![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the difference between BHP and HP curve |
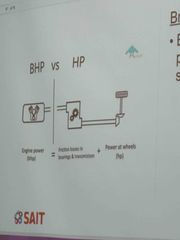
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is defrost mode in a heat pump for winter? |
It will run the system in cooling mode |
|
|
Will defrost make an ice pool on the outside unit after a defrost? |
Yes, you might need a riser to keep the heat pump above the snow. |
|
|
Will auxiliary heat turn on when the outdoor unit is on defrost? |
Yes, this will ensure the supply air is warm. |
|
|
What are the 2 ways to initiate a defrost? |
(1) Demand-frost method (monitors the pressures to detect frost). (2) time-temperature defrost (monitors temperature snap disc outside every 30,60, or 90 minutes) |
|
|
Where is the indoor coil installed on a residential furnace? |
Downstream of the furnace. (Aka in the normal place). |
|
|
What is the difference between closed loop and open loop geothermal loops? |
In a closed-loop geothermal heat pump system, a continuous loop of fluid (usually a mixture of water and antifreeze) circulates through buried pipes or vertical boreholes to exchange heat with the surrounding earth. Unlike an open-loop system, a closed-loop system doesn't extract or discharge water from the ground; it operates within a sealed loop. Closed-loop systems are more common and versatile, suitable for areas with limited water availability or specific geological conditions. |
|
|
How much pipe do you need per ton of cooling for a ground source heat pump? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
How much pipe do you need per ton of cooling? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
How deep does the loop need to go in a vertical loop? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
How much pipe do you need per ton of cooling? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
How deep does the loop need to go in a vertical loop? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
What is the minimum spacing between vertical holes? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
How much pipe do you need per ton of cooling? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
How deep does the loop need to go in a vertical loop? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
What is the minimum spacing between vertical holes? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
What is the minimum grade for a horizontal loop? |
Horizontal loops must be: • 10 ft below grade minimum (Alberta) and • 300 ft (or longer per ton) with 6 inch spacing Vertical loop bore holes (Alberta) must be must be: • 200-300 Ft deep, •250-300 Ft per ton in length, • 3-4" in diameter, • 20 ft spacing between holes (15 ft Min.) |
|
|
Does the heatpump hwt fully heat the water? |
No, only 25-50% of the heating bill is removed with a heat pump |
|
|
What is a CRAC unit? |
COMPUTER ROOM AIR CONDITIONER
A CRAC unit is an air conditioner for data centers, ensuring ideal conditions for electronic equipment by controlling temperature and humidity. |
|
|
Where do you install heat pumps? |
Outside of the drip line. (Away from the edge of the roof) |
|
|
Dont need data center on TQ |
Yup |
|
|
Does a crac system need under air floor? |
Yes, |
|
|
Dont need data center on TQ |
Yup |
|
|
Does a crac system need under air floor? |
Yes, |
|
|
Crac vs Crah |
CRAC VS CRAH • The main difference between CRAC and CRAH cooling units is that CRAC units use refrigerants and compressors, whereas CRAH units use chilled water and control valves. • CRAC cooling units have a simpler functionality as there is typically only one mode once turned on. |
|
|
What is liquid cooling direct to chip? |
Not on TQ
Liquid Cooling - Direct to Chip . This developing area shows promise for modern data center cooling, since it's cleaner and more efficient than air cooling. • Liquid cooling also means you don't have to maintain two separate systems, which boosts efficiency. |
|
|
Immersion cooling |
Immersion Liquid Cooling • Immersion cooling, also known as "direct liquid cooling'; iS a technique used for computer cooling, battery cooling, and motor cooling in which electrical and electronic components, including complete servers and storage devices, are mostly or fully submerged in a thermally conductive but electrically insulating liquid coolant. |
|
|
What is a DATA ROOM COOLING SYSTEM? |
Data Room Cooling Equipment . The data room cooling system is typically a split system with remote condensing units that provide precision controlled heating, cooling, humidification and dehumidification, and that is supplementary to the main building cooling system. |
|
|
What is economizer mode in Data room cooling? |
They just use a refrigerant pump and use the ambient air the reject heat. |
|
|
What grade do you need for a window shaker? |
Installation Procedures • In addition to ensuring that the window air conditioner installation is safe and secure, you must make certain that the positioning of the unit allows for sufficient condensate drainage. • Some types of units require a slope of ¼" grade toward the outside of the building to allow the condensate to flow and drip to the outdoors. • If the condensate does not drain properly to the outside, it can cause damage indoors. |
|
|
How do you install a condenser in respect to the prevailing wind? |
In a ductless split you want the unit 90 degrees from the airflow.
For a refrigeration, have the prevailing wind so it works with the fan and not against it. |
|
|
Do you need to know the weight of the new unit when installing it? |
Yes, Make sure that the surface on which the equipment is to be installed is designed to withstand the unit's weight. |
|
|
TQ: what needs to be on top of the curb before you put the unit down? |
Foam tape |
|
|
TQ?: What do you need to protect the unit? |

