![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
150 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The nurse prepares the client for an 8:00 outpatient electroconvulsive(ECT) treatment. Which question is most importantfor the nurse to ask? |
1. "Did you have anything to eat or drink before you came in today?"
2. "Have you had any headaches since your last treatment?" 3. "Who came with you to the hospital today?" 4. "Have you had much memory loss since you began your treatments?" |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to ECT. (1) correct—client givengeneral anesthesia for ECT; NPO after midnight (2) not relevant to ECT (3) not most important (4) memory loss is an expected outcome |
|
|
The client is diagnosed with a flaccid bladder following a spinal cordinjury. The nurse teaches the client about dietary changes. Which beverage,if selected by the client, indicates to the nurse that teaching is effective? |
1. Lemonade.
2. Prune juice. 3. Milk. 4. Orange juice. 5. Cranberry juice. 6. Tomato juice. |
Strategy: "Teaching is effective" indicates a correct statement. (1) promotes alkaline urine; should also avoid citrus juices, excessiveamounts of milk, and carbonated beverages (2) correct—promotesacidic urine, minimizes risk of urinary tract infection and stone formation;also use cranberry, tomato juice, bouillon (3) excessive amounts of milk promote alkaline urine (4) promotes alkaline urine; should also avoid citrus juices, excessiveamounts of milk, and carbonated beverages (5) correct—promotesacidic urine, minimizes risk of urinary tract infection and stone formation;also use cranberry, tomato juice, bouillon (6) correct—promotesacidic urine, minimizes risk of urinary tract infection and stone formation;also use cranberry, tomato juice, bouillon |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client with a long history of alcohol and drugdependence. It is most importantfor the nurse to include which action as part of discharge planning? |
1. Refer to a social service agency for assistance with housing.
2. Refer to an aftercare center in the community. 3. Encourage participation in Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) meetings with a sponsor. 4. Ask the client to obtain a prescription for an antidepressant medication. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) may be of some help, but will not directly provide support necessaryto maintain sobriety (2) may be of some help, but will not directly provide support necessaryto maintain sobriety (3) correct—self-helpgroups have greatest success rate as a sustained support system in the community (4) is information to indicate client depressed |
|
|
The client comes to the clinic for the hepatitis B vaccine. The clientasks if more than one injection is necessary. Which response by the nurseis best ? |
1. "A booster shot is required yearly."
2. "Additional injections are given at one and six months." 3. "Repeat doses are given at two and four months." 4. "Revaccination is not required." |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) yearly doses are given for flu shots, not for hepatitis B vaccine (2) correct—hepatitisB vaccine is repeated at 1 and 6 months (3) schedule for infant immunizations for IPV and DPT (4) inaccurate |
|
|
The nurse plans care for the client returning from surgery after a bowelresection with an IV of 0.9 % NaCl infusing at 100 mL/h into the left wrist.Which action, if performed by the nurse, is best? |
1. Change the IV tubing each time a new IV solution is hung.
2. Cleanse the IV site with an alcohol swab using a circular movement. 3. Limit manipulation of the cannula at the IV insertion site. 4. Adjust the drop rate to keep the total volume of IV fluids on schedule. |
Strategy: The topic of the question is unstated. Read the answer choicesto determine the topic. "BEST" indicates that this is a priority question.All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of each answer choice.Is it desired? (1) unnecessary, changed every 48 to 72 h (2) should move swab back and forth in two horizontal then verticaland then in a circular motion (3) correct—will preventdislodgment of needle (4) should give IV at rate ordered by health care provider, don't play"catch-up" with fluids |
|
|
The nurse notes that one of the staff members caring for clients hasa watery discharge from the right eye and the eye appears red. Which action,if taken by the nurse, is best? |
1. Send the staff member home.
2. Assess the staff member's compliance with standard precautions. 3. Assign the staff member only to clients with chronic diseases. 4. Reassign the staff member to clean the supply closet. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—extremetearing, redness, foreign body sensation are symptoms of viral conjunctivitis;highly contagious; infected employees cannot work until symptoms have resolvedin 3 to 7 days; the nursing supervisor should be notified (2) restrict from client contact and the client's environment (3) restrict from client contact and the client's environment (4) cannot work |
|
|
The nursing staff plans to use behavior modification techniques forthe elderly client who constantly screams. Which nursing assessment is necessaryto establish a successful program? |
