![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functional unit of the kidney:
blood flow from segmental aa.? Where do the arcuate aa. run? Terminal branches of the arcuate arteries ascend into the cortex, running between medullary rays (lobules) |
nephron
segmental --> interlobar --> arcuate --> interlobular --> afferent arterioles along the cortico-medullary border interlobular |
|
|
Which part of the nephron filters fluid from the blood?
Which part modifies the filtrate into urine? Tuft of fenestrated capillaries: What surround the glomerulus? |
renal corpuscle
tubular portion glomerulus Bowman's capsule |
|
|
Visceral layer of Bowman's capsule is made of:
Parietal layer of Bowman's capsule: What vessels take up substances resorbed by the tubular epithelium? |
podocytes
Strat. squamous epithelium peritubular capillaries |
|
|
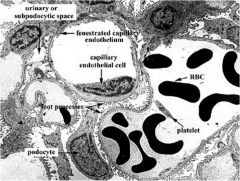
Describe the filtration barrier:
Glomerular capillaries allow _______ (4) to pass, and has barriers to ______________ (2). |
Fluid from capillaries --> fenestrated capillary endothelium --> basal lamina --> podocytes of visceral Bowman's layer--> all considering polyanionic charge
From capillaries leaks into the urinary space through a complex filtration barrier allow H2O, urea, glucose, small proteins block formed elements in blood, macromolecules |
|
|
Describe where extraglomerular vs introglomerular mesangial cells are located
|
1. Extraglomerular mesangial cells - found at vascular pole
2. Intraglomerular mesangial cells - found within renal corpuscle. |
|
|
Mesangial cells are modified __________.
4 fxns of mesangial cells? |
smooth muscle
contractile - control blood blow thru capillaries supportive - where renal corpuscle absent phagocytic - resorption/maintenance of basal lamina secretory - secrete PG's, endothelins (constrict arterioles) |
|
|
What are 4 components of the lamina rarae?
Pedicles of the podocytes are separated by __________. each pedicle has a glycocalyx made of __________. |
Type IV collagen
laminin fibronectin -charged proteoglycans filtration slits -charged podocalyxin |
|
|
Filtration slit diaphragm contains the protein _________.
What does nephrin do? Mutations in the nephrin gene are associated with ____________. |
nephrin
retard passage of molecules through fenestrae and basal lamina congenital nephrotic syndrome |
|
|
Describe the filtration process:
What part of the kidney do you see glomeruli? |
blood enters through afferent arteriole --> basal lamina catches large molecules --> -charged molecules caught by lamina and podocytes --> fluid passes through filtration slits to urinary space
cortex only |
|
|
What kind of epithelium is in the PCT?
Where are the nuclei? Describe the luminal border: Can you see the borders between cells? |
eosinophilic cuboidal/low columnar
central ragged, microvilli No |
|
|
What gets absorbed in the PCT?
Function of the Loop of Henle? Descending loop: permeable to what? Describe the filtrate. |
Na+, Cl-, H2O (via aquaporin-1)
help form hypertonic urine by forming an osmotic gradient in the interstitial fluid of the medulla permeable to H2O, salts isotonic at first --> more hypertonic (H2O reabsorbed) |
|
|
Ascending loop: contains what?
permeable to H2O? Describe the filtrate. |
Na+/K+/Cl- pump (symporter)
not permeable to H2O salt loss while keeping H2O = isotonic/hypotonic |
|
|
DCT: histology?
Histology and fxn of principal cells? Intercalated cells? |
low cuboidal epithelium, round/oval nuclei at apex, fewer microvilli (larger lumen)
principal - light staining, resorb Na+, secrete K+ intercalated - basophilic, secrete H+, HCO3- |
|
|
Macula densa:
Location and fxn? Sensitive to what? What makes up the juxtoglomerular apparatus? Which cells produce renin? |
regulate GFR by constricting the afferent arteriole
sensitive to Na+, Cl- macula densa, JG cells of afferent arteriole, extraglomerular mesangial cells (lacis, polkissen) JG cells |
|
|
Describe the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway:
Fxn? |
kidneys - renin to:
liver - angiotensinogen to ang I to: lungs - ang I to ang II (ACE) to: adrenal gland - aldosterone aldosterone to kidneys aldosterone - resorb Na+ |
|
|
Secreted by atrial myocytes , increases diuresis:
opposes action of _______, inhibits release of ______. secreted by DCT/CD cells, inhibits NaCl and water resorption: |
ANF
opposes aldosterone, inhibits ADH release urodilatin |
|
|
Collecting ducts: histology?
