![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
103 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What happens to BP during pregnancy ? |
1-2nd trimester = hypotension
3rd trimester = Pre-pregnancy BP |
|
|
What are the types of HTN in pregnancy ?
Characteristics |
-Pre-existing HTN (>140/90mmHg <20 weeks)
-Pregnancy-induced HTN ( > 20 weeks)
-Pre-eclampsia ( >140/90 mmHg + 0.3g/day proteinuria) ( >30/15 mmHg from booking appointment)
-Eclampsia ( >160mmHg + 0.3g/day proteinuria) (Pre-eclampsia + symptoms)
|
|
|
What are the values for HTN in pregnancy ? |
- >140/90 mmHg OR -> 30/15 mmHg from BP @ booking appointment
(If 150/100mmHg -> Anti HTN Rx)
(If 170/110mmHg --> IMMEDIATE Rx) |
|
|
If a patient has HTN during pregnancy , what additional Rx should they be given ?
Nutrition ect.. |
Folic acid 5mg
ASA
betamethasone (b/w 24-34 weeks) |
|
|
When should a patient with HTN be admitted? |
>140/90mmHg + proteinuria (>0.3g/day)
Abnormal biochemistry
Fetal distress
S/S - headache, visual disturbance, abdo pain |
|
|
What are the risk factors for Pre-eclampsia ? |
Previous HTN , pre-eclampsia
>40 yrs - afrocarribean FHx Smoking DM Obesity Chronic renal dx
Multiple pregnancy 1st partner Nulliparous |
|
|
What S/S of Pre-eclampsia ? |
Headache Visual disturbance
SOB (pulmonary oedema) Epigastric/RUQ pain
Frothy urine Peripheral oedema
Hyperreflexia , Clonus
|
|
|
What are the complications of HTN in pregnancy ? |
Cerebral hemorrhage
Blindness
ARDS, pulmonary edema
Liver failure - HELLP, DIC
Renal failure
Placental abruption, IUGR |
|
|
What Ix are indicated for Pre-eclampsia |
FBC, LFT, U&E Coagulation screen
USS Uterine/umbilical artery doppler (if delivery - partogram)
|
|
|
What would an abnormal uterine artery doppler show ? |
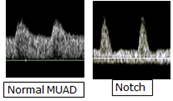
Notching |
|
|
What Rx are indicated for pre-eclampsia |
ASA
Betamethasone INJ (2x 12 hrs apart ) Fluid restriction (80mL/Hr)
If >150/100mmHg --> Labetalol (or Hydralazine/nifedipine if asthmatic) |
|
|
What Anti-HTN can you use in Pregnancy ? |
-Labetalol -Hydralazine -Nifedipine -Methyldopa |
|
|
What are the indications for inducing delivery in a pt with pre-eclampsia ? |
37 weeks gestation
S/S
Fetal distress
Unresponsive to Rx |
|
|
What is HELLP syndrome ?
Characterstics |
(DIC affecting liver)
Hemolytic + Elevated Liver + Low platelets
Characteristics: DIC , Schistocytes, Coca-cola urine , Liver failure , Clotting disorder
|
|
|
How do you monitor a pt with HELLP syndrome ?
Rx? |
Monitoring: Partogram, CTG, Uterine artery doppler
Rx: Fluid restriction (80mL/hr) Betamethasone INJ (2x 12 hrs apart)
-IV Labetalol/nifedipine/hydralazine -MgSulphate -VAGINAL delivery |
|
|
Why is a vaginal delivery indicated for HELLP syndrome ? |
b/c of coagulation disorder!!! |
|
|
What is eclampsia ? |
>160/110mmHg + proteinuria OR Pre-eclampsia + S/S or seizure |
|
|
When does eclampsia commonly occur ? |
Post-partum |
|
|
How do you Rx eclampsia ? |
(Same as HELLP) Monitoring: Partogram,CTG, Uterine artery doppler
Betamethasone (2x 12 hrs apart) Fluid restriction (80mL/hr)
IV labetalol/Nifedipine/Hydralazine MgSulphate Delivery |
|
|
What is a Dx contraindication in pre-eclampsia ?
What can be used instead? |
Syntometrine/Ergometrin ( a vasoconstrictor)
Instead use Syntocinon |
|
|
If Antepartum hemorrhage occurs , what management needs to be done ? |
USS
ABO, rhesus status
Anti-D @ 28 & 34 weeks
Betamethasone INJ (2x 12 hrs apart) |
|
|
What is the DDx of antepartum hemorrhage ?