1. Monitor the client's ability to complete activities of daily living (ADL).
2. Assess the client's levels of pain and correlate it with the response to analgesia. 3. Observe the client's behavior at regular intervals to obtain baseline information related to the screaming. 4. Ask the client why screaming is occuring and document it on the nursing assessment record. |
Strategy: Determine what is being assessed in each answer choice andhow it relates to screaming. (1) important because activities of daily living can contribute to thetargeted behavior of screaming; assessing only the area of ADLs does not providecomprehensive data for developing a behavior management program (2) important because activities of pain can contribute to the targetedbehavior of screaming; assessing only the area of pain does not provide comprehensivedata for developing a behavior management program (3) correct—to designan effective behavior modification program, accurate baseline data must firstbe collected about the target behavior in relation to frequency, amount, time,and precipitating factors (4) client may be unable to state screaming is occuring; asking "why"questions is nontherapeutic |
|
|
The nurse observes the student nurse check the placement of a nasogastric(NG) tube prior to administering an intermittent feeding. Which action, ifperformed by the student nurse, requires an intervention by the nurse? SATA |
1. The student nurse checks the pH of the contents aspirated from the NG tube.
2. The student nurse positions a stethoscope on the upper abdomen and listens as air is introduced into the NG tube. 3. The student nurse uses a large-barreled syringe to aspirate for stomach contents. 4. The student nurse flushes the NG tube with 30 ml of air before aspirating fluid. 5. The student nurse places the end of the NG tube in a cup of water and watches for bubble formation. |
"Requires an intervention" indicates incorrect behavior. (1) appropriate action; if client has for at least 4 hours, pH of gastricaspirate is 1 to 4 (2) correct—air injectedto lungs, pharynx or esophagus may transmit similar sound (3) acceptable action (4) appropriate action; enables easier aspiration of fluid (5) correct—not consideredacceptable procedure; if tube placed in lungs, may cause bubbling |
|
|
While scheduling the administration of bromocriptine, which nursingaction has the highest priority? |
1. The medication should be taken once a day for 6 weeks.
2. The medication should be taken with orange juice. 3. The medication should be taken in the morning and at bedtime. 4. The medication should be taken with meals. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer. Is it desired? (1) is taken twice a day for 2 to 3 weeks (2) unnecessary (3) will cause GI upset unless taken with meals (4) correct—will decreaseGI upset |
|
|
A brace is ordered for the young teen with scoliosis. The nurse determinesteaching is effective if the client makes which statement? |
1. "I will have my parents put bed-boards on my bed."
2. "I should decrease my caloric intake." 3. "I should only take showers." 4. "I will hold on the rail when going down the stairs." |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) bed-boards maintain proper vertebral alignment but can't correctlateral curvature of scoliosis (2) diet should be high-calorie due to age of child and growth requirements;diet doesn't affect curvature of the spine (3) either tub bathing or a shower is permitted (4) correct—preventsfalls, should also avoid slippery surfaces |
|
|
The nurse in a long-term care facility reviews the nurse's notes inthe client's chart. The nurse is most concerned by which entry? |
1. "Foley catheter draining clear urine and the pH is 6.5."
2. "Nonblanching of reddened intact skin is classified as a pressure ulcers" 3. "Vital signs are within normal limits." 4. "The client drinks three glasses of orange juice every day." |
Strategy: "MOST concerned" indicates something is wrong. (1) appropriate charting of normal urine (2) correct—blanchingor hyperemia that does not disappear in a short time is a warning sign ofpressure ulcers (3) although the charting is not objective, blanching of the skin takespriority because it indicates a problem (4) appropriate charting |
|
|
The nurse cares for clients in the outpatient clinic. The nurse returnsto the desk and finds four phone messages. In which order should the nursereturn the messages? |

|

Strategy: Identify the two most stable clients. Use the ABCs to determinethe most unstable client. Unstable, circulation. The client with nausea and vomiting needs tobe called first as dehydration may be a significant problem; need to findout what is causing the vomiting. unstable. The temperature of 103 is quite elevated for any client andadditional information needs to be obtained. Stable, infection. The decubitus ulcer dressing needs to be addressedsoon, but is not of as much importance as the previous two. Stable. Clinet is not in pain at this time. May be intermittent claudicationand needs to have this addressed but they are the most stable. |
|
|
The client has a bovine graft inserted into the left arm for hemodialysis.During the immediate postoperative period, which action, if performed by thenurse, is best? |
1. Restart the IV above the level of the graft.2. Take blood pressures on the right arm.3. Elevate the left arm above the level of the heart.4. Check the radial pulse on the left arm q4h.
