![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of the following is mostly hydrophobic? 1.Carbohydrates 2.Nucleic Acids 3.Lipids 4.Proteins |
Lipids |
|
|
Which of the following forms branched polymers? 1.DNA 2.Proteins 3.Carbohydrates 4.Lipids |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
Which of the following molecules is hydrophobic?1.Food colouring 2.Olive oil 3.Table Salt |
Olive Oil |
|
|
The cells of your body are surrounded by water. The outer layer of these cells is made of many non-polar molecules. What would happen if the outer layer of these cells was made of mainly polar molecules? 1.Water could not get in the cell. 2.The cells would be too heavy to float in water. 3.The cells would dissolve. 4.The cells could not interact with their environment. |
The cells would dissolve |
|
|
Which of the following is used for long term energy storage? 1.Carbohydrates 2.Nucleic Acids 3.Lipids 4.Proteins |
Lipids |
|
|
How will lipids respond when immersed in water? 1.The tails will orient away from the water 2.The heads will orient away from the water 3.The phospholipids will form crystals at the bottom of the solution 4.The phospholipids will dissolve evenly in the water |
The tails will orient away from the water |
|
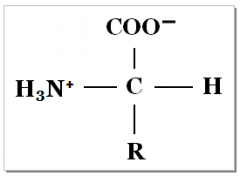
What type of Molecule is shown here? 1.Carbohydrate 2.Amino Acid 3.Lipid 4.Nucleotide |
Amino Acid , the amine and carboxyl groups (R chain) attached to a central carbon Make this an amino acid |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT characteristic of unsaturated fatty acids? 1.Have bends in the fatty acid chain 2.Solid at room temperature 3.Have double bonds 4.Also called oils |
Solid at room temperature |
|
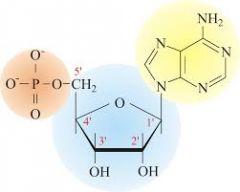
What type of molecule is shown here? 1.Carbohydrate 2.Lipid 3.Nucleotide 4.Amino Acid |
Nucleotide |
|
|
Which is not a function of proteins? 1.Form the bulk of cellular membranes 2.Move substances in/out of the cell 3.Recognition of specific particles 4.Maintains cell structure |
Form the bulk of cell membranes |
|
|
What monomer makes up an enzyme?
1.Amino Acid 2.Fatty Acid 3.Nucleic Acid 4.Protein |
Amino Acid |
|
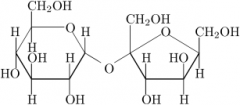
what is the function of this molecule? 1.Energy Storage 2.Structure 3.Communication 4.Information storage |
Energy Storage |
|
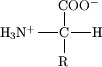
The molecule shown here is: 1.Amino Acid 2.Carbohydrate 3.Lipid 4.Nucleotide |
Amino Acid |
|
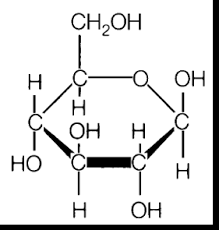
What type of Molecule is shown here: 1.Carbohydrate 2.Lipid 3.Nucleotide 4.Amino Acid |
Carbohydrate, this is a monosaccharide. |
|
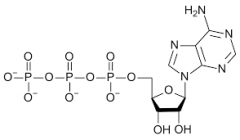
What type of molecule is shown here: 1.Amino Acid 2.Carbohydrate 3.Nucleotide 4.Lipid |
Nucleotide, this is an ATP molecule |
|
|
The ligand attaches to a protein at the: 1.Complementary site 2.Attachment site 3.Binding site 4.Ligand site |
Binding site |
|
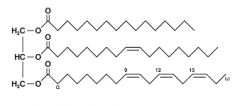
What is the function of this molecule? 1.Structure 2.Information Storage 3.Energy storage 4.Communication |
Triglycerides are used for Energy Storage |
|
|
Enzymes are usually: 1.Carbohydrates 2.Nucleic Acids 3.Lipids 4.Proteins |
Protein structures provide the complexity needed for enzyme function |
|
|
Which of these functional groups is hydrophilic? 1.Alcohols 2.Carboxyl 3.Phosphate 4. All of the above |
All of the above are hydrophillic (water loving) |
|
|
Which groups of macro molecules are used by humans for energy storage? 1.Lipids 2.Nucleotides 3.Carbohydrates 4.None of these 5.All of these |
Carbohydrates, lipids and Nucleotides are all used for |
|
|
Detergents are: 1.Polar 2.Non-Polar 3.Both 4.Neither |
Detergents are both polar and non-polar |
|
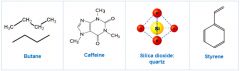
Which of the following molecules are organic ? |
Caffeine, Butane, and Styrene are all organic |
|
|
Proteins begin with an amino group and end with carboxyl group.In the case of nucleic acids: 1.The begin at the 5' end and end at the 2' end 2.They begin at the 5' end and end at the 3' 3.They begin at the 3' and end at the 5' end 4.It is the same in nucleic acids |
They begin at the 5' end and end at the 3'. |
|
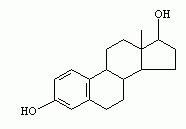
what is the function of this molecule: 1.Energy storage 2.Structure 3.Communication 4.Information storage |
Steroids (such as estrogen) are used for communication |
|
|
Denaturation: 1.Breaks the peptide bonds between amino acids 2.Unravels the 3D protein structure 3.Forms the bonds that hold together the 3D structure of proteins 4.Forms peptide bonds between amino acids |
Denaturation unravels the 3D protein structure but does not break apart the chain of amino acids |
|
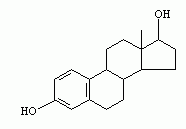
What molecule is shown here? 1.Carbohydrate 2.Lipid 3.Nucleotide 4.Amino Acid |
Lipid |
|
|
Why do enzymes work poorly at below optimum temperature? 1.The enzyme is unable to protonate the substrate 2.the enzyme is denatured 3.The substrate cant bind to the active site 4.The substrates do not have enough kinetic energy |
At lower temperatures, substrates have lower kinetic energy which slows down the reactions. |

