![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the main component of bronchial brushings and washings
|
ciliated columnar cells: have round/oval nuclei with slight variations in nuclear size, chromatin is finely granular, cytoplasm is pale, thin and usu basophilic
|
|
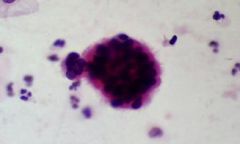
what is it
|
creola body - found often in asthmatic patients, composed of sloughed ciliated columnar cells
|
|
|
what is necessary to call a sputum sample adequate
|
alveolar macrophages
|
|
|
if see free cilia what should you think of
|
viral
|
|
|
what are plant cells and what is an alternate name
|
aka vegetable cells; usually are food contaminants from the mouth, usually have refractile cytoplasm, may be quite large - can mimic squamous ca (but rectagular, uniform and refractile cellulose wall)
|
|
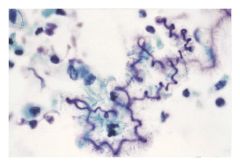
what are curschmann's spirals and when/where are they found
|
coiled strands of inspissated thickened mucus; dense core and lighter colored periphery
|
|
|
what is a langhans cells
|
multinucleated giant cells with nuclei as ring around outside
|
|
|
cytologic changes with radiation
|
- increased cell size
-multinucleation with prominent/multiple nucleoli -two-tone cytoplasm - cytoplasmic vacuolization |
|
|
cytologic changes with chemotherapy
|
- enlargement
- hyperchromasia - tiny invaginations of nuclear membrane - coarsely granular chromatin - macronucleoli and scant thin sometimes rectangular cytoplasm |
|
|
fx of keratinized scca in lung
|
- orange cytoplasm
- great variation in cellular and nuclear size/shape: (fiber cells, spindle cells, tadpole cells, cannibalized cells, multinucleated cells) - great variation in nuclear hyperchromasia -single cells - tumor diathesis |
|
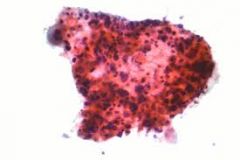
what is it
|
lung scca
|
|
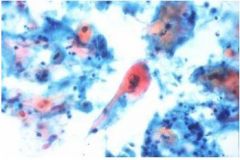
what is it
|
lung scca
|
|
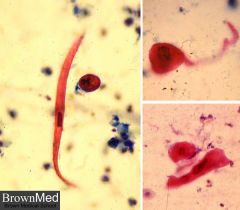
what is it
|
lung scca
|
|
|
strange name for poorly diff squamous ca on cytology
|
poorly differentiated epidermoid ca (probably call undifferentiated large cell carcinoma, probably squamous)
|
|
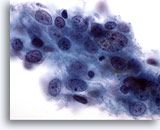
what is it
|
poorly differentiated large cell carcinoma, possibly squamous
|
|
|
what is another name for BAC (bronchoalveolar ca)
|
alveolar cell - arises from terminal bronchioles or in alveolar lining cells
|
|
|
BAC on cytology
|
columnar, no cilia, thick, 3D round or papillary clusters, subtle changes to nuclei, some nucleoli but not large
|
|
|
common sources of metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung
|
breast, GI, GU (uterus, prostate, kidney), melanomas, sarcomes of bone
|
|
|
histologic fx of adenocarcinoma (4)
|
1. columnar (includ vaculoes producing mucin), acinar (ball or grape like), papillaryy with scalloped or smooth outline
2. big nucleoli, sometimes multiple 3. thin cytoplasm, usually finely vacuolated 4. peripheral nuclei with often fine granular cytoplasm |
|
|
source of small cell carcinoma of lung
|
reserve cells or from Kultschitzky cells (SE producing cells)
|
|
|
frequency of small cell ca of lung
|
10-15%
|
|
|
alternative names for small cell ca
|
