![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Regarding secondary structure formation in a protein, the fact that atoms of the peptide bond lie in a plane contributes what influential factors?
|
The resonance stabilization energy of the planar structure is 88 kJ/mol;
A twist about the C-N bond involves a twist energy of 88 kJ/mol times the square of the twist angle; ***Twists can occur about either of the bonds linking the alpha carbon to the other atoms of the peptide backbone |
don't memorize energies; just know they are known
|
|
|
What is the main consequence of the amide plane?
|
Double bond nature of peptide bond causes planar geometry
|
|
|
|
What type of interactions dictate and stabilize protein structure?
|
Noncovalent interactions
|
|
|
|
What are the noncovalent interactions that dictate protein structure and their energies?
|
van der Waals: 0.4 - 4 kJ/mol
hydrogen bonds: 12-30 kJ/mol ionic bonds: 20 kJ/mol hydrophobic interactions: <40 kJ/mol |
VHIH
|
|
|
Where is the information necessary for folding the peptide chain into its "native” structure contained?
|
in the primary amino acid structure of the peptide
|
|
|
|
Angle about the C(alpha)-N bond is denoted _________.
Angle about the C(alpha)-C bond is denoted _________. |
phi
psi |
|
|
|
The entire path of the peptide backbone is known if...
|
all phi and psi angles are specified
|
|
|
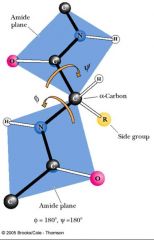
Peptide bond planes are joined by __________________________. The rotation parameters are φ and ψ.
|
the tetrahedral bonds of the alpha-carbon.
|
Many possible conformations about an alpha-carbon between two peptide planes are forbidden because of STERIC CROWDING.
|
|
|
Ramachandran determined that the _________________ combinations are the basis for ___________ secondary structures
|
sterically favorable;
preferred |
|
|
|
Unfavorable orbital overlap precludes some combinations of phi and psi. What are some unfavorable angles?
|
phi = 0°, psi = 180° is unfavorable;
phi = 180°, psi = 0° is unfavorable; phi = 0°, psi = 0° is unfavorable |
|
|
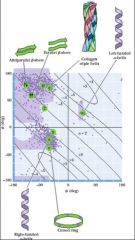
What two things does this plot tell you?
|
1) Describes acceptable ψ/φ angles for individual AA’s in a polypeptide chain.
2) Helps determine what types of 2o structure are present |
|
|
|
All secondary structures are ________ structures that are stabilized by __________ bonds.
|
local;
hydrogen |
|
|
|
________ is a ubiquitous component of protiens and was used to identify alpha helices.
|
Keratin
|
|
|
|
There may be several alpha-helical structures in a single polypeptide chain: true or false?
|
true
|
|
|
|
All H-bonds in the alpha-helix are oriented in the same direction, giving the helix a dipole with the N-terminus being ___________ and the C-terminus being ____________.
|
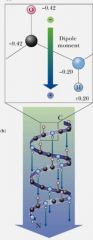
positive; negative
|
Arrangement of N–H and C=O groups (each with an individual dipole moment) along the helix axis creates a large net dipole for the helix.
|
|
|
Which AAs destabilize an alpha helix?
|
glycine and proline
|
|
|
|
Two amphipathic helices can associate through __________ interactions
|
hydrophobic
|
|
|
|
Beta-pleated sheet strands may be
a. parallel b. antiparallel c. either d. neither |
c. either
|
|
|
|
There are how many residues per turn in a beta pleated sheet?
|
Two
|
|
|
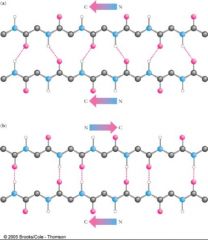
What does this image illustrate?
|
That anti-parallel beta sheets are more stable than parallel
|
|
|
|
Loops connect alpha-helices and beta-sheets. Loops usually contain ___________ residues.
Loops are found on ______________. |
hydrophillic ;
surfaces of proteins |
|
|
|
Turns are loops with:
a. different charges b. more than 5 AAs c. more than 7 AAs d. are often found to have proline and glycine e. are often found to have proline and glutamine f. c and d g. b and d |
g. b and d
|
|
|
|
How Do Polypeptides Fold into Three-Dimensional Protein Structures?
|
Secondary structures form wherever possible (due to formation of large numbers of H bonds)
Helices and sheets often pack close together |
|
|
|
Protein folding makes ________ bonds and minimizes ___________ contact.
|
H; solvent
|
|
|
|
Fibrous proteins are usually:
a. synthesized b. soluble c. insolube d. made of beta sheets e. made of alpha helices |
c. insoluble
|
|

