![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the characteristics of organic molecules |
Has C and H ---------- Covalent bonding ---------- Large and complex ----------- 30 percent of cells |
the strong but hermit sibling |
|
|
Life requires both |
Organic and inorganic molectules |
Think of fruit or juice |
|
|
What are the characteristics of inorganic compounds |
Has no c --------- Ionic bonding -------- Small and less compex --------- 70 percent of cells |
The small extrovert sibling |
|
|
What are some examples of organic compounds |
Carbohydrates Protein Fat/lipids Nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) |
|
|
|
What are some examples of inorganic compounds |
Acids Bases Salts Water |
Food |
|
|
Why is the chemical structure of compounds important |
It is often directly related to the function of the cell |
|
|
|
What is an ionic bond |
Give/take electrons usually between metal and nonmetals also negative and positive charges |
Good friends help friends |
|
|
What is a covalent bond |
Sharing electrons, typically between nonmetals |
Kids are taught to do what with items |
|
|
What are the characteristics of water |
Inorganic molecules Covalent bonds Polar molecule Held together by hydrogenbonds |
|
|
|
What are polar molecules |
One side is positive and other is negative |
Duality |
|
|
What charge is a ion if it has more protons than electrons |
Positive |
|
|
|
What charge is an ion if it has more electrons than protons |
Negative |
|
|
|
Why is water a versatile solvent and why is this good |
Water is a polar molecule. Leading it to be able to break apart opposite bonds since it can attract both -------- All cellular reactions happen in solution. speedier than in gas or solid. Easy movement of chemicals between cells and in organisms. Dissolves and removes waste from cells. |
Water is a home wrecker that takes both in the end after making them break up -------- Lubricant |
|
|
What is waters High heat compacity Why is it important |
High compacity to hold heat with little change in temp ----------- Temperature regulation. Keeps temp in the required temp range for organs. Sweating to regulate temp. Protects aquatic organisms from ranging temps, liquid is more dense than solid ice. |
Do you turn to ice in the cold? |
|
|
Why does water have high surface tension and why is it good? |
Force causes water to stick together making surface tension However it is diluted by dissolving a thing, the surface tension is weaker ------------ Movements of water across the cell membrane occur easily and effectively . Movement of water up xylem in plants. Habitat support for aquatic organisms. |
|
|
|
Why does water have Dissociation ability and why is it good |
Water molecules 'split' to produce equal amounts of hydrogen and hydroxide ions ------------------ Organisms are sensitive to PH levels in cell and body fluids. Water helps keep pH constant for effective metabolism. Cellular processes need this ability. |
|
|
|
What is the pH scale and how is it used |
The ph scale is used to indicate the concentration of acidity or alkaline a solution has |
|
|
|
[ ]- meaning |
A concentration ion |
|
|
|
What are characteristics of acids |
Split in H2O and releases H+ (proteins) Strong acids ionize completely in H2O, weak ones only partially ionize. All have PH value below 7 |
|
|
|
What are a few examples of acids |
Hydrobolic acids (HcL)- stomach acid Carbonic acid (H2CO3)- human blood Sulphuric acid (H2SO9)- not in body |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of bases |
Release Hydroxide ions (oH-) Strong completly ionize in h20, weak only partially ionize All have value above 7 |
|
|
|
What are a few examples of bases |
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) Bicarbonate (HCO3) in human blood Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) limestone |
|
|
|
What is it called when a acid reacts with a base and what kind of reaction is this |
Salt and water are produced Neutralization reaction |
|
|
|
What are biological buffers |
Chemical compounds which resist change in pG by either accepting or donating H+ or OH- |
|
|
|
What are a few examples of biological buffers |
Carbonic acid Hemoglobin (HHb) blood Bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) Phosphate salts |
|
|
|
What is the importance of biological buffers |

|
|
|
|
What are the building blocks for polymers? |
Monomers |
|
|
|
What is dehydration synthesis? |
The process of monomers becoming polymers while producing H20 |
|
|
|
What is hydrolysis? |
The proceeds of polymers breaking down into monomers while re adding H20 |
|
|
|
Is it true or false that all the major compounds are polymers? |
True |
|
|
|
What do proteins contain |
H (hydrogen) C (carbon) O (oxygen) N (nitrogen) |
|
|
|
What makes up proteins? |
Amino acids |
|
|
|
What are the types of amino acids? |
Essential (cant make ourselves) and nonessential (stuff we can make ourselves) |
|
|
|
What do amino acids contain? |
An amino group (NH2) and an acid group (-COOH) |
|
|
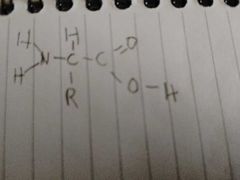
What is this? And what does the R represent? |
A amino acid |
|
|
|
Describe the process of amino acids and the bigger forms (amino acid, protein, polypeptide) |
Animo acid to polypeptide to proteins. |
|
|
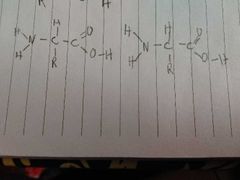
How do these bond and what is the type of bond |
A pepide bond. The o h and h make a water laking the c and n make a peptide bond |
|
|
|
What are the kinds of protein structure and what do they look like |
Primary- a linear araingment Secondary- twisted/spiral like Tertiary- a alpha helix that bends and folds on itself Quaterhary- many subunits of tertiary proteins bonded together with another compound |
|
|
|
How can changes in pH and temp protiens affects it |
Denture it _change the structure and inactivate it |
|
|
|
What are the three functions of proteins |
Fibrons- muscle, collagen/skin, keratin. Globular- enzymes, hormones, anibodie. Conjegated- protein + other compounds |
|

