem |
Midbrain, ponds, medulla. Primitive function. Damage- brain death |
|
|
|
Anterior Cerebral artery |
Bilateral oclusion -produce paraplegia, incontinence |
|
|
|
Middle cerebral artery |
Bilateral occlusion - produce contralateral hemiplegia and sensory impairment. Global, Wernicke’s, Broca’s aphasia |
|
|
|
Posterior cerebral artery |
Occlusion will produce: thalamic pain syndrome, cortical blindness. Pupil continues to function regarding light. |
|
|
|
Vertebral- Basilar artery |
Damage can cause: locked in syndrome, coma or vegetative state. |
|
|
|
Dysarthria |
Slurred speech due to the motor deficit of the tongue or essential speech muscles. |
|
|
|
Femoral nerve innervation? |
Vastus lateralis, Vastus medialis, Vastus intermedios Rectus femoris Iliacus Sartoreus Pectineus |
|
|
|
Dysdiadochokinesia |
Inability to perform rapidly alternating movements Example: pronation, supination |
|
|
|
Hemorrhagic stroke symptoms? |
A sudden severe headache, vomiting, high blood pressure. It’s a rapture of the blood vessel, and leaking of the blood into the brain. |
|
|
|
Glasgow Coma Scale |
Minimum 3, Maximum 15 8 or less correlated with COMA 9 - 12 moderate brain injury 13 - 15 mild brain injury |
|
|
|
Deep tendón reflex testing |
0 - no reflex 2+ normal response 4+ hyperactive reflex response, abnormal |
|
|
|
Primary risk factor for CVA? |
Heart disease |
|
|
|
The buttocks, posterior thigh, and posterior lower extremity associated with which dermatome? |
S2 - medial aspect S1 - lateral aspect ( little piggy) |
|
|
|
Achilles’ tendon reflex associated with which nerve root? |
S1 and S2 |
|
|
|
Which structure responsible for production of cerebrospinal fluid? |
Choroid plexus |
|
|
|
Which lobe of the brain receives auditory, motor, sensory, visual and memory information which is processed to provide meaning to the objects. |
Parietal |
|
|
|
Trendelenburg gait |
A gate pattern that denotes gluteus medius weakness, excessive lateral trunk flexion and weight shifting over the stance leg. |
|
|
|
Gluteus medius |
Superior gluteal nerve L4 - S1 Abduction Hip stability Ant/ internal Post/ external rotation of the hip. |
|
|
|
Positional changes detected by inner ear stimulating which primitive reflex? |
Tonic labyrinthine reflex |
|
|
|
Tabetic gait |
A high stepping ataxic gait pattern in which the feet slap the ground |
|
|
|
Locked - in syndrome |
a medical condition, usually resulting from a stroke that damages part of the brainstem, in which the body and most of the facial muscles are paralyzed but consciousness remains and the ability to perform certain eye movements is preserved. |
|
|
|
Fasciculations |
Involuntary contraction or twitching of the muscle fibers which are visible under the skin. Fasciculations are more common with the LMN disorders, and are topically absent in UMÑ disorders. |
|
|
|
Kernig’s sign |
Meningitis
Pain with hip flexion combine with knee extention |
Pain with hip flexion combine with knee extention |
|
|
Spinocerebellar tract ( dorsal) |
Ipsilateral subconscious proprioception, tension in the muscles, joint sense, posture and trunk and LOWER extremities |
|
|
|
Brostorm-Evans prosedure |
There are two common variations of Brostrom procedures: The Brostrom-Evans or the Brostrom-Gould procedure. Each procedure seeks to repair or recreate the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) to restore ankle stability. |
|
|
|
What muscle used for Brostorm- Evans prosedure? |
Peroneus Brevís Superficial Peroneal nerve L4-S1 Plantar flexion, eversión |
|
|
|
Spinocerebellar tract ( ventral ) |
Ipsilateral subconscious proprioception, tensión in the muscles,joint sense, posture of the trunk, UEs and LEs. Crossing and subsequent recrossing at the level of the ponds for subconscious proprioception. |
|
|
|
Spinocerebellar- olivary tract |
Ascends to cerebellum and relays information from cutaneous and proprioceptive organs |
|
|
|
Spinoreticular tract |
Afferent pathway for the reticular formation that influences level of consciousness |
|
|
|
1.Spinotectal tract ( Ascending ) 2. Tectospinal tract ( Descending ) |
1. Providing afferent information for spinovisual reflexes and assist with movement of eyes and head toward the stimulus. 2. Extrapyramidal motor tract responsible for CONTRALATERAL postural muscle tone, associated with auditory/ visual stimuli. |
