![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
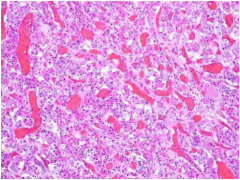
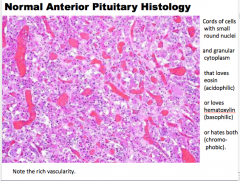
What is shown?
Describe the nuclei, cytoplasm, what are the three possible stains? |
|
|
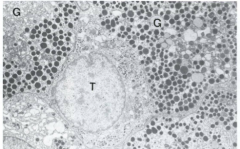
What is T and G? |
T = thyrotroph cell G = growth hormone cell (GH cells)
EM on pituitary adenomas not really done anymore |
|

These are all causes of what? |
Hypopituitarism |
|
|
What lobe does infarction involve? Why?
How much of the lobe must be lost for symptoms to occur? |

|
|
|
What are the four causes of pituitary infarction?
What is Sheehan syndrome? |

Sheehan = peripartum infarct of pituitary gland (pituitary gland enlarges during pregnancy becomes more vascularized and more sensitive to blood loss) |
|
|
What are some symptoms of Sheehan syndrome? When will you see it? |

1 month later because it takes a while before 75% of the anterior pituitary is lost |
|
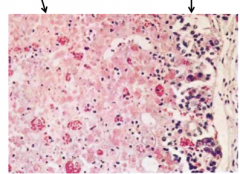
What is the gland? What are the two arrows pointing at? |
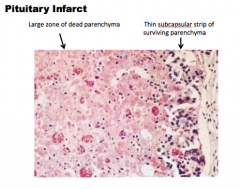
|
|
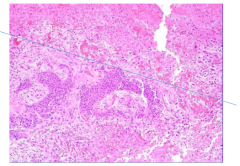
Is the pituitary infarct above or below the line? |
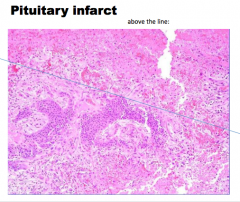
|
|
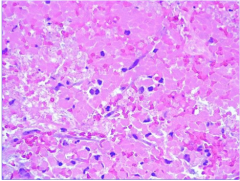
What is happening? What type of necrosis? What are the only viable cells? |
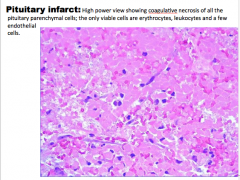
|
|
|
What are the three types of inflammatory lesions? |

|
|
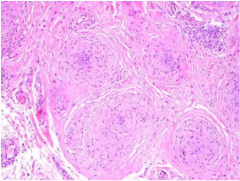
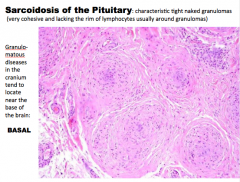
What is the gland? What is going on? What is lacking around the rim of the granulomas? Where do they usually locate? |
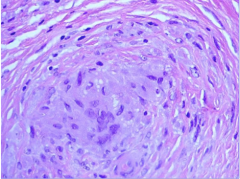
Non-caseating granuloma |
|
|
What does TB of the peripheral nervous system preferentially attack? |
BASAL cells of brain (don't confuse with sarcoidosis or TB) => DON'T WANT TO GIVE IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVES TO SOMEONE WITH TB!!! |
|
What is this? |

|
|
|
What are the four disease of hyperpituitism? |

|
|
|
Pituitary hyperplasia: Common or uncommon Two main types What type of gland involvement? Increase in what? What is an example? Disease? |

|
|
|
What is the most common cause of hyperpituitarism? They are what percent of intracranial neoplasms?
Most common in what ages?
|

|
|
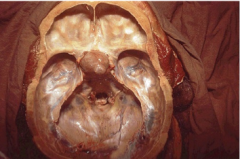
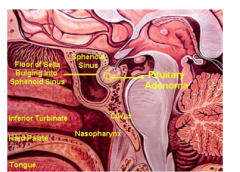
What is this? What are the two small tan structures on either side of the tumor?
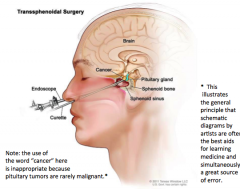
How could you get to a pituitary adenoma surgically without removing the top of the skull and the brain? How do you take this thing out? |
Pituitary adenoma in sella turcica
Optic nerves being pressed => bilateral vision problems
Transnasally |
|
|
What is the most common presenting sign of non-functional pituitary adenoma? |
Headache |
|
|
|
|
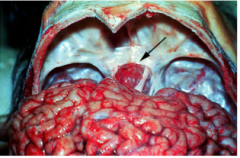
Congested, hemorrhagic pituitary adenoma. What is the white strip lateral to the tumor? What symptoms will the patient have? |

|
|
|
What are the pituitary adenoma types in order of most common to least common? |

|
|
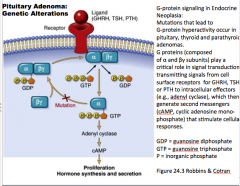
Look over |
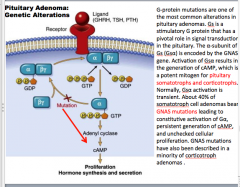
|
|
|
What is a pituitary adenoma producing prolactin? What is it the most common type of?
What is the mutation associated with it?
Two symptoms? |
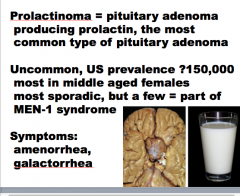
|
|

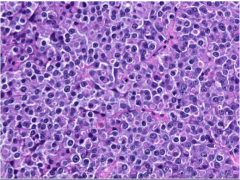
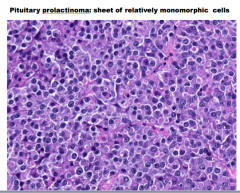
What is this the histopathology of? |
Pituitary prolactinoma |
|
What is the gland? Disease? Describe. |
|
|
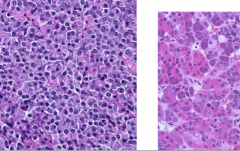
Left and right? |
Left = monomorphism => prolactinoma Right = normal |
|
|
What is SIADH caused by? Which lung tumor specifically?
Three symptoms? |

|
|
|
DI is a deficiency of which part of the pituitary gland?
What will the plasma Osm show? |

|
|
|
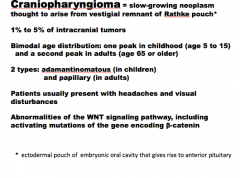
What is slow-growing neoplasm though to arise from vestigial remnant of Rathke pouch?
What percent of intracranial tumors?
Ages? Bimodal?
What are the two types?
What do patients present with?
Abnormalities of what signaling pathway? |
|
|
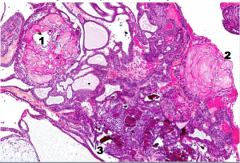
Identify 1, 2, and 3. What is the diagnosis? |
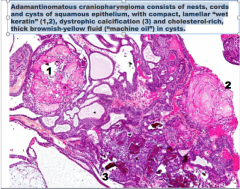
1 = wet keratin (looks like a keratin pearl with edema)
3 = cholesterol rich area from the wet keratin pearl |

