![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Enzymes |
-proteins that are catalysts of biochemical reactions -typically has a globular shape -complex 3-D structure |
Human pancreatic amylase |
|
|
Enzymes are biological catalyst |
-Increase the rate of reaction by lowering the energy of activation -Catalyze nearly all the chemical reactions taking place in the cells of the body -Have unique three dimensional shapes that fit the shapes of reactants |
. |
|
|
Enzymes lower a reactions activation energy |
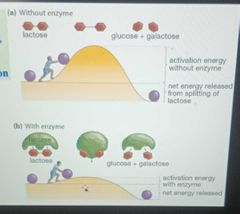
|
. |
|
|
First clear recognition was made by PAYEN and PERSOZ (around 1833) |
DIASTASE An alcohol precipitate of malt extract contained in a thermolabile substance that converted starch into sugar |
Basic concept |
|
|
Basic concept |
DUCLAUX(1898) use of -ase J.B.Sumner (1924-1930) first to crystallize |
|
|
|
Basic concept |
-more than 2500 biochemically important enzyme catalyzed reactions -characterized by specifically for substrates |
|
|
|
Effectors |
Modulates an enzymes activity
-Activators, inhibitors,both, or depending on conditions
SINGLE ENZYME -small single unit to large multiple units |
Basic concept |
|
|
Catalase |
- found in animal and plant cell -needed to speed up the breakdown of HYDROGEN PEROXIDE -breaks it down to OXYGEN and WATER |

the word equation for this looks like this |
|
|
Amylase |
-Found in saliva and in the pancreas -breaks down enzymes -breaks STARCH down to MALTOSE |

Word equation |
|
|
Potato phosphorylase |
-synthesis enzyme (builds up) -builds GLUCOSE-1-PHOSPHATE molecules into STARCH -the formation of starch is tested using iodine solution |

|
|
|
Enzymes and Reactions |

|
|
|
|
Catalytic efficiency |
High efficiency,10^3 to 10^17 faster than the corresponding uncatalyzed reactions |
|
|
|
Specificity |
High specificity, interacting with one or a few specific substrates and catalyzing only one type of chemical reaction |
|
|
|
Mild reaction conditions |
37°C, physiological pH, ambient atmospheric pressure |
|
|
|
Active site (Part of catalysts) |
Part of the enzyme where the reactants bind, where the biochemical reactions occurs |
basic parts of CATALYST |
|
|
Enzyme active site
|

-amino acid side chains interact,metal ions -various types of polar, non-polar, ionic interactions |
|
|
|
Active site |

|
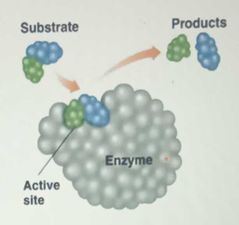
|
|
|
Lock and Key Model |
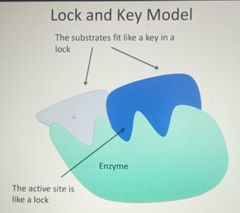
|
|
|
|
Basic enzyme diagram |
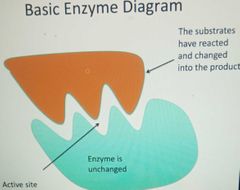
|
|
|
|
Parts of enzyme -Small nonprotein molecules (subunits) |
-cofactors (metal ions) Manganese,zinc, magnesium -prosthetic group (Covalently bonded to the enzyme) |
Parts of an enzymes |
|
|
Holoenzyme |
=apoenzyme+nonprotein part |
Parts of an enzymes |
|
|
Simple,conjugated |

|

|
|
|
Cofactors |

|
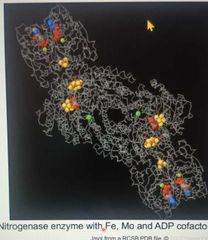
|
|
|
Enzymes -Cofactors |
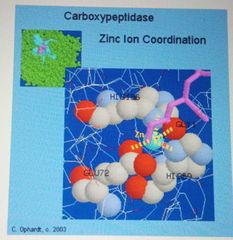
Metal ions present in trace amounts |
|
|
|
Metal Ions as cofactors |
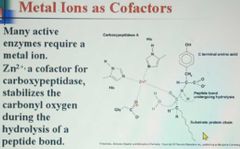
|
|
|
|
Enzyme cofactors
|
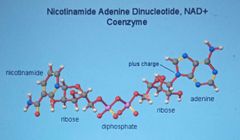
Coenzyme -non protein organic, maybe a vitamin |

|
|
|
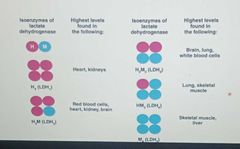
Isoenzymes |
Catalyze the same reaction in different tissues in the body |
|
|
|
EXAMPLE Lactate dehydrogenase |
Converts lactate to pyruvate,(LDH) consists of five isoenzymes |
|
|
|
Isoenzymes |
Different forms of an enzyme that catalyze the same reaction in different tissues in the body -they have slight variations in the amino acid sequences of the subunits of their quaternary structure |
|
|
|
Classification of enzymes |
-IUPAC -EC -four integer EC number and a name -common name: usually the principal specific reactant +-ase -Does not follow any rule *pepsin *rhodanese |
|
|
|
Naming Enzymes |

|
|
|
|
Classification of Enzymes |

|
|
|
|
Oxidoreductase, Transferases and Hydrolases |

|

|
|
|
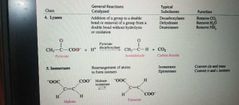
Lyases, Isomerases and Ligases |
|
|
|
|
Classification of Enzymes |

|
|
|
|
Oxidoreductases |

Catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions. |
|
|
|
Transferases |

Catalyze group-transfer reactions |
|
|
|
Hydrolases |

Catalyze hydrolysis |
|
|
|
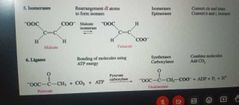
Lyases |
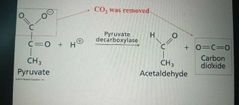
Catalyze lysis of a substrate
|
|
|
|
Isomerases |
Catalyze structural change within a single molecule |
|
|
|
Ligases |

Catalyze ligation, or joining, of two substrates |
|
|
|
Facilitation of proximity |

|
Modes of Enhancement of rates of bond cleavage |
|
|
Covalent Catalysis |

Amino acid side chains: nucleophilic groups |
|
|
|
Covalent Catalysis: Acetoacetate Decarboxylase |
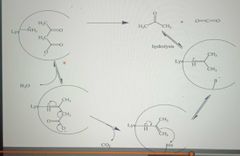
|
|
|
|
Modes of Enhancement of rates of bond cleavage/ catalytic mechanisms |
-General acid-base Catalysis -Binding Energy -Metal-ion Catalysis |
|
|
|
Acid-Base Catalysis |

|
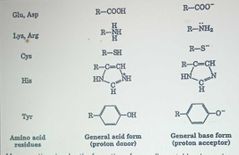
|
|
|
Binding energy catalysis (Method for improving the reactant rate) |

|
|
|
|
Metal ion catalysis(method) |

|
|
|
|
Modes of Enhancement of rates of bond cleavage/ catalytic mechanisms |
STRAIN, molecular DISTORTION, and shape change |

|
|
|
. |

|
|
|
|
Uses of enzymes |

|

|
|
|
Cont |

|

|

