![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Histologic presentation of reflux esophagitis
|
- basal cell hyperplasia
- elongation of papillae - inflammatory cells in epithelium |
|
|
What environmental factor increases the risk for developing barrett esophagus?
|
smoking (2x greater risk)
|
|
|
Stress ulcers: Cushing's & Curling's
|
Cushiing's: CNS trauma, surgical, accidental, tumors
Curling's: burns |
|
|
complications of pernicious anemia
|

|
|
|
Location of pernicious anemia gastric atrophy vs environmental atrophic gastritis
|
pernicious anemia: body & funds
environmental atrophic gastritis: antrum & body |
|
|
gross appearance of h. pylori gastritis
|
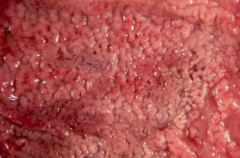
nodules = lymphoid aggregates
|
|
|
What is the etiology of duendenal ulcers?
|
nearly 100% are due to h. pylori infection
|
|
|
4 layers of a peptic ulcer
|
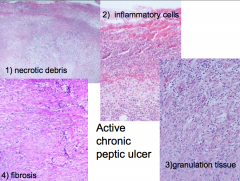
|
|
|
Cause of meckel's diverticulum
|
failure of involution of vitelline duct
|
|
|
What kind of ectopic tissue can be present in meckel's diverticulum?
|
ectopic gastric mucosa is present in 50% of cases
|
|
|
Gross vs microscopic presentation of microscopic colitis
|
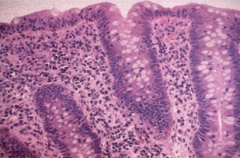
Gross: Normal
Micro: transmucosal lymphocytic infiltrate & inflammatory cells in surface epithelium |
|
|
Collagenous colitis gross & microscopic appearance
|
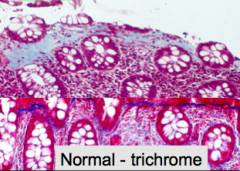
Gross: Normal
Micro: transmucosal lymphocytic infiltrate & inflammatory cells in surface epithelium w/ ***thick sub epithelial collagen band*** |
|
|
Histologic finding in celiac
|
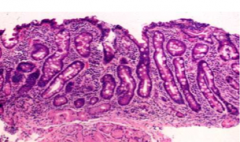
villous blunting & crypt hyperplasia
|
|
|
Whipple Disease etiology & histologic findings
|
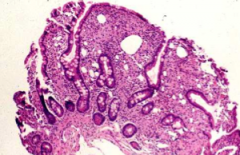
etiology: gram + actinomycete
histologic: blunting of villi & foamy macrophages |
|
|
Gross appearance of bowel in crohn disease
|
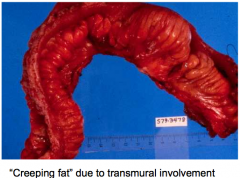
|
|
|
Unique pathologic feature of crohn disease:
|
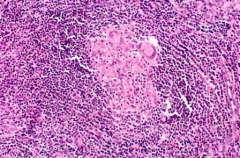
granuloma: present in 40-60% of cases
|
|
|
Which form of IBD has lymphoid aggregates?
|
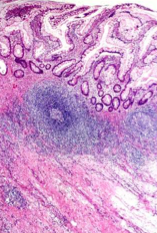
Crohn disease
|
|
|
What is a histologic sign of chronic ulcerative colitis?
|
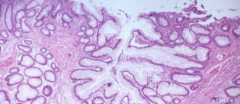
branching glands
|
|
|
Acute appendicitis histological appearance
|
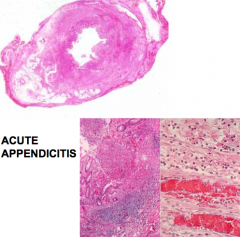
|
|
|
Pathophysiology of appendicitis
|
inciting event = luminal obstruction ➝ distention from luminal secretion → lymphatic obstruction then venous & arterial
|
|
|
Schulman's Rule for 2 indications for emergency general surgery
|
shock (end organ dysfunction) + peritonitis (generalized)
|
|
|
Schulman's sign
|
put hand on belly & jiggle around -- used to elicit peritoneal signs
|
|
|
What is non-inflammatory diarrhea? What are some common infectious causes?
|
large volume, watery stool
rotavirus, norovirus, choldera |
|
|
What is inflammatory diarrhea? What are some common infectious causes?
|
small volume, bloody & frequent
campylobacter, salmonella, shigella |
|
|
In someone with food poisoning that recently ate fried rice, suspect...
|
bacillus cereus
|
|
|
Which enteric infection is associated with the development of Guillain-Barre syndrome?
|
Campylobacter jejuni
|
|
|
Unique features of non typhoid slamonella
|
- foodborne transmission -- often poultry
- contact w/ reptiles |
|
|
Which bacteria?