|
|
|
Spinothalamic tract ( anterior ) |
Sensory tract to light touch and pressure. Decussates |
|
|
|
Spinothalamic tract ( lateral ) |
Sensory tract for pain and temperature sensation |
|
|
|
Spinothalamic tract ( lateral ) |
Sensory tract for pain and temperature sensation Decussates |
|
|
|
Corticospinal tract ( anterior ) |
Piramidal motor tract responsible for ipsilateral voluntary, discrete ( благоразумный ), and skilled movements. |
|
|
|
Corticospinal tract ( anterior ) |
Piramidal motor tract responsible for ipsilateral voluntary, discrete ( благоразумный ), and skilled movements. |
|
|
|
Corticospinal tract ( lateral ) |
Pyramidal motor tract responcible for CONTRALATERAL voluntary movement |
|
|
|
Result of damage to Corticospinal tract? |
1.Babinski sign 2.Absent superficial abdominal reflexes 3. Cremasteric reflex |
|
|
|
Pyramidal tracts vs Extrapyramidal tracts |
The pyramidal tracts (corticospinal tract and corticobulbar tracts) may directly innervate motor neurons of the spinal cord or brainstem (anterior (ventral) horn cells or certain cranial nerve nuclei), whereas the extrapyramidal system centers on the modulation and regulation (indirect control) of anterior (ventral) horn area. |
|
|
|
Brudzinski sign |
Flexion of the neck facilitates flexion of the hips and knees Meningitis |
|
|
|
Arnold- Chiari malformation? How many kinds? |
Developmental deformity of the hindbrain( Cerebellum, Ponds) Type 1: herniation of cerebellum tonsils, no symptoms Type 2: malformation of the brain stem and cerebellum, leading to the extension of medulla and cerebellum through the foramen magnum, produces progressive HYDROCEPHALUS. |
|
|
|
Subarachnoid space |
The area between the arachnoid and Pía mater that contains CSF and circulatory system for the cerebral cortex |
|
|
|
Burnnstrom Synergy Patterns Lower Extremity Flexion Inversión only one common thing with LEE |
Hip flexion, ABD, external rotation Knee flexion to approximately 90 degrees Ankle dorsi flexion, inversion Toe extention
|
|
|
|
Burnnstorm Synergy Patterns Upper Extremity Flexion For UEE, wrist and finger flexion the same |
Scapular retraction and/ or elevation Shoulder external rotation, ABD to 90 degrees Elbow flexion Forearm supination Wrist and finger flexion |
|
|
|
What are the most coming sites of non- operative osteoporotic fracture ? |
Distal radius, proximal femur, vertebral body Tibial plateau is NOT common site. |
|
|
|
Contralateral impairment |
Thalamus Medulla Oblongata (myencephalon ) |
|
|
|
Brown-Sequard syndrom |
Incomplete SC injury, stab wound. Same side: paralysis, vibration, position sense ( corticospinal, dorsal column) Contralateral side: temperature, pain ( lateral spinothalamic tract ) |
|
|
|
Muscles innervated by TIBIAL NERVE |
Soléis Popliteus Plantaris Tibialis posterior Gastrocnemius Flexor hallucus Longus Flexor Digitorum Longus |
|
|
|
Sensory receptors |
Epidermis Pain, itch |
|
|
|
Sensory receptors |
Epidermis Pain, itch Dermis- just pain |
|
|
|
Sensory Receptors Markel’s disk |
Stratum spinous Touch |
|
|
|
Sensory Receptors Meissner’s Corpuscle |
Papillary dermis Touch |
|
|
|
Sensory receptors Ruffin isn’t corpuscle |
Papillary dermis Wormth |
|
|
|
Sensory receptors Ruffini’s corpuscle |
Papillary dermis Wormth |
|
|
|
Sensory Receptors Krause’s end bulb |
Papillary dermis Cold |
|
|
|
Sensory Receptors Pacinian corpucle |
Reticular dermis Pressure and vibration |
|
|
|
Saltatory conduction |
Decreases the use of sodium-potassium pumps and increases speed of conduction |
|
|
|
Afferent ( sensory) cranial nerves |
Olfactory Optic Vestibulocochlea ( acoustic nerve) |
|
|
|
Afferent/ Efferent Cranial nerves |
Trigéminas Facial Glosopharyngeal Vagus |
|
|
|
Q angle |
Measured in supine Mail 13 degrees Femail 18 degrees |
|
|
|
Yerganson’s test |
For Bicipital tendinitis Therapist resists active forearm supination and shoulder lateral rotation while palpating bicipital groove. Positive: pain in the bicipital groove |
|
|
|
Lateral epicondylitis test |
Extensor Capri Radialis Longus and Brevis Test: Elbow flexed, forearm pronates, wrist flexed. Therapist stabilizes the elbow with one hand, and and resist active extension of the third digit with other hand ( proximal interphalangial joint.