|
Strategy: Determine the outcome of each answer choice. (1) IVs should not be started in the grafted arm (2) correct—BP shouldalways be taken on the opposite arm from the graft (3) unnecessary (4) important to assess circulation in extremity; priority is to preventcomplication |
|
|
The nurse observes late decelerations of the fetal heart rate whilethe client is receiving oxytocin IV to stimulate labor. Which actions shouldthe nurse take? |
1. Change the fluids to Ringers lactate.
2. Discontinue the oxytocin infusion. 3. Assist client to bathroom and measure urine. 4. Turn client to the left side. 5. Apply oxygen at 8 L/min by mask. 6. Increase the primary IV infusion flow rate. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? 1) Changing to a different solution will not be helpful. 2) CORRECT— Discontinuingthe oxytocin is the first step to take. 3) The client should not go to the bathroom and emptying the bladderwill not be helpful. 4) CORRECT— Turningthe client to the left side will aid in blood flow to the placenta. 5) CORRECT— Giving theclient oxygen will help provide additional oxygen to the fetus. 6) CORRECT— Increasingthe fluid infusion will give more volume for transfer of oxygen to the fetus. |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client recovering from abdominal surgery. Duringambulation, the client reports a dull ache in the left leg. Which action shouldthe nurse take first? |
1. Place the client on bedrest with extremity elevated.
2. Place a pillow under the client’s knee. 3. Encourage the client to ambulate more frequently. 4. Obtain thigh-high compression stockings. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—promotesvenous return and decreases venous pressure, relieving pain and edema untilantocoagulants are started. (2) obstructs venous flow, increasing chance for thrombus formation (3) can cause pulmonary emboli, ambulation begins after the start ofantocoagulant therapy (4) used to prevent deep vein thrombosis, should be on bedrest initially |
|
|
The middle-aged client begins outpatient therapy sessions for managementof a phobic disorder. The nurse identifies which intervention is most effective to reduce the client symptoms? |
1. Antianxiety medication.
2. Group psychotherapy. 3. Systematic desensitization. 4. Biofeedback. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) may be used for social phobia or social anxiety disorder (2) may benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy (3) correct—phobic disordersare learned responses; learned responses can be unlearned through certaintechniques, such as behavior modification; systematic desensitization is aform of behavior modification; is a strategy used in conjunction with deepmuscle relaxation to decrease the extreme response to anxiety-producing situationsas they are gradually exposed; then exposure is increased; goal is to eradicatethe phobic response by replacing it with the relaxation response (4) one learns to control the autonomic nervous system; is usually moreuseful for reducing stress associated with physiologically based disorders |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client diagnosed with Cushing's syndrome. Whichnursing action is the priority? |
1. Implement measures to prevent skin breakdown.
2. Plan measures to prevent infections. 3. Teach the client signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia. 4. Instigate measures to prevent fluid overload. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) clients are susceptible to skin breakdown and infections (2) clients are susceptible to skin breakdown and infections (3) impaired glucose tolerance often leads to hyperglycemia, but isnot highest priority (4) correct—respirationsare the first priority; clients with Cushing's syndrome are prone to fluidoverload and CHF due to sodium and water retention |
|
|
The nurse assesses the client diagnosed with a detached retina. Which observation supports this diagnosis? |
1. Loss of acuity in the peripheral visual field.
2. Increased lacrimation, blurred vision. 3. Conjunctivitis, dilated pupils bilaterally. 4. Photophobia, loss of a portion of the visual field. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) loss of peripheral vision occurs with glaucoma; loss of acuity occurswith cataracts (2) occurs with ocular infections (3) has no correlation with detached retina (4) correct—bright flashesof light and client stating that portion of visual field is dark are classicsymptoms |
|
|
The client takes indomethacin 150 mg/day divided in 3 doses. The medicationis supplied as 25 mg/5 mL. How much medication will the nurse administer perdose?Type the answer in the blank. |
calc |
150 mg ÷ 3 = 50 mg/dose 25 mg/5 mL = 50 mg/X X = 10 mL |
|
|
The child comes to the school nurse with a honey-colored crusted lesionbelow the right nostril. Which action should the nurse take first ? |
1. Remove the scab.
2. Apply a wet cloth to the lesion. 3. Notify the child's parents. 4. Contact the health department. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) notify parents first; loosen scab with Burrow's solution compress;gently remove, topical ointment (2) notify parents first; treated with systemic antibiotics, antibacterialsoap (3) correct—describesimpetigo, highly infectious superficial bacterial infection; notify parentsso they can contact the health care provider (4) unnecessary to report impetigo to the health department |
|
|
Which nursing action is the priority foran infant admitted with a positive stool culture for Salmonella? |
