![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is motivation essential for? |
CHANGE |
|
|
|
What are viscerogenic needs? |
Primary needs like sex, air, water, food. |
|
|
|
What are psychogenic needs? |
Secondary like belonging, social interaction, etc. |
|
|
|
What is intrinsic motivation? |
The urge and desire to complete something for its own sake rather than for some external reward. |
|
|
|
What is extrinsic motivation? |
The desire to complete a behaviour due to a promised reward or to avoid a certain punishment. |
|
|
|
What is Solomon's theory of motivation? |
That people will seek affective contrast e.g. drug addiction, things that provide excitement and break up routine. |
|
|
|
What is Henry Murray's theory of motivation? (2 parts). |
That there are psychological motives internally: dominance, affiliation & achievement. And that we seek something because we lack something. |
|
|
|
What is the McClelland theory of motivation? |
That people learn their needs based on experience, and that these needs are a need for achievement, power and affiliation. |
|
|
|
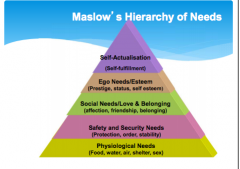
What is Maslow's hierarchy? |
A theory of motivation based on a pyramid of ascending needs (motivation) that provide satisfaction, and as needs diminish so does motivation. It starts with air, food etc and leads up to self actualisation. |
|
|
|
What is emotion? |
Inferred complex sequence of reactions to a stimulus including cognitive evaluations, subjective understandings, autonomic & neural arousal & impulses to action. |
|
|
|
What is curiosity, in terms of motivation? Who was the theorist? |
Intrinsic motivation. Berlyne. |
|
|
|
What is the Bandura theory of motivation based on? What did this theory suggest? |
Self efficacy. Belief that an individual can perform changes to produce their desired result. Internal motivation. |
|
|
|
What was the James Lange theory of emotion? |
Emotion was a response to physiological changes within the body. |
Crit: assumes there is a unique physiological stamp to each emotion. |
|
|
What was the Cannon-Bard theory of emotion? |
That emotions and physiological changes happen simultaneously. |
Crit: physiological responses happen much quicker, usually. |
|
|
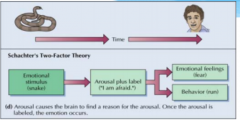
What is Scachter & Singer's two factor theory? |
Stimulus, time/appraisal, emotion attached. AKA a label is just applied to general physical arousal & attributing arousal to a source. |
|
|
|
What is Lazarus's cognitive appraisal theory of emotion? |
We learn what to expect from stimuli with experience e.g. phobias. Cognitive appraisal determines physiological arousal. |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of emotions? (3) |
1. Enhance memory 2. Modulate approach/avoidance behaviours 3. Emotions induce motivation. |
|