Characteristics |
Placenta previa (plainless bleed + Abnormal lie/high presenting part)
Vasa previa (painless bleeding + fetal distress)
Placental abruption (Painful hard woody uterus + fetal distress )
Uterine rupture (Periotnism + DIC + ↓ contractions + fetal distress)
Cervical dx (Painless light bleeding)
Show - NORMAL!:) |
|
|
When does antepartum hemorrhage occur ? |
>24 weeks gestation |
|
|
What Ix are indicated for antepartum hemorrhage ? |
FBC ABO/Rhesus status Kleinhauer betke
USS Partogram/CTG |
|
|
What should be cautioned in antepartum hemorrhage ? |
Vaginal examination! (exclude placenta previa!) |
|
|
What is placenta previa ?
Risk factor S/S Ix |
Implantation of placenta in lower uterine segment
Risk factor: previous C-section, Multiple pregnancies , Multiparity
S/S: Painless bleed + Abnormal lie/high presenting part
Ix: USS |
|
|
What is the classification for placenta previa ?
Management ? |
Type I - @ lower uterine segment Type II - touching the cervix Type III - overlying the cervix Type IV - covering the cervix + no dilatation allowed
Type III/IV --> C-section @ 38 weeks/Hemorrhage |
|
|
Picture of placenta previa |
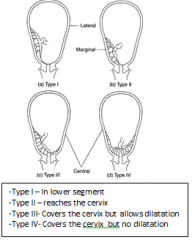
|
|
|
What is placenta acreeta ?
S/S
Complication |
Placental attachment to myometrium
S/S: Delayed stage 3 (i.e placenta doesn't detach!)
Complication: PPH |
|
|
What is vasa previa ?
Types? |
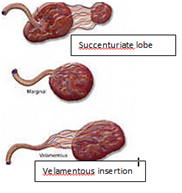
Abnormal attachment of fetal vessels to placenta (overlying cervical os & unprotected from Wharton's jelly)
@ labour -> damage to fetal vessels
Subtypes ; Velamentous (Cord insertion further away from placenta). Succenturiate lobe (Insertion to an abnormal extra lobe) |
|
|
For vasa previa , describe
S/S Rx ? |
S/S: Painless bleed + fetal distress
Rx: C-section URGENT. (b/c occurs @ labour) |
|
|
What is placental abruption ?
Where is the blood loss from? |
Seperation of placenta from uterus
Blood loss from fetal circulation |
|
|
For placental abruption, describe
Risk factors S/S Rx |
Risk factors: HTN, Smoking, Trauma
S/S: Painful Hard woody uterus (bleeding variable) + Fetal distress
Rx: Delivery @ 38 weeks/hemorrhage (if viable --> C section. If stillbirth -> Vaginal)
|
|
|
What are the complications of placental abruption / |
DIC (commonest cause of DIC in pregnancy)
Couvelaire's uterus (Bleeding into myometrium -> peritoneal cavity)
Maternal/fetal death |
|
|
For uterine rupture ,describe
Risk factors S/S Rx |
Risk factor: previous C-section, Syntometrine/syntocinon
S/S: ↓ contractions , Peritonism , high head presentation , fetal distress
Rx: Laparotomy/C-section |
|
|
How much is PPH ?
Vaginal C-section |
Vaginal <500mL
C-section <1L |
|
|
When can PPH occur up to ? |
stage 3 --> 6 weeks post-partum
(PPH >1 day - due to endometritis/retained products ) |
|
|
What is PPH caused by ?
Complications ? |
4T's
Tone Tissue Trauma Thrombin (i.e coagulation disorders)
Complications: DIC/Shock/Sheehan's |
|
|
What is the management of PPH ? |
ABCDE
(MSC) Uterine massage + bimanual compression IM/IV Syntometrine Carboplast/misoprostol |
|
|
What are the different ways of fetal assessment ? |
Head/abdo circumference
CTG
USS - Biophysical assessment
Doppler USS |
|
|
What does CTG compare ?
Describe |
Fetal HR cf. Contractions
(Dr. C. BraVADO) Define Risk Contractions (1x 2-3mins) Baseline Rate (110-160bpm) Variability (5-25bpm) Accelerations (1x10mins) Decelerations (late = hypoxia) Overall score = Suspicious/pathological? |
|
|
What are early decelerations caused by ? |
Compression of fetal head
O.K (occur & resolve w/ contractions) |
|
|
What are variable decelerations caused by ? |
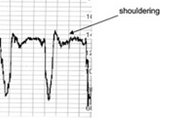
Compression of cord
Associated w/ shouldering |
|
|
What are late decelerations caused by ? |
Fetal hypoxia
WORRYING! |
|
|
What does the biophysical profile of the fetus assess? |
(ABC TM) Amniotic fluid Breathing Circulation- HR
Tone Movement
(2pt if normal) (Normal = 8-10) |
|
|
What does an umbilical artery doppler show ?
