![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Saccades |
most frequent eye movements characterized by rapid, "jump and rest" foveations of objects that occur when we scan a scene or read |
|
|
|
Smooth pursuit movements |
Eye movement characterized by a smooth motion without abrupt stars and stops. |
|
|
|
When are objects clearest? |
when we look directly at them |
|
|
|
differentiate between cones and rods |
cones = colour, fine detail rods = light/ motion |
|
|
|
Fovea |
area in the back of the eye consisting entirely of cones. area of clearest vision |
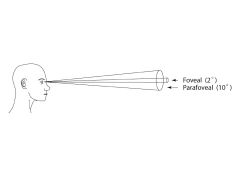
|
|
|
why do we have both rods and cones? why not just cones? |
advantage of rods: sensitive to motion in peripheral vision, has help us survive and evolve. rod vision better for fainter images. |
|
|
|
why do we move our eye? |
so we can see things clearly |
|
|
|
foveate |
to look directly at something |
|
|
|
how do animals that cant move their eyes compensate? |
with head movements |
|
|
|
vestibular movements |
eyes move in head (while head is moving) |
|
|
|
vergence movements |
eyes move closer together as things get closer to us |
|
|
|
microsaccades and drifts |
jiggling of eyes due to stimulation of photo-receptors |
|
|
|
how are saccades different in adults and children? |
adults can make larger (30 degree) saccades than infants (10 degrees) (known as hypometric saccade) |
|
|
|
name ways to monitor eye movements |
1. post-experiment video review 2. contact lens method 3. electrooculogram 4. LED-based corneal reflection 5. video based corneal reflection |
|
|
|
post-experiment video review for monitoring eye movements |
experimenters set up video recorder to know when subjects move eyes cons: lots of work to look at hours of video, many get tired of watching recordings so theyre not accurate, can't get subjects back when finally see that they moved eyes |
|
|
|
contact lens method of monitoring eye movements |
subject has to wear lens with wire and mirror, if ss moves eyes at all beam of reflected light moves to detect eye movement |
|
|
|
Electrooculogram to monitor eye movements |
works well if already studying ERPs, like EEG, electrodes placed around eye to detect movement cons: not very precise |
|
|
|
LED-based corneal reflection method to monitor eye movements |
goggles with LED. Eye movements cause reflection differences, head stabilized. |
|
|
|
Video based corneal reflection method to monitor eye movements |
infrared camera and light source. eye movements cause reflection to change. ss cant see the light. can create "hot spots" of where people are looking on screen |
|
|
|
what are the 3 pairs of ocular muscles responsible for? |
1. up and down motion 2. side to side 3. rotational |
|
|
|
What brain areas are involved in saccade programming? |
superior colliculus is active prior to and during saccades and attn shifts these cells are sensitive to visual movement and location |
|
|
|
Stimulus - driven saccade |
saccades initiated by sensory events |
|
|
|
goal-driven saccades |
saccades initiated on the basis of the observers goals and intentions |
|
|
|
True or False: initiation of saccades are generally under voluntary control? |
True |
|
|
|
True or False: saccades can be voluntarily suppressed? |
True, but saccade programming can be both goal-driven and stimulus driven. |
|
|
|
Describe how saccades are ballistic? |
once a particular trajectory has been calibrated and then the saccade is triggered, the eye can move without further programming. |
|
|
|
what are the advantages and disadvantages of ballistic eye movements? |
A: once initiated they are extremely rapid and require no additional feedback D: during programming, they require precise information about their destination. calibration is a relatively slow process |
|
|
|
Why are smooth pursuit eye movements not ballistic? |
Signals sent to the eye muscles must be constantly updated and revised via a feedback loop that codes current object position and cognitive expectations about motion. allows us to maintain tracking accuracy. |
|
|
|
which is faster, saccades or smooth pursuit eye movements? |
saccades - 220 ms |
|
|
|
Under-pursuit |
when the position of an object's image on the retina slips out of the foveal regions thus becomes blurry |
|
|
|
Describe Grimes (1996) visual suppression study |
method: ss wore eye-movement monitoring devices. during brief intervals when eyes in motion, visual scene would change Results: ss unaware of changes in scene |
|
|
|
Saccade suppression |
attention becomes disengaged during saccade, and to avoid blurring effect, visual analysis is suppressed then updated once saccade is complete |
|
|
|
How are smooth pursuit eye movements like analog attention shifts? |
attention remains engaged during smooth pursuits |
|
|
|
Meridian Effect |
target-detection response slower when cue and target are on opposites sides of the unseen vertical meridian that divides the right and left hemifields |
|
|
|
Why are saccades subject to the meridian effect? |
because direction re-calibration must occur when making successive saccades in different directions, which requires extra time. |
|
|
|
Express Saccade |
Very short latency (100ms) saccades that are produced by the fixation-offset effect. result of attentional disengagement prior to the saccade preparation process |
|
|
|
Experiment: Express Saccade |
method: 1. overlap condition - fixation point remained visible, 2. gap condition - fixation point disappears shortly before target Findings: saccade quicker when fixation point disappears Why?: allows us to disengage our attn. before saccade |
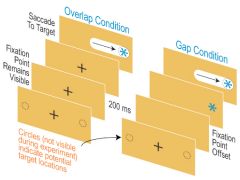
|
|
|
anit-saccade |
target appears in left hemifield, saccade to the opposite direction to the right hemifield |
|
|
|
pro-saccade |
saccades made directly to target locations. express saccades only occur during this type of task. |
|
|
|
Differences between saccades and smooth pursuit movements |

|
|
|
|
Feature map |
Feature map sends signal to master map about where something could be. |
|