|
|
|
|
What kind of damage to the extrapyramidal tracts results in? |
Significant parálisis Hypertonicity Exaggerated DTR Clasp-knife reaction |
|
|
|
Types of sensation 1. Superficial 2. Deep 3. Cortical |
1. Temperature, pain, light touch 2. Proprioseption, kinesthesia, vibration 3. Barognosis, Stereognosis, two-point discrimination, localization of touch, bilateral silmuntaneous stimulation |
|
|
|
What is weight bearing status for patient one week post op. with lateral ankle reconstruction? |
Non-weight bearing with bilateral axillary crutches. |
|
|
|
Idiopathic |
relating to or denoting any disease or condition which arises spontaneously or for which the cause is unknown. |
|
|
|
Idiopathic osteoporosis |
Idiopathic osteoporosis refers to the development of osteopenia and fractures with minimal or no trauma in otherwise young, healthy individuals who are not postmenopausal or have other, identifiable secondary causes of osteoporosis. |
|
|
|
Perception |
Ощущение |
|
|
|
What is bucal administration of the drug? |
Drug is placed between cheeks and gums ( absorbs through the oral mucosa). |
|
|
|
Is walking backwards on the treadmill open- chain exercise? |
No, it’s closed-chain exercise |
|
|
|
R side of the heart |
Tricuspid Pulmonary valves |
|
|
|
L side of the heart |
Mitral Aortic valves |
|
|
|
regurgitation |
the action of bringing swallowed food up again to the mouth. |
|
|
|
Регургитация |
Регургита́ция — быстрое движение жидкостей или газов в направлении, противоположном нормальному, возникшее в полом мышечном органе в результате сокращения его стенки. Наиболее частой причиной регургитации (в ЖКТ)... Читать ещё |
|
|
|
What is positive test for Clarke’s sign ? |
Patellofemoral dysfunction. The examiner presses down on the patella and asks PT to contract quadriceps. Positive test is pain or inability to hold the contraction. |
|
|
|
What STROKE STANDING TEST used for? |
To identify SPONDYlOLISTHESIS. Single-leg hyperextension. |

|
|
|
Waddell’s Signs |
Test which help asses whether a patient is faking back pain (malingering back pain, придуманная боль) |
|
|
|
Burns’ test |
Test for differentiating between organic and non-organic pain. Patient requires to kneel, bend over the chair and touch the floor. (malingering back pain) |
|
|
|
Hoover’s test |
Patient puts heel pressure one at the time, on the PTA’s hands while supine. (malingering back pain) |
|
|
|
Symptom magnification syndrome, also known as MALINGERING. |
Non- organic pain (брехня) Waddell’s sign Hoover’s test Burn’s test |
|
|
|
Phonophoresis |
Ultrasound which helps with absorption of medication. |
|
|
|
What is loos-packed position for tibiofemoral joint? |
25 degrees of flexion |
|
|
|
What is loose-packed position for hip joint? |
30 degrees flexion 30 degrees ABD Slight external rotation |
|
|
|
What is loos-packed position for talocrural joint? |
10 degrees of plantar flexion |
|
|
|
What is loos-packed position of glenohumeral joint? |
55-70 degrees of ABD 30 degrees of horizontal ABD 0 degree of rotation |
|
|
|
What parts of the brain ANTERIOR CEREBRAL ARTERY supplies? |
1. Medial part of FRONTAL and PARIETAL lobe. 2. BASAL GANGLIA 3. CORPUS CALOSUM |
|
|
|
What pt can experience with damage to the ANTERIOR CEREBRAL ARTERY? |
1. Contralateral motor and sensory loss, with LEs affected more than UEs. 2. Mental impairment and behavioral changes. 3. Apraxia and slow movement 4. Urinary incontinence. |
|
|
|
What MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY supplies? |
Lateral cerebral hemispheres: Frontal, Parietal, Temporal |
|
|
|
What pt can experience with the damage to the MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARYERY? |
1. Contralateral motor and sensory loss, with face and UEs affected more than LEs. 2.Perceptual deficits 3. Homónymous hemianopsia 4. Broka’s, Wernicke’s, Global aphasia. |
|
|
|
What POSTERIOR CEREBRAL ARTERY supplies? |
1. OCCIPITAL lobe 2. Medial and inferior TEMPORAL lobe 3. Thalamus 4. Midbrain |