1. Change diet to clear liquids.
2. Initiate intravenous fluids. 3. Maintain contact precautions. 4. Apply cloth diapers. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) may be appropriate, but is not a priority over answer choice 3,which will prevent transmission (2) may be appropriate, but is not a priority over answer choice 3,which will prevent transmission (3) correct—preventstransmission of this bacterium to other individuals (4) may be appropriate, but is not a priority over answer choice 3,which will prevent transmission |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client admitted 4 days ago for treatment ofalcohol dependence. The nurse notes the client has slurred speech, ataxia,and uncoordinated movements, and reports a headache. Which action should thenurse take first? |
1. Observe the client for 8 hours to collect additional data.
2. Perform a complete physical assessment. 3. Collect a urine specimen for a drug screen. 4. Encourage the client to talk about whatever is causing distress. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Is thisa situation that requires validation? Yes. (1) will not provide the data that a physical assessment would; maybe a medical emergency requiring an immediate intervention (2) correct—best wayto identify possible physical complications of alcohol dependence is througha complete physical assessment (3) should be done after the physical assessment is completed (4) inaccurate because the symptoms are most likely caused by physicaland not psychological stressors |
|
|
The nurse identifies which client as being at highest riskof developing pulmonary embolus? |
1. The 19-year-old client 4 days postpartum diagnosed with a placenta previa at 28 weeks gestation.
2. The 22-year-old client diagnosed with leukemia with a platelet count of 120,000/mm3 (0.12x1012/L), hemoglobin 9.0 g/dL (5.59 mmol/L). 3. The 40-year-old client who is obese and diagnosed with multiple pelvic fractures due to a motor vehicle accident 2 days ago. 4. The 65-year-old client who had a fractured hip repaired 10 days ago and is currently receiving daily physical therapy. |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to pulmonary embolism. (1) not at risk for pulmonary embolism (2) at high risk for bleeding (3) correct—obesity,immobility, and pooling of blood in the pelvic cavity contribute to developmentof pulmonary emboli (4) client does not have a high risk for pulmonary emboli |
|
|
The nurse supervises the student nurse administer a tube feeding toa client via a Levin tube. Which action, if performed by the student nurse,indicates a proper understanding of the procedure? |
1. The Levin tube remains unclamped for 30 min after the feeding.
2. Sterile equipment is used to administer the feeding. 3. The amount of the feeding is varied according to the client's tolerance. 4. The tube feeding is given at room temperature. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) clamping tube between feedings prevents introduction of air andloss of liquid (2) clean, not sterile, supplies are required (3) health care provider will order amount of feedings; usually beginwith a small amount and increases 50-100 mL until nutritional requirementsmet (4) correct—minimizesintestinal cramping |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client diagnosed with venous thromboembolismof the left leg. Which nursing goal is appropriate for the client? |
1. Decrease inflammatory response in the affected extremity and prevent embolus formation.
2. Increase peripheral circulation and oxygenation of the affected extremity. 3. Prepare the client and family for anticipated vascular surgery on the affected extremity. 4. Prevent hypoxia associated with the development of a pulmonary embolus. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) correct—importantto prevent the complication of pulmonary embolism in clients at high risk (2) relates to arterial disease (3) surgery is not anticipated for this client (4) preventing embolism is the first priority |
|
|
The nurse is called to the room of the client 4 days after abdominalsurgery. The client had been coughing and said "It felt like something gave."The nurse observes that the edges of the incision have separated, and a smallloop of the bowel protrudes through the incision. The nurse should place theclient in which positions? |
1. Head of the bed elevated 30°.
2. Head of the bed tilted down. 3. Head of the bed elevated 15°. 4. Head of the bed elevated 90°. |
Strategy: Answers are all implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) semi-Fowler's; too high, puts pressure on abdominal area (2) Trendelenburg position; impedes respiratory excursion (3) correct—low Fowler's;reduces stress on suture line, may be placed supine with hips and knees bent (4) high Fowler's; too high, puts pressure on abdominal area |
|
|
On a home health visit, an elderly client tells the nurse, "This neighborhoodhas really gone down. I feel like a prisoner in my own home with all the troubleout there." Which nursing response by the nurse is best? |
1. "Have you and your neighbors formed a Neighborhood Watch?"