What is abnormal ? |
Shows placental resistance to blood flow
Abnormal = notching |
|
|
Why are pregnant women hypercoaguable? |
↑ Clotting factors
↓ natural anticoagulants (Protein C/S, Antithrombin) |
|
|
What is prophylactic Rx of DVT in pregnancy ?
|
LMWH @ delivery + 7 days post-partum
|
|
|
What nutritional supplements should pregnancy women receive ? |
400mcg Folic acid ( 5mg if HTN, epileptic, DM)
300mg Fe
10mcg Vitamin D |
|
|
What Dx are teratogenic ? |
ACEi Betablockers (poor growth) NSAIDS ( premature closure of ductus arteriosis) Warfarin AED (Carbamazepine, valproate) Methotrexate Carbimazole Lithium (Ebsteins anomaly) Tetracycline Sulphonylureas (Gly-, Gli)
Thalidomide Diethylstillbestrol |
|
|
What Dx should be avoided in breastfeeding ? |
Amiodarone (neonatal hypothyroidism) BDZ Cytotoxic dx
Bromocriptine (DA agonist) |
|
|
What effects does pregnancy have on pharmokinetics ?
Absorption Distirbution Metabolism excretion |
Absorption - ↓ morning sickness
Distribution - ↑ Plasma volume & fat . ↓ protein binding (hemodilution)
↑ Metabolism and excretion (↑ hepatic metabolism & GFR) |
|
|
What are infections that can transmit through the placenta ? |
TORCHeS
Toxoplasmosis Rubella CMV HIV Herpes Simplex/Zoster Syphillis
Parvovirus B19 (Hydrops fetalis) Group B strep/ E.coli/Listeria |
|
|
What are the characteristic of neonatal toxoplasmosis |
Chorioretinitis Cataracts
tram-like intracranial calcifications |
|
|
What are the characteristic of neonatal Rubella |
Cataracts + deafness
PDA/pulmonary artery stenosis
Purpura |
|
|
What are the characteristic of neonatal CMV |
Unilateral deafness
Periventricular leukomalacia
Chorioretinitis
Purpura
|
|
|
What are the characteristic of neonatal HIV |
recurrent infection
Chronic diarrhoea |
|
|
What are the characteristic of neonatal Herpes Simplex |
Conjunctivitis
Temporal lobe encephalitis |
|
|
What are the characteristic of neonatal Herpes Zoster ? |
Microophtalmia
Microcephaly
Limb hypoplasia |
|
|
What are the characteristic of neonatal Syphillis |
Hydrops fetalis snuffles Rash on palms/soles
(late) Hutchinson teeth Saber's shins Saddle node Deafness |
|
|
How do you manage HIV in pregnancy ? |
Antiretroviral Rx @ 28-32 weeks gestation Neonatal antiretroviral Rx
C-section
no breasfeeding |
|
|
How do you manage herpes zoster contact in pregnancy |
If immunized --> PO acyclovir if <24 hrs of symptoms
If non-immunized -> IV Varicella Ig
(can detect immunisation by serum varicella Ig) |
|
|
If a neonate is septic , what ABx would you give ? |
IV Cefotaxime |
|
|
What are the risk factors for neonatal infection ? |
maternal pyrexia near labour
PROM >24 hrs
Group B strep +ve in mother , Previous Group B Strep in baby
Pre-term
Meconium aspiration |
|
|
What is hemorrhagic disease of newborn ?
Rx? |
Coagulation dx in neonates due to Vit K deficiency
Rx: Prophylactic vit K IM (iN ALL NEONATES) |
|
|
What is transient tachopnea of newborn ? |
Poor resorption of fluid from lungs --> transient tachopnea
Self-limiting & resolves within 1 day |
|
|
What are the characteristics of fetal alcohol syndrome |
Mental retardation
flat face, smooth philtrum, thin upper lip, epicanthal folds, Upturned nose
Short
VSD |
|
|
What are the characteristics of down syndrome ? |
Variable learning disability low set ears Epicanthal folds
Brushfield spot Single palmar crease 5th clinodactyly 1st wide spaced toe
Early onset dementia ALL/AML VSD/ASD |
|
|
What screening test are performed in neonates ? |
Automated hearing test
Guthrie test @5 days ( PKU, MACAD, CF, Sickle cell, Hypothyroidism)
Infection -TORCHeS, HCV/HBV vaccination |
|
|
When do the baby blues occur ? |
3-7 days post-partum |
|
|
When does post-natal depression occur ?
Rx? |
within 1 month ( peaks @3 months)
Rx: Sertraline |
|
|
What is puerpural psychosis ?