|
|
|
What patient can experience with damage to the POSTERIOR CEREBRAL ARTERY? |
1. Contralateral motor and sensory loss. 2. Visual AGNOSIA, oculomotor nerve palsy, homonymous hemyanopsia. 3. Involuntary movement 4. Pusher syndrome 5. THALAMIC PAIN SYNDROME |
|
|
|
What VERTIBROBASILAR ARTERY supplies? |
Medular Ponds Cerebellum |
|
|
|
What pt can experience with the damage to the VERTIBROBASILAR ARTERY? |
1. Wide variety of symptoms ipsilaterally and contra-laterally. 2. Can have cranial nerve involvement 3. Ataxia 4. Locked- in syndrome 5. Wallenberg’s syndrome. |
|
|
|
Dysphagia |
Difficulty swallowing |
|
|
|
Wallenberg syndrom |
Rear condition in which infarction or stroke occurs in the lateral MEDULLA. Ipsilateral: Hornets Syndrome, Tinnitus, Palatina- pharyngeal-larengeal paralysis Contralateral: loss of pain and temperature over the body |
|
|
|
Capsular end feel for knee 1.Flexion 2.Extension |
1. Soft ( muscle on fat/ muscle) 2. Firm ( capsular and ligament stretching) |
|
|
|
Capsular end feel for elbow extension? |
Bony/ hard ( bone on cartilage) |
|
|
|
Empty end feel? |
Usually it occurs when the clinician can not bring limb through the full ROM due to the pain . |
|
|
|
Plumb line alignment |
• Posterior to coronal suture • Through the external auditory meatus • Through the axis of the odontoid process ( Dens of Axis) • Midway of shoulder • Through the bodies of lumbar vertebrae • Posterior to the hip, anterior to the knee, anterior to the lateral malleolus • Through the calcaneocuboid joint |
|
|
|
Metabolic alkalosis |
Metabolic alkalosis is a condition that occurs when your blood becomes overly alkaline. Alkaline is the opposite of acidic. Our bodies function best when the acidic-alkaline balance of our blood is just slightly tilted toward the alkaline. |
|
|
|
Heart rate of the new born? |
70-170bpm |
|
|
|
Characteristics of COMPLEX REGIONAL PAIN SYNDROME? |
Abnormal release of NOREPINEPHRINE (sympathetic) in peripheral tissues, resulting in pain and increased sensitivity to peripheral stimulation. |
|
|
|
Integumentary: Red, Yellow, Black system. |
Red: pink granulation tissue Goal: Protect wound, maintain moist environment Yellow: moist, yellow slough Goal: remove exudate and debris; absorb drainage Black: black, thick Escher firmly adhered. Goal: debride necrotic tissue |
|
|
|
What bony provenances at risk for skin breakdown in a prolonged sitting position? |
Spines of the scapular Vertebral spinous processes Ischial tuberosity |
|
|
|
Vaulting gait |
compensatory mechanism used by transfemoral amputees to assist toe clearance during the prosthetic swing phase. It is defined by a plantar flexion of the contralateral ankle during the single-limb support phase. |
|
|
|
Vaulting |
A gait pattern where the swing leg advances by compensating through the combination of elevation of the pelvis and plantar flexion of the stance leg. |
|
|
|
How much oxygen nasal cannula delivers per minute? |
6 liters per minute |
|
|
|
Standard seat size of average adult W/C is? Armrest height? |
Width 18 inches Depth 16 inches Armrest- 9 inches above the seat |
|
|
|
With GASTROESOPHAGEAL reflux disease, what position is recommended for sleeping? |
Left sidelying |
|
|
|
Which of the following respiratory changes is MOST expected as are Doly of aerobic training? |
Increased diffusion capacity |
|
|
|
Diffusion capacity? |
Measures the transfer of gas from air in the lung. |
|
|
|
Diaphoresis |
Sweating to the unusual degree |
|
|
|
Pronator Teres |
Origin: med epicondyle Insertion: lateral surface of the radius Median nerve C6,C7 |
|
|
|
distensibility |
Растяжение |
|
|
|
Position for presence of the lateral epicondylitis? |
Wrist extension, forearm supination. |
|
|
|
Where wrist flexors originated? |
Medial Epicondyle |
|
|
|
Hallux Valgus deformity Shortening of the FLEXOR HALLUCIS BRAVIS, swellings of MTP joint |