2. "It must be very difficult for you to live in this neighborhood." 3. "I see a lot of police cars, so you should be pretty safe." 4. "Tell me what has happened to make you feel that you are not safe." |
Strategy: Remember therapeutic communication. (1) jumps ahead to solutions without adequately defining the problem (2) empathetic response, but does not obtain more information from theclient or encourage the client to continue (3) false reassurance (4) correct—assessingthe basis for client's fears and encouraging client to talk about them isthe first positive step |
|
|
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is ordered for the client scheduled tohave the left kidney removed due to renal disease and hypertension. Whichnursing action has the highest prioritythe evening before the IVP? |
1. Administer a cathartic enema to cleanse the bowel.
2. Obtain information about client allergies. 3. Instruct the client to be NPO after midnight. 4. Teach the client x-rays will be taken at multiple intervals. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Is theassessment appropriate? Yes. (1) implementation; contains correct information, but is not a priority (2) correct—assessment;clients sensitive to iodine can develop anaphylaxis; client should be askedspecifically about allergies to iodine; iodine is present in the radiopaquematerial that is injected IV (3) implementation; contains correct information, but is not a priority (4) implementation; test may be canceled if the client is allergic toiodine |
|
|
The nurse cares for the 8-lb, 8-oz newborn. The infant’s historyindicates the mother was given magnesium sulfate IV 4 g in 250 mL D5Wseveral hours before delivery. The nurse is most concernedif which finding is observed? |
1. Temperature 97.6°F (36.5°C).
2. Apical pulse 140 bpm. 3. Respirations 18/min. 4. BP 80/50. |
Strategy: "MOST concerned" indicates a complication. (1) normal temperature 98.6°F (37.0°C), magnesium sulfate doesnot affect temperature (2) normal pulse 120-140 bpm, magnesium sulfate does not affect cardiacsystem of infant (3) correct—magnesiumsulfate can cause slowing of respirations and hyporeflexia; normal respirations30-60/min (4) normal BP 60/40-80/50, magnesium sulfate does not affect BP |
|
|
The nurse assists the client from the bed to the chair for the firsttime after a right total hip replacement. It is most importantfor the nurse to take which action? |
1. Assist the client to stand on the right leg and pivot to a low soft chair, keeping the hips straight.
2. Assist the client to stand on the left leg and pivot to a straight-backed chair, flexing the hips slightly. 3. Ask the client to bear weight equally on both legs, bend at the waist, and sit in a low soft chair. 4. Assist the client to stand on both legs and take a few steps to a straight-backed chair. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) should not bear weight on affected side, dislocation may occur (2) correct—preventsdislocation (3) no weightbearing on affected leg, dislocation may occur (4) no weightbearing on affected leg, dislocation may occur |
|
|
At approximately 18:00, the nurse begins to open the nurses' notes forthe 15:00-23:00 shift. The last entry is noted for 13:00, and there is nosignature. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate? |
1. Leave approximately three or four lines for the previous nurse to enter information and sign the chart.
2. Review with the client the activities after 13:00 and enter what are determined to be the activities after 13:00. 3. Begin documenting on the next line below the last entry and make a note for the previous nurse to make a late entry to complete the chart. 4. Do not enter anything until the previous nurse has been notified of the problem and returns to the unit to complete documenting. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) blank lines should never be left in the nurses' notes (2) nurse should chart only the care that s/he has administered (3) correct—previousnurse can make a "late entry" to add any additional information (4) unnecessary |
|
|
The client begins doxepin hydrochloride 75 mg PO tid. The nurse shouldrecommend a change in the client's therapy if which finding occurs? |
1. The client refuses to speak and sits quietly in the room.2. The client becomes excitable and develops tremors.3. The client refuses to eat breakfast.4. The client sleeps 18 hours a day.
|
Strategy: Think about the cause of each assessment and how it relatesto Sinequan. (1) not relevant to this medication (2) correct—doxepinHCL is an antidepressant; signs of overdosage include excitability and tremors (3) not relevant to this medication (4) not relevant to this medication |
|
|
Which guideline is appropriate for the nurse to give a mother concerningthe developmental stage of her 7-year-old child? |
1. Periods of shyness are to be expected.
2. Nightmares are not characteristic of this age and should be investigated. 3. The child should be encouraged to care for younger sibling. 4. Punishment may be necessary for acts of independence. |
Strategy: Remember growth and development. (1) correct—normal fordevelopmental stage, beginning to show independence from parents (2) nightmares are frequently experienced at this age (3) should be encouraged to be independent, not responsible for sibling,inappropriate for this age group (4) should allow child to be increasingly independent without punishment |
|
|
The client is scheduled for a cardiac catheterization and the nurseteaches the client about the procedure. Which statement, if made by the clientto the nurse, indicates an understanding of the teaching? |
1. "I'm going to feel cold during the procedure."