- more common in cooler countries - foodborne = undercooked pork - dysentery w/ terminal ileitis (mimics appendicitis)*** |
Yerseinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
What is unique about shigella?
|
- high risk of person-to-person transmission
|
|
|
Which bacteria?
- food borne transmission - dystentery - can cause hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) |
enterohemorrhagic E.Coli
* most common strain = 0157:H7 |
|
|
Most common cause of traveler's diarrhea is ______________. What kind of diarrhea does it cause?
|
enterotoxigenic E.Coli; non-inflammatory diarrhea
|
|
|
Treatment for C. diff
|
metronidazole & oral vancomycin
+ fecal transplant = very effective |
|
|
What is the most common enteric infection?
|
campylobacter jejuni
|
|
|
If you suspect a patient has CMV colitis (ie. they are immunosupressed), how do you make the dx?
|
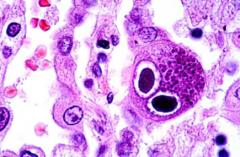
Colonoscopy & biopsy:
- giant cells w/ cytomegaly & large nuclei containing basophilic inclusions (owl's eyes, halo rim) |
|
|
Which enteric virus is common in infants and young children that causes vomitting?
|
rotavirus
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of viral diarrhea in adults? What setting is this commonly seen?
|
norovirus; cruise ships
|
|
|
What is the most common intestinal parasite in the US?
|
giardia
|
|
|
Diagnosis & Treatment of Giardiasis
|
Dx: stool sample
Tx: metronidazole, tinidazole |
|
|
Which commonly prescribed medication puts patients at increased risk for developing an enteric infection?
|
PPI
|
|
|
Which two bacteria present as curved, gram negative rods?
|
campylobacter jejuni & vibrio cholera
|
|
|
Treatment for food poisoning?
|
fluids & electrolyte replacement
Abx are not indicated since they resolve quickly |
|
|
Acute cholecystitis is caused most commonly by gallstones obstructing....
|
the neck or cystic duct
|
|
|
Gross appearance of chronic cholecystitis
|
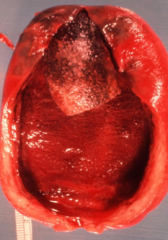
- thick fibrotic wall
- smooth or dulled serosa due to fibrosis |
|
|
What is a classic histologic appearance of chronic cholecystitis?
|
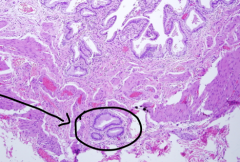
Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses: benign glands below the muscular is layer
|
|
|
4 risk factors for cholesterol gallstones
|
Four F's:
- Fat - Female - Fertile - Forty |
|
|
Cholesterolosis: what is it? What is the classic gross appearance?
|
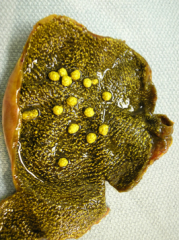
- excessive accumulation of cholesterol w/in the lamina propria of the gallbladder
- mucosal yellow flecks --> "strawberry gallbladder" |
|
|
Location of cholesterol stones vs calcium bilibrubinate stones
|
cholesterol: gallbladder only
calcium bilirubinate stones: arise anywhere in the biliary tree |
|
|
calcium bilirubinate stones: color? radio-opaque?
|
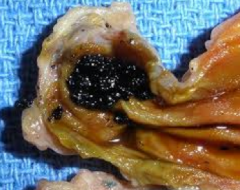
black
radio opaque 50-75% of the time |
|
|
Location of brown pigment stones
|
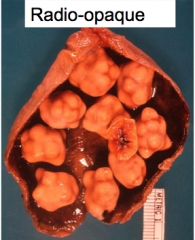
intra & extrahepatic bile ducts
|
|
|
Gross & microscopic appearance of acute pancreatitis
|
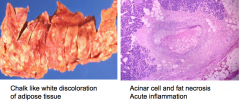
fat necrosis
|
|
|
What occurs in the most severe cases of acute pancreatitis?
