![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
HIV ia a |
RNA retrovirus |
|
|
HIV infects... |
CD4+ T cells, macrophages and dendritic cells |
|
|
HIV progresses to... |
AIDS- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndome |
|
|
HIV has no... |
vaccine |
|
|
HIV Subtypes |
1. HIV-1: has around 11 subtypes (clades), major type of HIV 2. HIV: found in West Africa, much slower infection |
|
|
HIV originates from |
SIV Simian Immunodeficiency Virus |
|
|
HIV-1 origination |
monkey-chimpanzee/ gorilla-human |
|
|
HIV-2 origination |
monkey-human |
|
|
earliest documented case in 1959 in Africa called |
skinny disease |
|
|
HIV is a global |
pandemic |
|
|
more than .... carry the virus |
40 million |
|
|
only...are officially diagnosed |
5% |
|
|
every 24 hours the infected numbers |
15000 |
|
|
every 24 hours...die |
8000 |
|
|
leading cause of death in sub-Saharan Africa |
2.5 million AIDS deaths |
|
|
contrary to belief it is transmitted |
heterosexually as well |
|
|
HIV envelope |
1. a glycolipid envelope w/spikes called gp 120 2. means it is easy to inactivate |
|
|
HIV has two strands of |
identical RNA |
|
|
HIV has what enzyme |
1. reverse transcriptase 2. allows it to reproduce in the host |
|
|
AZT and HIV antivirals... |
targeted reverse transcriptase |
|
|
|
|
|
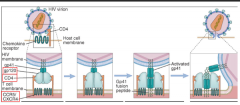
HIV must attach to both ... for infection to occur |
CD4+ and chemokine receptors |
|
|
once in the host cell, viral RNA is.. |
released and transcribed into DNA by reverse transcriptase |
|
|
newly formed viral DNA is incorporated into human DNA chromosome by the enzyme |
integrase |
|
|
new DNA can either |
produce more virus or can remain latent as a provirus |
|
|
of those infected % individuals never produces disease |
5% remain latent as a provirus |
|
|
HIV can undergo rapid changes in |
antigenic makeup which helps it evade the host defences- inducing drug resistance |
|
|
diagnosis for HIV |
1. repeatedly reactive tests for HIV antibodies 2. Virus PCR: virus load from blood |
|
|
Monitoring HIV: viral load |
keep track of number of HIV particles in blood |
|
|
monitoring HIV: CD4+ cells |
1. below 200/nm^3 is indicative of clinical AIDS 2. this occurs because CD4+ cells only live for 2 days when infected 3. virus inhibit new production of T cells |
|
|
stage A infection |
infection is asymptomatic or causes chronic swollen lymph nodes |
|
|
stage B infection |
persistent infections by opportunists like C. albicans, VZV, cryptosoridia, hairy lekoplakia |
|
|
stage C= clinical AIDS |
defined by "indicator conditions" such as C. albicans infections of the respiratory mucosa, CMV eye infections, TB, Pneumocystis pneumonia, toxoplasmosis of the brain and kaposi's sarcoma |
|
|
mild, flu-like symptoms for HIV may go... |
unnoticed |
|
|
oral candidiasis HIV |
1. usually caused by C. albicans 2. most common infection is thrush |
|
|
Oral leukoplakia HIV |
1. usually asymptomatic, no treatment needed 2. characterized by white lesions EBV |
|
|
HIV gingivitis and periodontitis |
symptoms 1. severe pain 2. bleeding gums 3. loosening of teeth |
|
|
ocular infections with HIV |
very common, ranging from bening HIV retinopathy to sight threatening viral infections |
|
|
most common HOV ocular infection |
CMV retinitis, very serious |
|
|
Varicella-zoster retinitis |
severe necrotizing retinitis |
|
|
leading cause of mortality and morbidity in HIV infected patients |
HIV pulmonary disease |
|
|
most dangerous pulmonary HIV disease |
Pneumocystis jirovechi Pneumonia |
|
|
PJP |
1. insidious onset 2. early diagnosis and treatment important 3. dry cough- no purulent sputum |
|
|
antibiotic for PJP |
trimethoprim-sulfa "septra" |
|
|
first infectious complication for HIV |
mycobacterial diseases |
|
|
HIV increases reactivation of |
latent infections |
|
|
HIV patients have ... annual risk of developing active disease |
5-10% |
|
|
HIV increases the risk of |
symptomatic disease/ mycobacteria diseases after infection |
|
|
HIV increases dissemination of |
TB |
|
|
kaposi's sarcoma associated with infection of |
HHV 8 |
|
|
Kaposi's Sarcoma treated by |
radio theraphy |
|
|
Kaposi's disease defining illness of |
AIDS |
|
|
usually seen in infected homosexual men |
vascular neoplastic disorder |
|
|
kaposi's sarcoma appears as |
cutaneous red-purple nodules or plaques |
|
|
sites usually affected by Kasopi's Sarcoma |
legs, feet, mucous membranes, hard palate, nose, trunk and scalp |
|
|
TRANSMISSION OF HIV |
1. contact with bodily fluid 2. sexual contact 3. blood contamination from needles, transplants and blood transfusions 3. transmission more effective if sores are present |
|
|
blood as bodily fluid of contamination |
has highest viral load 100000+ viruses/ml |
|
|
semen as a bodily fluid of contamination |
not as high as blood, around 50 viruses/ml |
|
|
vertical transmission of HIV |
1. pregnancy, delivery and breast feeding 2. artificial insemination: semen contaminated with HIV |
|
|
prevention of neonate infection |
1. antivirals during pregnancy and the first 6 months |
|
|
HAART |
combination of anti-HIV medicines |
|
|
problem with treatments |
rapid development of resistance |
|
|
when do we treat |
as soon as infection is found |
|
|
how to check for resistance? |
looking through HIV genome sequence |
|
|
TRUVADA |
1. uses combination of two RT inhibitors 2. can be used PrEP or pre-exposure, giving 75% protection 3. use for actual treatment for the disease in combination w/other drugs |
|
|
cure for HIV?
|
there is no cure for HIV |