When does it occur
Rx? |
2-3 weeks post-partum
Depression + psychosis
Rx: Emergency admission + ECT |
|
|
What is the commonest metabolic disorder in neonates ? |
Hypothermia -> hypoglycemia -> hypoxia |
|
|
How do you calculate "corrected gestational age" |
Actual age (weeks) - (# weeks preterm)
(Term = 40 weeks) |
|
|
If a child is born @ <32 weeks , when will they reach their milestones ? |
2 yrs old |
|
|
If a child is born @ 32-36 weeks , when will they reach their milestones ? |
1 yr old |
|
|
What is classified as normal birth weight ?
Low ? Very low? Extremely low ? |
Normal =3.5kg
Low <2.5 kg
Very low <1.5 kg
extremely low <1.0kg |
|
|
If a pregnancy is at high risk of pre-term birth , what management Rx should be performed ? |
Anti-D INJ within 72 hrs (or @ 28 & 34 weeks)
Betamethasone INJ (2x 12 hrs apart)
Delay cord clamping for 1 min
Warmth (plastic bag + heater)
|
|
|
What conditions commonly affect pre-term babies ? |
Hypothermia, hypoglycemia, hypoxia
Sepsis
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia , RDS
PDA
Retinopathy of prematurity
Interventricular hemorrhage
NEC |
|
|
How do you Rx sepsis in a neonate
If meningitis if unknown origin ? |
If meningitis -> IV Benzylpenicillin + gentamycin
If unknown origin -> IV cefotaxime |
|
|
What are the S/S of neonatal RDS
Rx?
|
Immediately after birth --> resp distress (grunting, nasal flaring, tachypneic, Indrawing)
Rx: A) CPAP B) Intubation + Artificial surfactant
|
|
|
prophylaxis for neonatal RDS ? |
Betamethasone 2xINJ 12 hrs apart weekly
if high risk - Betamethasone 72 hrs prior to labour
(works best @ 24 hrs) |
|
|
Intraventricular hemorrhage is caused by what ?
Risk factor ? Ix? Prophylaxis ? |
Premature babies w/ germinal matrix present in ventricles --> labour -> hemorrhage of germinal matrix
Risk factors: Prematurity, RDS
Ix: USS of anterior fontanelle
Prophylaxis: antenatal betamethasone
|
|
|
What is Necrotising enterocolitis ?
When does it occur ? S/S Ix Rx |
Ischemic bowel & colon Within 1 week of birth
S/S: Poor feeding, blood stool, abdominal distention, vomitting
Ix: AXR URGENT - shows air in bowel
Rx: NBM IV penicillin + met + gent
|
|
|
How can NEC be prevented ? |
Breastfeeding |
|
|
Pudendal nerve contains which nerve roots ?
Does it supply parasympathetic or sympathetic supply ? |
S2-4
Parasympathetic |
|
|
Which uterine ligament is commonly ligated during sterilization ? |
Round ligament |
|
|
Which ligament attaches the uterus to the sacrum? |
Uterosacral ligament |
|
|
Which ligament attaches the cervix to the pelvic brim?
Is it located medial or lateral |
Cardinal ligament
Lateral |
|
|
Which ligament is the strongest uterine ligament ? |
Uterosacral ligament |
|
|
What does the round ligament attach to ? |
Uterine fundus --> into inguinal canal --> labia majora |
|
|
Which ligaments attach the uterus
Posteriorly Anteriorly Laterally ? |
Posterior = uterosacral
Anteriorly = Round ligament
Laterally = Cardinal ligament |
|
|
Which ligament attaches the ovaries to the uterus ? |
Broad ligament |
|
|
What are the stages of prolapse |
Stage I - within vagina Stage II - @ Hymen Stage III- Past Hymen Stage IV - Procidentia |
|
|
What are the S/S of prolapse |
"feeling of something coming down" Itch Bleed
Urinary S/S- stress incontinence, Retention
Bowel S/S- Constipation, Dyschezie (painful) |
|
|
Management of prolapse |
Lifestyle - avoid heavy lifting, coughing, straining
TOP estrogen
Pessaries - reassess every 6 months
Surgery |
|
|
What surgical options are there for a uterocoele |
Sacrohysteropexy
Hysterectomy (If family complete) |
|
|
What surgical options are there for a vaginal vault prolapse ? |
Manchester repair (meshes + shortening cervix & uterosacral ligament)
Sacrocolpopexy
Colpocleisis ( closure, ONLY if not sexually active) |
|
|
What Surgical options is there for cystocele ? |
Anterior colporrhaphy |
|
|
What surgical options is there for rectocele ? |
Posterior colporrhaphy |
|
|
What is the Gold standard Ix for endometriosis ? |
Laparoscopy |
|
|
What cancers does the OCP protect against ? |
Endometrial Ovarian Colorecal |
|
|
Name e.g of GnRH analogues |
Buserelin
Goserelin |

