![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2 differential for skull base tumors? |
Chordoma Chondrosarcoma |
|
|
Chordoma Location ? Commonest 3 location in order ? T2 signal |
Midline Sacrum>> clivus >> C2 vertebral body Bright |
|
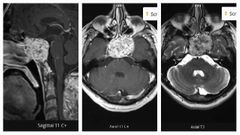
Finding Diagnosis |
There is a large, well defined, T1 isointense mass lesion centred over the clivus, with small high signal foci, which my represent intratumoural haemorrhage. The lesion is T2 hyperintense and shows vivid, but heterogeneous, enhancement on post-contrast images. It is invading the sphenoid sinus anteriorly, and the pontine cistern posteriorly, where it also abuts the basilar artery. It invades both cavernous sinuses, more pronounced on the left side with evidence of encasement of the left internal carotid artery (cavernous portion). Chordoma |
|
|
Main differential for clivus chordoma is ? |
Chondrosarcoma |
|
|
Differences BTW chordoma and chondrosarcoma of clivus? |
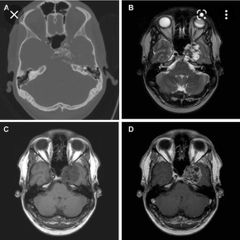
Chordoma midline Chondrosarcoma lateral with ring and arcs calcifications |
|
|
3 ddx for dural tumors? |
Meningioma commonest Hemangiopericytoma Mets |
|
|
Meningioma Commonest location It's effect on bones ? |
Cerebral convexities Hyperostosis |
|
|
What is hemangiopericytoma ? How it differ from meningioma? 2 |
Soft tissue sarcoma They both enhance homogenously and might have dural tail Hemangiopericytoma ( invade the bones and don't calcify ) meningioma causes hyperostosis and get calcifications. |
|
|
Most common primary that mets to the dura? How it is different than primary tumors? |
Breast CA but 80% will go to grey white matter junction. More edema than primary tumors |
|
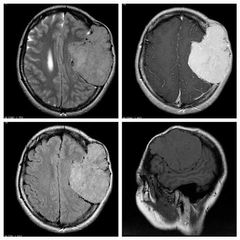
Finding Diagnosis |
MRI demonstrates a very large extra-axial mass eroding through the bone. It vividly enhances and had large feeding vessels around the margins. There is no evidence of invasion into the brain. Hemangiopericytoma |