2. "I can get up and walk to the bathroom immediately after the procedure." 3. "The nurse will be checking my foot pulses after the procedure." 4. "I won't be able to eat for 24 hours before the procedure." |
Strategy: "Understands teaching" indicates that you are looking fora true statement. (1) may feel burning sensation when dye injected (2) on bedrest 8 to 12 h after procedure with pressure dressing appliedover catheter insertion site (3) correct—peripheralpulses checked every 15 min for 1 h, then every 30 min for 2 h, then every4 h (4) NPO midnight before procedure |
|
|
The client had an aortic aneurysm resection 2 days ago. A complete bloodcount reveals a very low red blood cell count. The nursing assessment is most likely to reveal which information? |
1. Fatigue and exertional dyspnea.
2. Nausea and vomiting. 3. Pallor and dizziness. 4. Vertigo and flushing. 5. Malaise and tachycardia. 6. Hypertension and constipation. |
Strategy: Think of how low oxygen levels effect the body. 1) CORRECT— Tirednessand difficulty obtaining enough oxygen. 2) Nausea and vomiting are not symptoms of lack of oxygen. 3) CORRECT— Low redcell levels cause paleness and lack of oxygen causes dizziness, especiallyon changing position. 4) Vertigo and flushing are not symptoms of low red cell/oxygen levels. 5) CORRECT— Malaiseor tiredness comes from low red cell/oxygen levels; tachycardia is the body'sway of attempting to compensate for the low oxygen levels. 6) Hypertension and constipation are not related to low oxygen levels. |
|
|
The health care provider orders fentanyl 100 micrograms every 2 hoursPRN for pain for a client. The client asks the nurse for the medication atbedtime. Before administering the pain medication, the nurse should take whichaction? |
1. Determine if the pain is psychological.
2. Read the client’s chart to see if the client has a history of addiction. 3. Try several other comfort and pain relief measures. 4. Ask the client about the location, character, and intensity of the pa |
(1) should assess client first (2) not highest priority, should assess client first (3) need to assess before implementing action (4) correct—assessmentfirst step in nursing process |
|
|
The nurse assesses the pregnant client with a diagnosis of mitral stenosisand heart failure (HF). The nurse identifies that which finding in the client'shistory has a direct correlation with the current problem? |
1. History of rheumatic fever 4 years ago.
2. Presence of ventricular septal defect as an infant. 3. Heart disease in both the maternal and the paternal families. 4. Persistent ear infections and mastoiditis as a child. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) correct—most commoncause of mitral valve problems is a history of rheumatic fever with a subsequentcomplication of carditis, which affects the valve (2) does not contribute to mitral valve disease (3) does not contribute to mitral valve disease (4) does not contribute to mitral valve disease |
|
|
The nurse prepares a client for a paracentesis. It is MOST importantfor the nurse to take which action? |
1. Keep the client NPO 12 hours before the procedure.
2. Ask the client to void just before the procedure. 3. Initiate a bowel preparation program 24 hours before the procedure. 4. Place the client supine during the procedure. |
Strategy: Answers are all implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) does not need to be NPO (2) correct—preventspuncture of bladder (3) bowel preparation unnecessary (4) would make it more difficult to drain fluid; patient should be positionedsitting upright at side of bed with feet supported |
|
|
The nurse is caring for the client in the ICU. Hemodynamic monitoringis accomplished by way of a Swan-Ganz catheter. The nurse is aware that thistype of monitoring will provide which information? |
1. Measures the circulatory volume in the coronary arteries.
2. Indirectly measures the pressure in the ventricles. 3. Analyzes the adequacy of pulmonary circulation. 4. Directly measures the adequacy of carbon dioxide exchange. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) not a function of this catheter, and does not reflect hemodynamicmonitoring (2) correct—CVP readingsmeasure the pressure in the right ventricle, the Swan-Ganz catheter measuresthe pulmonary artery wedge pressure, which is an indirect reading of the pressurein the left ventricle (3) not a function of this catheter, and does not reflect hemodynamicmonitoring (4) not a function of this catheter, and does not reflect hemodynamicmonitoring |
|
|
The client is admitted with a diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia (ticdouloureux) involving the maxillary branch of the affected nerve. When performingclient teaching, it is most importantfor the nurse to include which instruction? |
1. "Report an increase in blurred vision."
