![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

identify the labeled structures:
|
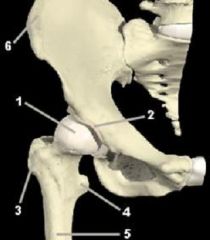
1. femoral head
2. acetabulum lining 3. greater trochanter 4. lesser trochanter 5. femur 6. iliac crest |
|
|
Alignment and mechanics of hip will effect alignment, mechanics and pain at:
1. 2. 3. |
1. knee
2. ankle 3. foot |
|
|
Femoroacetabular articulation ... body weight to lower ...
|
Transmits
extremity |
|
|
Femoroacetabular articulation is a ... joint held in place by surrounding musculature and four ligaments:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
Ball and socket
1. iliofemoral ligament 2. ischiofemoral ligament 3. pubofemoral ligament 4. capitis femoris |
|
|
the hip is composed of the ...
|
Femoroacetabular joint
|
|
|
what are the major motions of the hip:
1. 2. 3. |
flexion/extension
AB/AD-duction internal and external rotation |
|
|
extension in the hip is stabilized mostly by:
|
ligamentous structures
|
|
|
hip flexion limited (stablized) mostly by ...
... are main structures limiting flexion |
muscular structures
Hamstrings |
|
|
Bending knee will alleviate ... tension, thus permitting further ... of hip.
|
hamstring
flexion |
|
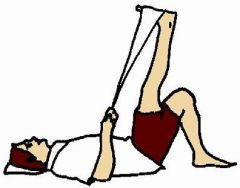
what is this a picture of:
|
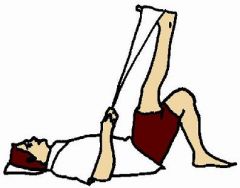
hip flexion
|
|
|
what is the primary extensor in the hip:
|
gluteus maximus
|
|
|
what is the primary flexor in the hips:
|
Iliopsoas
|
|
|
what is the primary extensor of the knee:
|
Quadriceps
|
|
|
what are the primary flexors of the knee:
|
Semimembranosus
semitendinosus |
|

identify the labeled structures:
|

(see figure)
|
|
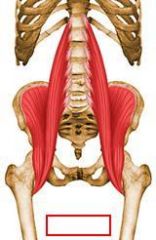
identify the muscle:
|

(see figure)
|
|
|
Bony abnormality (arthritis) or other pathology (abscess) will also cause pain upon ... and must be differentiated as cause of hip pain. Consider this if hip pain is present with (extension/flexion) even after releasing ...
|
hip flexion
flexion hamstrings |
|
|
what does the following describe:
Hip held in externally rotated position and restricted to internal rotation. |
External rotation dysfunction
|
|
|
what is the cause of External rotation dysfunction:
|
Usually due to tight external rotators
|
|
|
what are the hip external rotator muscles:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. piriformis
2. iliopsoas 3. obturators 3. gemelli |
|

identify the labeled structures:
|

(see figure)
|
|

what does the picture depict and what is the restriction:
|

External rotation of hip
Restricted to internal rotation |
|
|
what does the following describe:
Hip held in internal rotation and restricted to external rotation. |
Internal rotation dysfunction
|
|
|
what can cause Internal rotation dysfunction:
|
1. Usually due to tight internal rotator muscles or
2. by spasm of gluteus medius and minimus muscles |
|
|
what are the internal rotator muscles:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. semimembranosis
2. semitendinosus 3. TFL 4. adductor magnus 5. adductor longus |
|

what does the picture depict and where is the restriction:
|

Internal rotation of hip
Restricted to external rotation |
|

1. normal Angle of Inclination of Hip is:
2. Increased angle of inclination is called: 3. Decreased angle of inclination is called: |
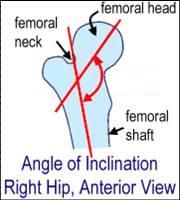
1. 120-135
2. coxa valga 3. coxa vara |
|
|
what is Patrick’s test (FABERE test):
|
1. Flexion/Abduction/External Rotation/Extension
2. Bring hip through these motions in order. Monitor quality of barrier |
|
|
what is “Capsular pattern” :
|
pain throughout ROM
|
|
|
what does “Capsular pattern” signal when you do Patrick’s test (FABERE test):
|
signals arthritic or infectious joint.
|
|
|
what does Barrier pain without capsular pattern suggest in Patrick’s test (FABERE test):
|
sacroiliac ligament pathology
|
|
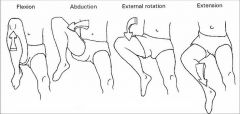
what does the diagram depict:
|

Patrick’s test (FABERE test)
|
|
|
Ortalani tests for unstable or dysplastic hip. Bring legs into ..., and push on femoral head ...
|
abduction/flexion (frog)
anteriorly |
|
|
Barlow tests for hip dislocation. Bring hips into ... and push ... on femoral head.
|
adduction/flexion
posteriorly |
|
|
Barlow is knees (apart/together)
Ortolani is knees (apart/together) |
together
apart |
|
|
Straight Leg Raise Test will test for:
1. Raise affected leg until pain is experienced if pain begins <80° flexion |
Hamstring Pain vs. Nerve Root Pain
2. Lower leg 5° and add foot dorsiflexion |
|
|
in Straight Leg Raise Test, if pain elicited by dorsiflexion indicates ...
|
nerve root irritation
|
|
|
... pain is usually only in posterior thigh, nerve root pain can go down to the ...
|
Hamstring
foot |