|
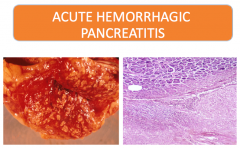
|
|
|
What is a key histologic finding of pancreatic pseudocysts?
|
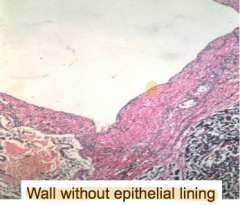
|
|
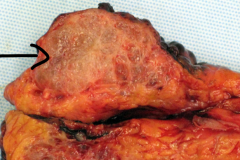
Benign pancreatic lesion w/ central scar, commonly seen in women in the 7th decade of life:
|
serous microcystic cystadenoma
|
|
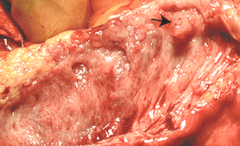
Sex prevalence of intraductal papillary mutinous neoplasm? Common location?
|
- M > F
- more common in pancreatic head than tail *unique; most of these are F > M |
|
|
Major risk factor for the development of pancreatic adenocarcinoma
|
smoking ➝ 2-3x ↑ risk
|
|
|
3 main symptoms of pancreatic adenocarcinoma
|

|
|
|
Primary location of pancreatic adenocarcinoma? What is the common presentation?
|
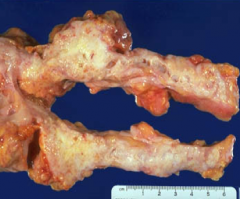
60% occur in the head ➝ biliary obstruction & jaundice
|
|
|
pancreatic adenocarcinoma histology
|
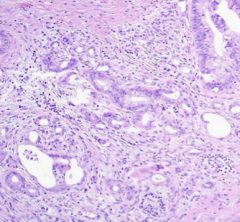
- infiltrating irregular glands
- ↑ fibroblasts, lymphocytes & ECM |
|
|
2 types of invasion seen pancreatic adenocarcinoma
|
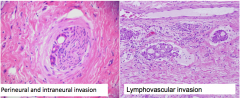
|
|
|
Characteristic features of pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma: gross appearance & histology
|
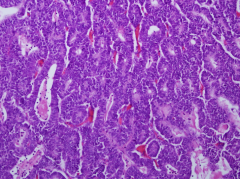
- well circumscribed, soft & fleshy mass
- granular cytoplasm due to eospinophilic zymogen granules - + IHC stain for exocrine enzymes (ie. chymotrypsin, amylase, lipase) |
|
|
What is a classic histologic finding in alcoholic cirrhosis (aside from steatosis & mallory bodies)?
|
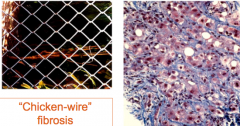
"chicken-wire" fibrosis aka peri-cellular
|
|
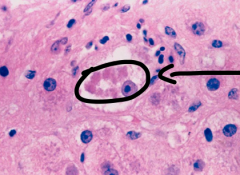
This is an example of a ________, commonly present in ___________.
|
mallory bodies, alcoholic cirrhosis
|
|
|
What is the histologic appearance of hepatocyte in Hep B?
|
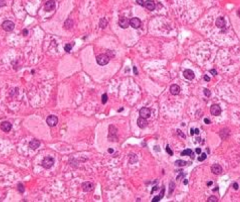
ground glass hepatocyte
|
|
|
Hep C histology: what kind of infiltrate? any other features?
|
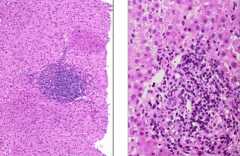
primarily lymphocytic infiltrate & lymphoid aggregates
|
|
|
What is interface hepatitis? What are 2 diseases it is commonly seen in?