2. "Eat soft, warm foods." 3. "Change positions slowly." 4. "Chew food on the affected side." |
Strategy: Answers are all implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) unnecessary, does not occur with this condition (2) correct—intensefacial pain experienced along nerve tract is characteristic of this condition;nursing care should be directed toward preventing stimuli to the area anddecreasing pain (3) intervention for Ménière's disease (4) chewing food on unaffected side less likely to trigger an attack |
|
|
An abdominal wound irrigation with a normal saline solution is orderedfor the client. To perform this procedure, the nurse should take which action? |
1. Warm the irrigating solution to 110.0ºF (43.3ºC).
2. Establish a sterile field that includes the irrigating equipment. 3. Direct the irrigating solution at the outer edges of the wound, then the center of the wound. 4. Aspirate the irrigating fluid with a syringe to prevent accumulation in the wound. |
Strategy: Answers are all implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) too warm, should be room temperature or 90-95°F (32.2-35.0°C) (2) correct—requiresstrict aseptic technique (3) may cause new microorganisms to be flushed into wound (4) fluid should drain by gravity |
|
|
The lab reports a lecithin/sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio of 3:1 for a clientwho has been on bedrest 48 hours in an unsuccessful attempt to arrest prematurelabor at 33 weeks gestation. Based on this result, the nurse anticipates whichaction to occur? |
1. Administration of ritodrine hydrochloride.
2. Initiation of an oxytocin drip. 3. Delivery of the infant by cesarean. 4. Continuation of bedrest until otherwise indicated. |
Strategy: Determine the significance of each answer choice and how itrelates to the L/S ratio. (1) no longer necessary, as the results indicate sufficient lung maturityfor safe delivery (2) although the lungs are mature enough for safe delivery, client wouldeither be allowed to progress naturally to a vaginal delivery or would havea cesarean, but not induced (3) correct—becausethe lungs are adequately mature, there is no need to attempt to postpone labor;delivery by cesarean is generally preferred for preterm infants (4) is no longer necessary with adequately mature lungs |
|
|
The nurse cares for clients in the hospital. Which nursing activitiesbest promote nighttime rest for elderly hospitalized clients? |
1. Tell the client how to call for help if needed.
2. Place a clock at the bedside. 3. Postpone explanation of further tests the client will need. 4. Restrict visitors so that the client is not stimulated in the evening. 5. Identify normal evening bedtime routines. 6. Keep bright light in room to prevent falls. |
Stragegy: Think about going to sleep and resting, what is needed? 1) CORRECT— If the clientdoes not need to worry about getting help, sleep will be easier. 2) Having a clock is not usually helpful for sleeping. 3) CORRECT— Giving theclient information that may be troubling will not help with sleep. 4) Having visitors may help the client relax and should not be restricted. 5) CORRECT— Followingnormal routines will help the client fall asleep and stay asleep. 6) Bright lights will prevent deep sleep. |
|
|
The nurse has just received report from the previous shift. In whatorder should the nurse see these clients? |

|

Strategy: Identify the least stable clients to see first and the moststable to see last. Unstable, unexpected; The diabetic client is likely experiencing hypoglycemia. Stable, unexpected, circulation, real; The client with renal failureis retaining fluid and needs to be assessed. Stable, expected, circulation; New postop clients need to be assessedearly in the shift. stable, expected, circulation; The diarrhea needs to be addressed, butis least important of these clients. |
|
|
The client admitted with a diagnosis of metastatic cancer has been receivingchemotherapy for 3 months. The client’s lab values include RBC 3.8 million/mm3 (3.8 x1012/L), WBC2,000/ mm3 (2 x109/L),Hgb 9.3 g/dL, platelets 50,000/ mm3 (50 x109/L).Which nursing diagnosis is most appropriatefor this client? |
1. Decreased cardiac output.
2. Ineffective thermoregulation. 3. Risk for injury. 4. Ineffective airway clearance. |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to the lab values (1) will increase due to decreased oxygenation caused by anemia (2) no change in temperature (3) correct—due to lowplatelet count, normal platelets 150,000-400,000/ mm3 (15-40x109/L), decrease causes problems with blood clotting (4) no information about airway problems |
|
|
The young client with a postoperative abdominal abscess had a draininserted. Which assessment by the nurse is BEST? |
1. Amount of the drainage.
2. Character of the drainage. 3. Consistency of the drainage. 4. Amount of suction on the drainage system. |
Strategy: Think about the significance of each assessment and how itrelates to a wound abscess. (1) lower priority (2) correct—with thiscomplication, the character of the drainage, purulent or otherwise, is a majorpriority to note and report (3) lower priority (4) unnecessary |
|
|
When caring for the elderly client with a depressed affect, which nursingaction is most appropriate to helpthe client to complete activities of daily living? |
1. Medicate the client before the activities begin.
2. Develop a written schedule of activities, allowing extra time. 3. Assist the client with grooming activities so it doesn't take as long. 4. Provide frequent forceful direction to keep the client focused. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) will not increase the client's independence and may interfere withthe client's self-esteem (2) correct—writtenschedule with built-in extra time will allow client to understand what isexpected and will allow client to participate at a slower pace (3) will not increase the client's independence; allow extra time forcare (4) will not increase the client's independence and may interfere withthe client's self-esteem |
|
|
The client is returned to the room following an appendectomy. The nursenotices a large amount of serosanguineous drainage on the dressing. It is most important for the nurse toobtain an answer to which question? |
1. "Were there any intraoperative complications?"
