![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Coccidioides immitis infection |
Coccidioidomycosis |
|
|
Colony Morphology |
Coccidioides immitis |
|
|
Microscopic: |
Coccidioides immitis |
|
|
Arthroconidia are extremely infectious. Cultures must be handled cautiously, grown only in tubes. A biological safety cabinet must be used when handling suspected cultures. Do not make slide cultures of these organisms. |
Coccidioides immitis |
|

|
Coccidioides immitis |
|
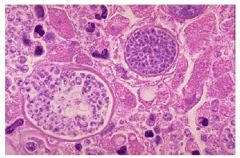
|
These large spherules with a thick wall and filled with endospores are characteristic for Coccidioides immitis growing in tissues. The spherule at the left is bursting to expel its endospores, which grow and continue the infection. |
|
|
is endemic to the desert southwest of the U.S. |
Coccidioides immitis |
|
|
Infections: |
Blastomyces dermatitidis |
|
|
Slow growth; 14 days to mycelial forms mature. Hold suspected cultures for 8 weeks. Process specimens immediately. |
Blastomyces dermatitidis |
|
|
Colony Morphology |
Blastomyces dermatitidis |
|
|
Microscopic:
– Septate hyphae with short or long conidiaphores – Round or pear shaped conidia – lollipop appearance – Older cultures have thick walled chlamydoconidia – Yeast cells have a “Broad base bud” |
Blastomyces dermatitidis
|
|

|
Blastomyces dermatitidis |
|
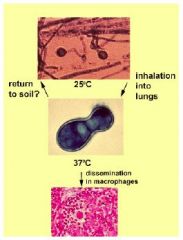
|
Blastomyces dermatitidis |
|
|
Slow growth; 15 - 20 days to mycelial forms mature. Hold suspected cultures for 8 weeks. Process specimens immediately |
Histoplasma capsulatum |
|
|
Infections: |
Histoplasma capsulatum |
|
|
Colony Morphology |
Histoplasma capsulatum |
|
|
Microscopic: |
Histoplasma capsulatum |
|

|
Histoplasma capsulatum inside macrophages |
|
|
Very slow growth; 21 days to mature |
Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis |
|
|
Infections: |
Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis |
|
|
Colony Morphology |
Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis |
|
|
Microscopic: |
Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis |
|
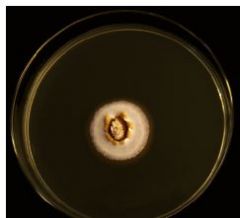
|
Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis |
|
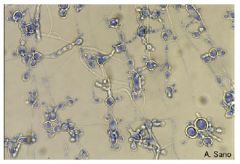
|
Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis |
|
|
Only true pathogen in Penecillium genus |
Penicillium marneffei |
|
|
Infections: |
Penicillium marneffei |
|
|
Colony Morphology |
Penicillium marneffei |
|
|
Microscopic: |
Penicillium marneffei |
|
|
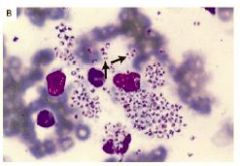
Penicillium marneffei Other Tests |
Exoantigen and PCR tests |
|
|
Penicillium marneffei |
|
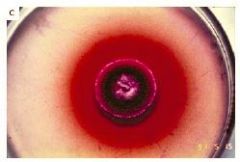
|
Penicillium marneffei |
|
|
other tests for Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis |
Convert mold to yeast phase |
|
|
other tests for Histoplasma capsulatum |
- DNA Probes are available |
|
|
other tests for Blastomyces dermatitidis |
-- DNA Probes are available |
|
|
other tests for Coccidioides immitis |
– DNA Probes are available |
|
|
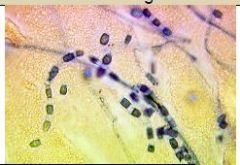
Mode of transmission of systemic mycosis |
Inhalation of infected conidia |
|
|
Coccidioides immitis |
|
|
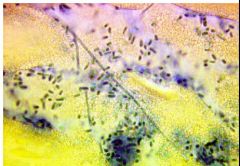
can be isolated from soil, decaying vegetation, |
Malbranchea sp. |
|
|
Malbranchea sp. |
|
|
Due to the existence of arthroconidia |
Malbranchea and Coccidioides |
|
|
grow moderately rapidly at 25°C. They are raised or flat, with or without furrows, and powdery, |
Malbranchea |
|
|
endemic in North America. Mississippi, |
Blastomyces dermatitidis |
|
|
25°C- Septate hyaline hyphae and unbranched short conidiophores are observed. Conidiophores at right angles to hyphae. The conidia are unicellular and solitary. |
Blastomyces dermatitidis |
|
|
25°C - The growth rate is slow to moderately rapid. The texture is membranous and downy to woolly. The surface color is white to beige and reverse is pale to brownish. |
Blastomyces dermatitidis |
|
|
Microscopic mold phase looks similar to B dermatitidis, is not biphasic |
Scedosporium apiospermum |
|
|
endemic in the Tennessee- Ohio- Mississippi river valleys |
Histoplasma capsulatum |
|
|
At 25°C - Hyphae: septate + hyaline produce hyphae-like conidiophores which arise at right angles to the parent has macro- and microconidia. Macroconidia are tuberculate, thick-walled, round, unicellular, hyaline, lg w/ of fingerlike projections macroconidia aka tuberculochlamydospores or |
Histoplasma capsulatum |
|
|
At 25°C - Colonies slow growing, granular to cottony. white, becomes buff brown with age. not sensitive to cycloheximide From the reverse, yellowish orange color. Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA), brain heart infusion agar |
Histoplasma capsulatum |
|
|
Microconidia (microaleurioconidia) are unicellular, hyaline and round, with a smooth or |
Histoplasma capsulatum |
|
|
differs from Histoplasma capsulatum by not being dimorphic, not forming microconidia |
Sepedonium sp. |
|
|
25°C - hyphae are often sterile If present, |
Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis |
|
|
25:Colonies are filamentous, slow growing, leathery, flat to wrinkled, woolly, cottony or |
Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis |
|

|
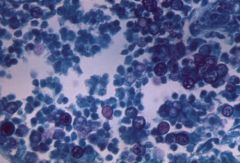
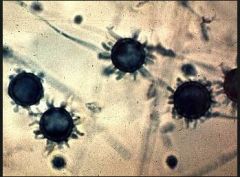
Blastomyces dermatiditis |
|
|
Blastomyces dermatiditis |
|
|
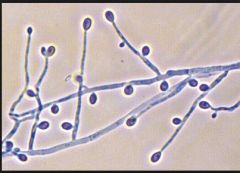
Histoplasma capsulatum macroconidia and microconidia |
|
|
Scedosporium apiospermum |
|

|
Scedosporium apiospermum |