Responsive to what hormone? Contain what transmembrane protein? |
distinct borders, cuboidal/columnar epithelium, poorly stained
ADH/vasopressin Aquaporin-2 (AQP-2) |
|
|
What are cells located between capillary loops that replace normal ct cells?
|
1. Contractile to reduce (receptors for angiotensin II) or increase
(receptors for vasodilator atrial natriuretic factor) blood flow through capillaries 2. Support in regions where the visceral layer of Bowman's capsule is not present 3. Phagocytic, function in resorption/maintenance of the basal lamina (intraglomerular only) 4. Secrete prostaglandins & endothelins |
|
|
How do you tell the difference between the proximal and distal tubule micro
|
Proximal will be slightly bigger with aggrevated border
distal will be nice and smooth and slightly smaller |
|
|
Name the five segments that the segmental part of the renal arteries supply
|
1. apical
2. anterosuperior 3. anteroinferior 4. inferior 5. posterior |
|
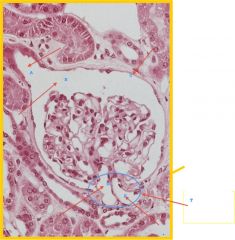
Identify all
|
a. urinary pole- where bulk operations begins
b. urinary space c. parietal layer of Bowman's capsule d. efferent arteriole e. afferent arteriole f. vascular pole |
|
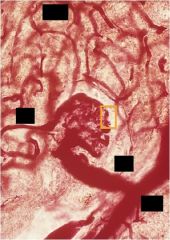
Label yellow spot and all black squares
|
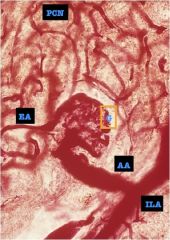
|
|
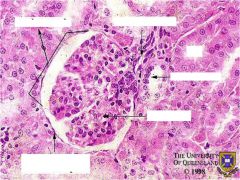
Nephron Label parts
|
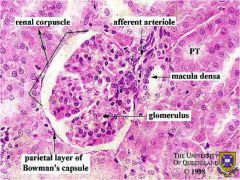
|
|
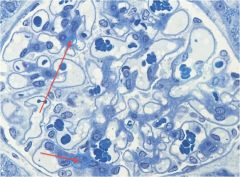
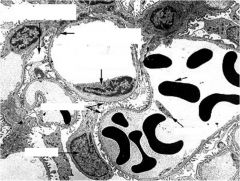
what are the things being pointed to and what do they do?
|
Mesangial Cells-
- Contractile – reduce/increase blood flow through capillaries ● Supportive in area where the visceral layer of the renal corpuscle is absent ● Phagocytic – resorption & maintenance of the basal lamina * ● Secretory – secrete prostaglandins & endothelins (induce constriction of aff/eff arterioles). |
|
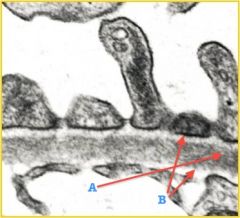
This is basal lamina... what is A and B and what does B contain?
|
a. lamina densa
b. lamina rarae- Type IV collagen, Laminin, Fibronectin, Negatively-charged, proteoglycans |
|

|
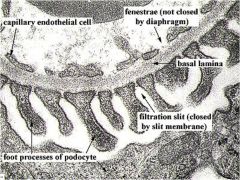
|
|
|
|
|

What part of nephron is this and how can you tell?
|
PCT- due to rugged villi
|
|
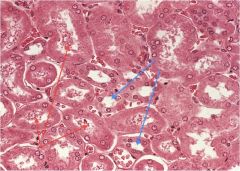
Which are pct's and which are dct's?
|
Blue= dct
Red= PCT |

