![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Psychology |
Science of behavior and mental processes |
|
|
|
ABC’s of psychology |
A-affect B-Behavior C-Cognition |
|
|
|
RCT |
Randomized Control Trial |
|
|
|
Dualism |
Humans possess a mind and body. |
|
|
|
Structuralism |
Describing the structure of the mind and it’s operations. structuralism never caught on in the U.S. |
|
|
|
Correlation coefficient |
Correlation coefficient(r) is a statistic that yields a number between -1.00 and +1.00 |
|
|
|
Experiment |
Used to investigate relationships between manipulated events and measured events. |
|
|
|
Variable |
Anything about a person or situation that can be changed. |
|
|
|
Independent variable |
Cause/ exercise |
Variable manipulated |
|
|
Dependent variable |
Effect |
|
|
|
Meta-analysis |
Statistical procedure of combining the results of several smaller studies to more clearly see the relationship between dependent and independent variables. |
Minimizes the errors that can plague. |
|
|
APA ethical guidelines |
Ethical treatment of human and animal subjects. |
Do no harm |
|
|
Neuroscientists |
Scientists concerned with the development, structure, function, chemistry, pharmacology, and pathology of the nervous system. |
|
|
|
Neuron |
A microscopic cell that transmits information- in the form of neural impulses from one part of the body to another. |
|
|
|
Cell Body(soma) |
The largest concentration of mass in the cell and other structures necessary for the neurons life. |
|
|
|
Glia |
Provide the structure of the brain. |
|
|
|
Dendrites |
Structures that reach out to receive messages, or neural impulses, from nearby neurons. |
|
|
|
Axon |
A long protuberance extending from the neuron’s cell body that carries neural impulses to other neurons, muscles, or glands. |
|
|
|
Myelin |
A white substance composed of fat and protein. Cells that are of their own kind. Acts as a protection to other cells. |
|
|
|
Brain weight/ fact |
The brain is about 3 pounds and uses about 20% of all the oxygen your body takes in. The brain can not be without oxygen for very long. |
|
|
|
What happens to dead neurons? |
Functions of dead neurons can be taken over by surviving neurons. New research suggests that’s growth of new neurons does occur in the adult brains, but not as frequently as before and right after birth. |
|
|
|
How many nerve cells does a person lose a day? |
About 300 per day |
|
|
|
Visual cortex |
The visual cortex makes up about 30% of the brain. For example, if you become blind the visual cortex will take over the persons sense of touch, not immediate but learned as you use the sense of touch. |
|
|
|
Brain re training |
Your brain can be “re-wired” by “re-training” the brain to use the neurons/nerve cells in a different part of the brain. |
|
|
|
Function of Nuerons |
Transmit numeral impulses from one place in the nervous system to another. |
|
|
|
Resting neuron |
When the neuron is “at rest” the electrical charge inside that neuron has a significantly more negative charge(-70mV) than is found outside the neuron. |
|
|
|
Action potential |
When the neuron fires. Occurs and travels rapidly down the neuron; at this point, polarity reverses, and the inside actually becomes positively charged compared to the outside(+40mV). |
|
|
|
Depolarization |
(+ goes into -) ion channels open |
|
|
|
Synapse |
Where one neuron communicates with other cells. |
|
|
|
Synaptic cleft |
A microscopic gap between the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrites(or cell body) of another neuron. |
|
|
|
Synapse fact |
A synapse in which transmission is from upper left to lower right, as an impulse enters the axon terminal, vesicles release neurotransmitter chemicals into the synaptic space, or cleft. The neurotransmitter then either excites or inhibits an impulse in the next neuron. |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters |
Chemical compound |
|
|
|
Acetylcholine(ACH) |
Widely used in peripheral nervous system as either an excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitter. |
|
|
|
Botulism |
Blocks the release of acetylcholine at neuron/muscle-cell synapses, which can cause paralysis of the respiratory system and death unless antidote is given. |
|
|
|
Dopamine |
Associated with the thought and mood disturbances of some psychological disorders, as well as impairment of movement. |
|
|
|
Norepinephrine |
Involved in activation, vigilance, and mood regulation. It is associated with high levels of emotional arousal, such as increased heart rate, blood pressure, and perspiration. Cocaine increases the release of norepinephrine leading to a state of agitation and a “high” mood state. |
Cocaine increases the releas |
|
|
Medulla |
It’s nuclei control involuntary functions such as coughing, sneezing, tongue movements, and reflexive eye movements. The lowest structure in the brain. |
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
It’s role is to smooth and coordinate rapid body movements. Most intentional voluntary movements originate in higher brain centers(the mortar area of the cerebral cortex) and are coordinated by the cerebellum. “Automatic” done without really thinking about it. |
|
|
|
Amygdala |
In the lambic system: produces reactions of rage or aggression when stimulated. Makes you recognize “fear”. |
Feel no remorse, no empathy |
|
|
Hypocampus |
Involved with the formation of memories. No new memories-30 seconds |
|
|
|
Thalamus |
A relay station for impulses traveling to and from the cerebral cortex. |
|
|
|
Cerebral cortex |
The large, soft, lumpy, creviced outer covering of the cerebral cortex(cortex means “outer bark” or covering). The outer covering of the brain that makes us uniquely human by giving us the ability to think, reason, and use language. |
|
|
|
Sensory area |
An area of the cerebral cortex where most voluntary activity is initiated. |
|
|
|
Association area |
Area of the cerebrum where sensory input is integrated with motor responses and where cognitive functions such as problem solving, memory, and thinking occur. |
|
|
|
Frontal lobes |
Front of the two hemispheres of the brain, Are the largest and are defined by two large crevices called the central fissure and lateral fissure. |
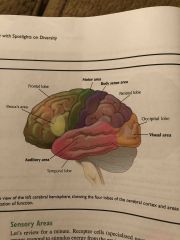
|
|
|
Interpretation |
What’s happening “right here” |
|
|
|
Perception |
A process that involves the selection, organization, and interpretation of stimuli. |
|
|
|
Vision |
We equate visual experience with truth or reality, as in the expression “seeing is believing” |
|
|
|
Light |
The stimulus for vision is a form of electromagnetic energy we call light. Understanding the nature of light can help us understand how vision works. |
|
|
|
Color constancy |
Allows you to perceive the color of a familiar object as constant, despite changing lighting conditions. |
|
|
|
Size constancy |
The tendency to see objects as unchanging in size regardless of the size of the retinal image they produce. |
|
|
|
Self-reference theory |
Whenever we look out into the world we only pay attention to the things we care about |
|

