![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
sound |
result of vibrations of molecules as they are compressed at certain pressures |
|
|
frequency |
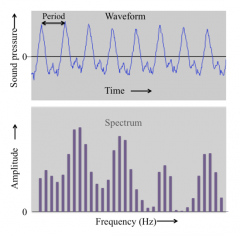
number of cycles between high and low pressure in one second; affects pitch; sensitivity to sound is dependent on frequency |
|
|
timbre |
perceptual dimension of sound determined in part by its complexity; distinguish different qualities of sound |
|
|
outer ear |
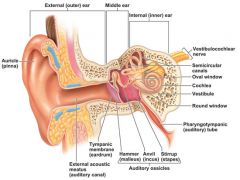
includes pinna/auricle, ear canal, and ear drum |
|
|
pinnae |
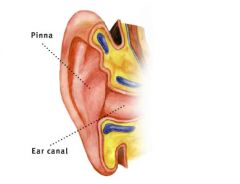
funnels sound into ear canal; sound bounces off depending on direction; changes spectrum of sound entering ear which can be useful in locating sound; bouncing location changes the timbre of the sound |
|
|
middle ear |
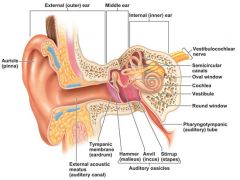
includes ossicles |
|
|
ossicles |
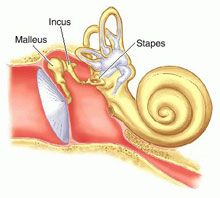
vibrations in ear cause 3 ossicles to vibrate; act as amplification system to overcome reflection of sound and it travels from air to fluid-filled chamber |
|
|
cochlea |
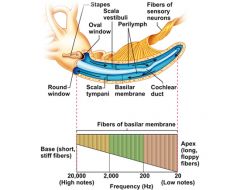
frequency analyzer that breaks complex sounds into discrete frequency components; filled with fluid and lined with cilia that move back and forth |
|
|
frequency resolution |
ability to hear 2 frequencies that are very close to each other as different sounds |
|
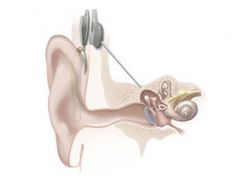
cochlea implants (CI) |
electronic device that provides a sense of sound to someone who is hearing impaired; picks up sound and transduces it into electrical impulses |
|
|
pitch |
attribute of sound; allows the ordering of sound on musical scale; dependent on frequency of sound waves |
|
|
fundamental frequency |
lowest frequency of periodic wavelength; changing can results in changes of overall frequency |
|
|
tonotopic organization |
anatomical separation of frequencies in the ear; maintained by primary auditory cortex |
|
|
place code |
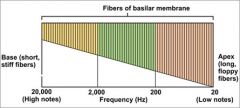
brain knows pitch based on the location of the nerve fibers that are stimulated; important for high-pitched sounds |
|
|
temporal code |
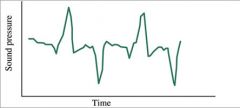
brain knows pitch based on firing rate of nerve fibers |
|
|
Volley Principle |
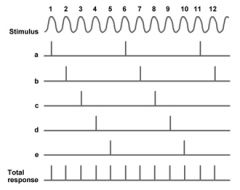
auditory nerve as a whole produces volleys of impulses for sounds; for sounds which a single axon cannot fire that fast (high frequency sounds) |
|
|
overtones |
give musical instruments specific timbres |
|
|
harmonics |
series of tone whose frequency is a multiple of fundamental frequency |
|
|
pattern recognition |
identification of particular sound sources by auditory system; timbre recognition is a form of pattern recognition |
|
|
timing cue |
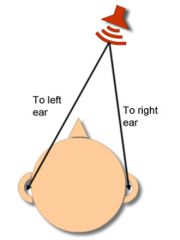
sounds coming from 1 side of the head will arrive at the ear on that same side first; sounds arriving to the middle will arrive at both ears at the same time; used to locate sound sources; information is sent to the parietal lobe |
|
|
olfactory mucosa |
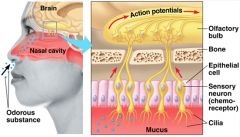
mucous membrane lining top of nasal sinuses containing the olfactory receptors |
|
|
olfactory bulbs |
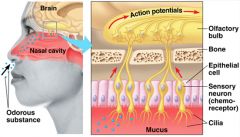
stalk-like structures located underneath frontal lobes; contain neural circuits which perform first analysis of olfactory information |
|
|
anosmia |
loss of smell and flavour; damage to receptor cells of olfaction |
|
|
pheromones |
chemical substance released by animal; serves to influence physiology/behaviour of other members of the same species; important in communication and social groups |
|
|
taste buds |
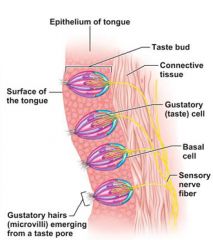
where taste receptor cells are located around the mouth |
|
|
homunculus |
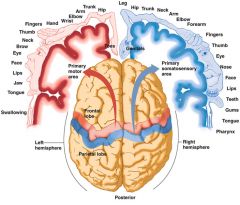
relative sizes of parts related to cortical representation; refers to somatotopic map of the body in the brain |
|
|
primary somatosensory cortex |
region of somatosensory cortex that receives information directly from somatosensory systems |
|
|
somatotopic representation |
spatial organization of body parts maintained in the brain; body parts are represented next to adjacent area |
|
|
thermoreceptors |
nerve endings sensitive to stimulation by heat; help regulate body temperature; includes warm and cool fibers |
|
|
pain receptors |
free nerve endings in the body; react to extreme pressure, extreme hot and cold, and tissue damage |
|
|
kinaesthic senses |
provide information about position and movements of limbs in space |
|
|
vestibular senses |
detect changes in movement, acceleration, 3 rotational directions |
|
|
semicircular canals |
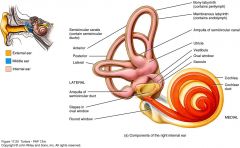
3 organs in inner ear that respond to rotational movements of head; indicate rotational movement in each of the three dimensions |