oat cell ca or anaplastic ca
|
|
|
two ways to distinguish small cell ca from lymphocytes
|
1. small cell cells are slightly larger (12-20 vs 7-10)
2. nuclei of lymphs don't mold usually |
|
|
histologic fx of small cell ca
|
- dark nuclei
- coarse chromatin (more than adenoca) - hard to see cytoplasm - nuclear molding - smudging/crushed nuclei |
|
|
way you will find small cell ca in sputum and washings
|
- usually as single cells or very small clusters
|
|
|
way you will find small cell ca in brushings
|
often large groups several layers deep with some single cells/small clusters
|
|
|
fx of undifferentiated large cell ca
|
no squamous or columnar fx
-large nuclei with large nucleoli thickened nuclear membrane coarse chromatin |
|
|
size of cocciomycoses
|
20-60uM (comparison lymphocyte ~7 uM)
|
|
|
blastomycoses, nature of budding, size
|
broad based budding
5-20 uM |
|
|
cryptococcus, nature of bud, fx, size
|
mucoid capsule, teardrop budding, 5-20 uM
|
|
|
fx of aspergillus
|
septate, fork-stick branching, uniform width
|
|
|
fx of mucor
|
nonseptate, ribbon, right angle branching
|
|
|
calcium oxalate
|
envelopes
|
|
|
triple phosphate
|
coffin lids
|
|
|
cysteine
|
stop signs
|
|
|
tyrosine
|
needles
|
|
|
cholesterol
|
notched plates, stair steps
|
|
|
potential pitfall for small cell ca and how to distinguish
|
reserve cell hyperplasia; very small cellular size, no necrosis
|
|
|
what is the source of a Charcot-Leidin crystal
|
eosinophil degranulation by product
|
|
|
fx of ferruginous bodies
|
asbestos fibers, dumbbell shaped, yellow-black in Pap stain
|
|
|
common sources of psammama bodies in lung
|
- primary pulmonary adenoca
- mesothelioma - metastatic thyroid, ovarian - TB - alveolar microlithisasis (not= to corpora amylacea) |
|
|
alternaria where found
|
water contaminant - pigmented fungus,septate
|
|
|
fx of HSV in lung
|
multinucleation, molding, peripheral margination
also eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions (cowdry A) |
|
|
fx of cmv in lung
|
nuclear enlargement; large basophilic intranuclear inclusions with halo, cytoplasmic enlargement
|
|
|
fx of measles
|
multinucleation; eosinophilic intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions (larger intranuclear?)
|
|
|
Fx of RSV in lung
|
necrosis, giant cells, multinucleation with basophilic cytoplasmic inclusions with halo
|
|
|
fx of adenovirus in lung
|
smudged nuclei with large inclusion that fills entire nucleus
|
|
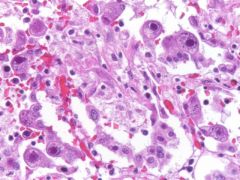
what is it
|
cmv
|
|
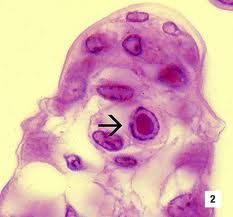
what is it
|
cowdry type A inclusions in HSV
|
|
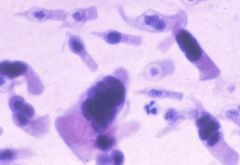
what is it
|
adenovirus
|
|
|
fx of legionella
|
Looks like necrosis.
Mononuclear cells look dirty (nuclear dust). If stained with warthrin-starry, you'd see bacilli. |
|
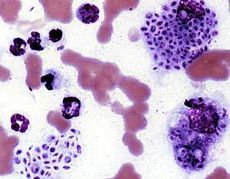
what is it
|
sporotrichosis - intracellular yeast with slight halo, 2-4 um
|
|
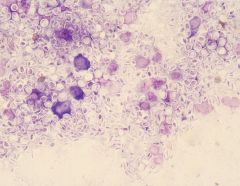
what is it
|
sporotrichosis - intracellular yeast with slight halo, 2-4 um
|
|
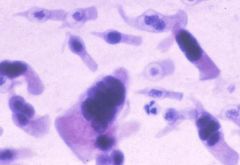
what is it
|
adenovirus
|
|
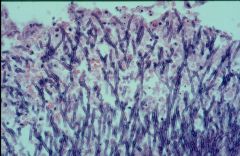
what is it
|