The unit must be lifted using spreader bars to prevent the slings from damaging the unit. The spreader bars should be equal to the width of the unit. |
|
|
Power must be turned on for how long before start up? |
24 hrs before start-up. (pressure of the refrigerant and temperature of the oil are important on start up.) |
|
|
What is the building envelope? |
Barrier between Conditioned vs uncondition spaces |
|
|
Dont worry about roof penetrations because its not on the test. |
Yup |
|
|
How many feet from the edge? B-52 or B-149? |
10 ft is B-52 6ft is B-149 |
|
|
Sleepers must be made of what type of material? |
Non-combustible |
|
|
Sleepers must be made of what type of material? |
Non-combustible |
|
|
Insulation on a liquid line if it passes through an ambient room warmer than the condensing temperature? |
True If the room is warmer it will remove subcooling… not a happy txv. |
|
|
What is the maximum voltage imbalance? |
2% |
|
|
What must the supplied voltage be within? Percentage? |
10% |
|
|
If you have 2 slab evaporators and they are stacked which one is the first stage? |
First stage is the lower one! |
|
|
How far down should horizonal loops be? |
10 ft down |
|
|
If you have 2 slab evaporators and they are stacked which one is the first stage? |
First stage is the lower one! |
|
|
How far down should horizonal loops be? |
10 ft down |
|
|
How far apart should vertical loops be? |
20 feet apart |
|
|
What is the outdoor design condition? |
The balance point where the heat pump can meet the demands of the home. |
|
|
All glycol piping underground need to be…? |
Fused joints.
Hydrostatic pressure test to 100 psi |
|
|
Where is the surge line and why do we stay away from it? |
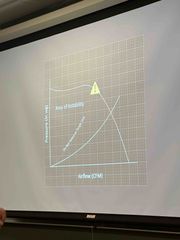
The operating point becomes unbalanced leading to unstable operation |
|
|
What is the operating point?
TQ:What can cause fan surge? |
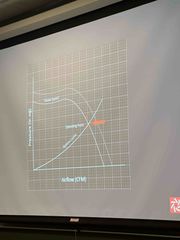
The point on the graph where the rpm and pressure
A large fan running too slowly. It starts hoping on the graph in the flat spot. Providing 0 CFM to whatever CFM starts dropping in relation to pressure. |
|
|
Relationship between RPM AND CFM? |
(RPM(2)/RPM(1)) = ((CFM(2)/CFM(1)) If RPM = 2 Then CFM = 2 |
|
|
What is the relationship between RPM AND SP |
(RPM(2)/RPM(1))^2 = (SP(2)/SP(1)) |
|
|
Relationship rpm and hp |
(RPM(2)/RPM(1))^3 = (hp(2)/hp(1)) |
|
|
Backwards inclined is non-overloading? |
True Forward inclined is overloading |
|
|
Flex duct is…. |
Terrible |
|
|
What is direct vs indirect drive? |
Motor connected directly or with a belt. - (1/64” per inch) Remove plug on bottom of motor (depending on how its mounted) from motor housing -loosen motor mount and remove tension on belt, remove belt, replace and tension belt before tightening down motor mount. |
|
|
What are the 3 fan groups? |
Fan Wheel Groups K Wheel - Blades cannot be adjusted; Simple basic fan A Wheel - Blades can be adjusted but only when stopped C Wheel - Blades can be adjusted while the fan is running |
|
|
What is a cross flow fan? |
It has the air going perpendicular the the shaft. |
|
|
What is the difference between BHP and HP? |

"BHP" stands for brake horsepower, and "HP" stands for horsepower. Both terms are often used interchangeably, but technically, BHP refers to the engine's output before losses like friction and other external factors, while HP represents the power delivered to the wheels. In practical terms, the difference is often negligible for everyday discussions about a vehicle's power. |
|
|
The fan law curves are on the test and not the graphs of the curves. |
Yep |
|
|
VAV summary notes on test |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
VAV summary notes 2 |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the difference between cool aisle and hot air containment? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is an edge data centre? |
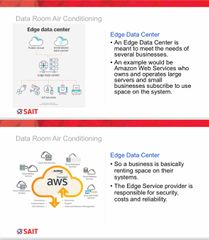
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is an enterprise data centre vs and edge data centre? |

Edge is multiple corporations |
|
|
What height is a heat pump set to? |
12-24 inches above the ground |
|
|
In a MUA with a heating coil what needs to happen if the freeze stat trips? |
Open zone valve, turn on pump, close dampers, turn off fan |
|
|
What causes noisy and drafty office space from the diffuser? |
High velocity/volume |
|
|
How do you test a geothermal loop? |
100 psi hydrostatic |