Hallux valgus deformity is a very common pathological condition which commonly produces painful disability. It is characterised as a combined deformity with a malpositioning of the first metatarsophalangeal joint caused by a lateral deviation of the great toe and a medial deviation of the first metatarsal bone |
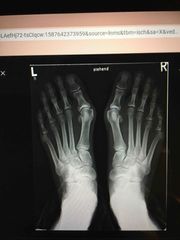
|
|
|
What is the best none invasive action the best beneficial for the HALLUX VALGUS condition? |
Recommend shoe with a wide toe box. |
|
|
|
What is heel cup would be appropriate to use for? |
Bone spur |
|
|
|
Spinal fusion |
Used for pain with unstable spinal segment, advanced arthritis or uncontrollable peripheral pain. Bone is harvested from the pt’s body ( iliac crest), and used to fuse two vertebrae together. Screws generally used to immobilize the segment. |
|
|
|
When LAMINESCOPY usually performed? |
Disc protrusion, and spinal stenosis. |
|
|
|
Visual Analog Scale |
Effective tool to obtain subjective intensity ratings of vertigo, light - headedness, dysequilibrium, and oscillopsia. 10 cm LINE |
|
|
|
Cauda Equina Lesion, presentation of the injury? |
Below L1 spinal level. Usually incomplete, as a resort considered to be a peripheral nerve injury. Characteristics: flaccidity, areflexia, and impairment of bowel and bladder function. |
|
|
|
Posterior cord, presentation of the injury? |
Very rare condition, tumor or vascular infarct to the posterior spinal artery Loss of proprioception, two-point discrimination, graphesthesia, stereognosis. MOVEMENT AND PAIN - intact Wide-based steppage gait |
|
|
|
Cerebellum gait? |
Staggering gait patern |
|
|
|
Double step gait pattern? |
Alternate steps are of the different length or at the different length |
|
|
|
Ausculation |
Listening to the sounds |
|
|
|
Crackle sound Synonymous with RALES. |
1.Discontinued, high-pitch piping sound 2. More often during inspiration 3. Due to the fluid accumulation in the distal airways, or when collapsed alveoli reopens during inspiration |
|
|
|
Pleural friction rub |
Crackling sounds with both inspiration and expiration |
|
|
|
Placement of hands with diaphragmic breathing? |
Dominant on rectus abdominus, should rais Non dominant on sternum, should have minimal movement. |
|
|
|
How long should each position last during the drainage of secretion? |
3-5 min |
|
|
|
What is normal hematocrit value for mails and females |
Males - 40 to 54 Females 37 to 47 mL/dL |
|
|
|
Inflammatory Pfase |
1-10 days Epithelialization begins in 24 hours |
|
|
|
Proliferation Phase |
3 to 21 days |
|
|
|
Avascular layer of the skin? |
Epidermis |
|
|
|
Rhonchi sound |
Low-pitched describes as “snoring” or “gurgling” Inspiration and expiration Air passing through the secretion. |
|
|
|
Wheeze sound |
Continuous “musical” or whistling sound, but variable Most frequently expiration, can be inspiration Commonly associated with ASTHMA and BRONCHITIS |
|
|
|
Stridor |
Continuous high-pitched wheeze heard with inspiration or expiration |
|
|
|
Charcot-Mary-Tooth disease |
Hereditary disorder, characterized by motor and sensory neuropathy. Progressive mm wasting and diminished deep tendon reflex. Initially affects dorsi flexors and EVERTORS, resulting in foot drop, STEPPAGE GAIT. It involves intrinsic mm of the hands, difficulty to grasp things. |
|
|
|
Guillain-Barre Syndrom |
Weakness begins distally and progresses proximal. LMN. BULBAR PALSY is common Etiology associated with bacterial and viral infections,surgeries, vaccines. CAMPILOBACTER JEJUNI |
|
|
|
Bulbar Palcy |
Cranial nerves 9,10,11,12 LMN, Medullary Oblongata Speech, swallowing, facial muscles. |
|
|
|
Huntington’s Disease |
Genetically transmitted neurological disorder of CNS. Degeneration of Basal Ganglia and Cerebral Cortex Ataxic gait, choreoathetoid movement, speech deterioration, unintentional facial expression, mental deterioration is common. |
|
|
|
Latency |
The time between onset of a stimulus and peak of the ensuing action potential |
|
|
|
Tortícolis |
Condition there head turned to one side. Tortícolis named for the side of the limited lateral flexion |
|