aspergillus - 45 angle, septate hyphae
|
|
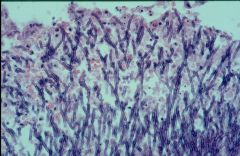
what is it
|
aspergillus - 45 angle, septate hyphae
|
|
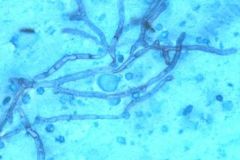
what it is
|
aspergillus - 45 angle, septate hyphae
|
|
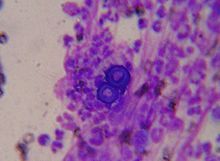
what is it
|
blastomycosis - broad based buds, 8-20uM, found in N. America
|
|
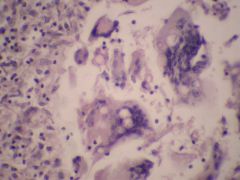
what is it
|
blastomycosis - broad based buds, 8-20uM, found in N. America
|
|
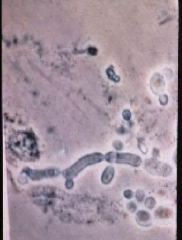
what is it
|
candida - 2-10 um
|
|
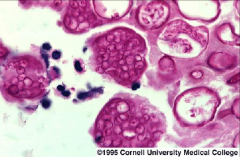
what is it
|
cocciomycosis - valley fever, found in N. American deserts, spherules (15-60uM), endospores (1-2uM)
|
|
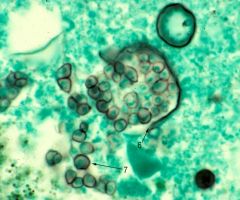
what is it
|
cocciomycosis - valley fever, found in N. American deserts, spherules (15-60uM), endospores (1-2uM)
|
|
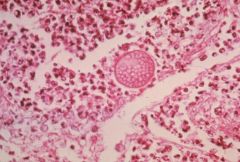
what is it
|
cocciomycosis - valley fever, found in N. American deserts, spherules (15-60uM), endospores (1-2uM)
|
|
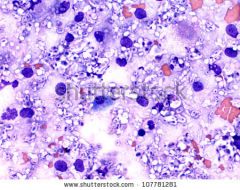
what is it
|
cryptococcus - yeast, narrow based buds, 4-15 um
|
|
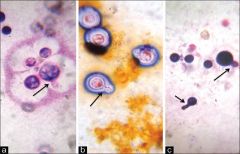
what is it
|
cryptococcus - yeast, narrow based buds, 4-15 um
|
|
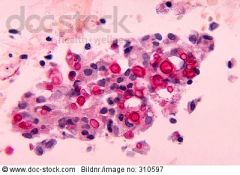
what is it
|
cryptococcus - yeast, narrow based buds, 4-15 um
|
|
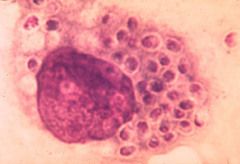
what is it
|
histoplasmosis - 1-5 uM, intracellular small budding yeast, Ohio/Mississippi river valley
|
|
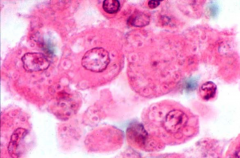
what is it
|
histoplasmosis - 1-5 uM, intracellular small budding yeast, Ohio/Mississippi river valley
|
|
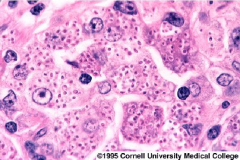
what is it
|
histoplasmosis - 1-5 uM, intracellular small budding yeast, Ohio/Mississippi river valley
|
|
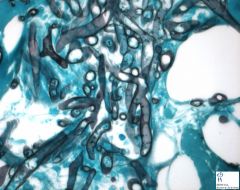
what is it
|
rhizopus (one of zygomycosis/phycomycosis); variably sized ribbon hyphae, nonseptate, 90 degree branching, 10-30 uM
|
|
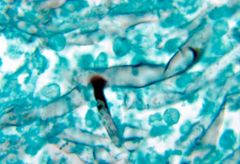
what is it
|
mucor (one of zygomycosis/phycomycosis); variably sized ribbon hyphae, nonseptate, 90 degree branching, 10-30 uM
|
|
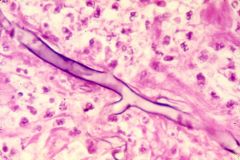
what is it
|
mucor (one of zygomycosis/phycomycosis); variably sized ribbon hyphae, nonseptate, 90 degree branching, 10-30 uM
|
|
|
name four of the phycomycosis family
|
mucor, rhizopus, cunninghamella, absidia
|
|
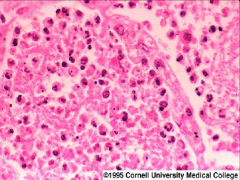
what is it
|
legionella
|
|
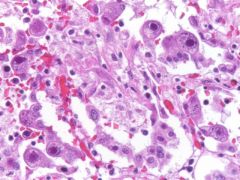
what is it
|
cmv
|
|
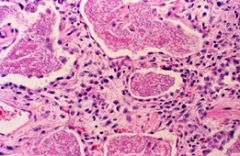
what is it
|
pcp - hard to visualize on h&e but cup shaped (squashed ping pong balls) on gs, no buds, sometimes in alveolar casts
|
|
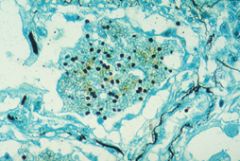
what is it
|
pcp - hard to visualize on h&e but cup shaped (squashed ping pong balls) on gs, no buds, sometimes in alveolar casts
|
|
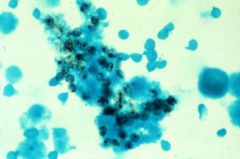
what is it
|
pcp - hard to visualize on h&e but cup shaped (squashed ping pong balls) on gs, no buds, sometimes in alveolar casts
|
|
|
fx of wegener's granulomatosis on cytology (4)
|
granular background debris composed of necrotic collagen, giant cells, pmns, epithelioid histiocytes
|