|
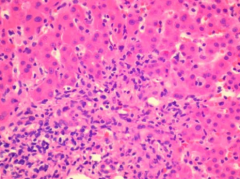
inflammatory infiltrate spilling over into parenchyma from the portal tracts. notice the presence of plasma cells
seen in Hep C & AIH |
|
|
Histologic appearance of primary biliary cirrhosis
|
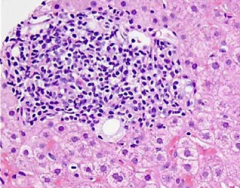
- bile duct is obscured by inflammatory cells
- can also have granuloma formation |
|
|
What is a unique microscopic appearance of severe primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
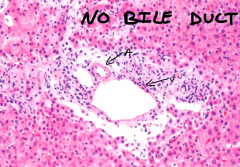
the absence of a bile duct
|
|
|
What is the microscopic appearance of severe primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
periductal concentric fibrosis
|
|
|
What is the unique pattern seen on prussian blue stain in patients with genetic hemochromatosis?
|
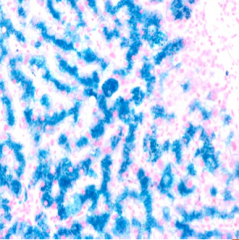
cannilicular pattern
|
|
|
Inflammatory infiltrate in NASH? How is that different from alcoholic steatohepatitis?
|
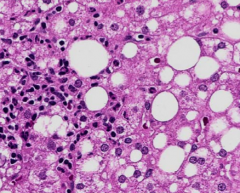
NASH: lymphocytic (pictured)
alcoholic: neutrophilic |
|
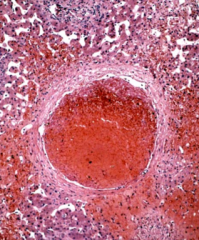
?
|
central vein thrombosis w/ congestion of the sinusoids
Budd Chiari Syndrome |
|
|
Gross appearance of liver cell adenoma? major complication?
|
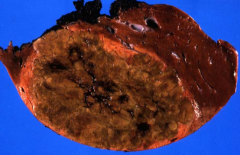
solitary tumor, 10-30cm, adjacent liver is NONCIRRHOTIC
may cause severe hemorrhage |
|
|
Gross appearance of focal nodular hyperplasia
|
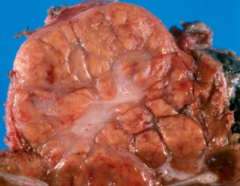
central scar
|
|
|
most common malignant tumor of the liver
|
metastasis
|
|
|
Microscopic appearance of fibrolamellar HCC
|
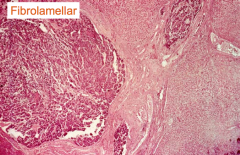
↑ eosinophilic infiltrate w/ fibrotic bands
|
|
|
Definition of failure to thrive
|
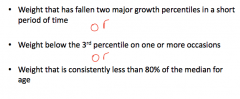
|
|
|
3 causes of failure to thrive
|
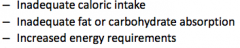
|
|
|
Use of labs/imaging in the workout for failure to thrive?
|

|
|
|
What is the treatment goal in FTT with regards to intake?
|
↑ food intake to 1.5x basal requirement
|
|
|
Management of GERD in infants:
|
- consider thickened formula
- prone position when NOT sleeping (↑ SIDS risk if sleeping prone) |
|
|
High yield history question to ask when considering a dx of Hirschsprung's disease
|
When was the child's first BM?
< 10% of patients w/ Hirschsprung's pass stool within 1st 24 hrs |
|
|
What is the cause of most constipation in pediatrics?
|
functional rather than organic causes
|
|
|
In jaundice baby beyond 10 days of life you should ALWAYS order...
|
conjugated bilirubin levels
|
|
|
describe physiologic jaundice of the newborn
|
- delay in bilrubin conjugation
- jaundice, AFTER the first 24 hrs of life - unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia |
|
|
If a neonate is stall jaundice after __ days = concern!
|
10
|
|
|
An infant has a conjugated bilirubin > ____ % of othe total = concerning!
|
20
|
|
|
2 clinical features of neonatal cholestasis
|

|
|
|
What is a major cause of neonatal cholestasis that must be investigated?
|
biliary atresia
|
|
|
the most common reason for OLT in childhood
|
biliary atresia
|
|
|
in patient w/ biliary atresia, the best results of the Kasai procedure are within the first...
|
8 weeks
|
|
|
The most common cause of liver disease in children
|
neonatal hepatitis
|
|
|
Natural hx of neonatal hepatitis
|
60% improve w/in the 1st yr of life
|