2. "Has the dressing been changed?" 3. "Why didn't the recovery room nurse report any drainage?" 4. "Was a tissue drain placed during surgery?" |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to an appendectomy. (1) doesn't indicate understanding that drainage may be normal afterthis surgery (2) first dressing usually changed by health care provider (3) doesn't indicate understanding that drainage may be normal afterthis surgery (4) correct—drain isfrequently placed during surgery to prevent accumulation in wound, dressingshould be reinforced |
|
|
The nurse cares for a client in her third trimester of pregnancy. Thenurse is MOST concerned by which assessment finding? |
1. The client reports epigastric pain.
2. The client reports shortness of breath. 3. The client states she has increased rectal pressure. 4. The client has gained of 33 pounds during her pregnancy. |
Strategy: Think about the cause of each symptom and how it relates topregnancy. (1) correct—is usuallyindicative of an impending convulsion (2) expected observation (3) expected observation (4) is important to address, but is not as high a priority as answerchoice 1 |
|
|
The middle-aged adult is seen in the emergency department for reportsof severe right-flank pain. The client is 20 pounds overweight, lives a sedentarylifestyle, and was treated for urinary tract calculi 4 years ago. Which action,if performed by the nurse, is most important? |
1. Ensure that the client has nothing to eat or drink.
2. Obtain a "clean-catch" urine specimen for analysis. 3. Provide warm packs to relieve discomfort. 4. Measure and strain the client's urine. |
Strategy: "MOST important" indicates discrimination is required to answerthe question. (1) should force fluids to 3,000 mL/day to assist client to pass stone (2) not most important, used to identify infection (3) not most important, analgesics given to reduce discomfort (4) correct—will documentpassage of stone and allow composition to be analyzed |
|
|
The nurse supervises a student nurse teach the client about a newlyprescribed medication. Which action, if observed by the nurse, requires anintervention? |
1. The student nurse glances at the clock when instructing the client.
2. The student nurse uses culturally appropriate language and teaching materials. 3. The student nurse begins instructions to the client discussing information that concerns the client. 4. The student nurse chooses a time for teaching when there are no visitors. |
Strategy: "Requires an intervention" indicates that you are lookingfor an incorrect behavior. (1) correct—lack ofattending behaviors are always a barrier to learning (2) appropriate teaching strategy (3) appropriate teaching strategy (4) appropriate teaching strategy |
|
|
Prior to a caesarean delivery, the client is treated for abruptio placenta.The nurse cares for the client during the postpartum period. Which symptomis suggestive of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)? |
1. The client's vital signs are: BP 90/58, temperature 101.0°F (38.3°C), pulse 112/min, respirations 18/min.
2. The client’s laboratory results are Hgb 13 g/dL, HCT 40% (0.40 volumn fraction), WBC 7,000/ mm3 (7x109/L). 3. The client is nauseated, lethargic, and has vomited three times. 4. There is oozing blood from the venipuncture site and abdominal incision. |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to DIC. (1) may indicate hemorrhage or sepsis (2) results normal, DIC would be reflected in clotting studies (PT,PTT) (3) nonspecific, could be related to anesthesia or pain medication (4) correct—DIC is anacquired clotting disorder from overstimulation, prolonged oozing from sitesof minor trauma first symptom |
|
|
The 4-week-old infant with symptoms of pyloric stenosis is brought tothe outpatient clinic by the parent. Which statement does the nurse expectthe parent to make about the infant's symptoms? |
1. "My infant's bowel movements have turned black and sticky."
2. "I really have to encourage my infant to suck the bottle." 3. "My infant is fussy and seems hungry all the time." 4. "My infant spits up green liquid after feeding." |
Strategy: Determine how each statement relates to pyloric stenosis. (1) not expected with pyloric stenosis, suggestive of blood in stool (2) sucking problems not expected with pyloric stenosis (3) correct—becomeslethargic, dehydrated, and malnourished (4) would expect emesis to contain milk or formula, should not be bile-colored |
|
|
The health care provider(HCP) prescribes cimetidine 300 mg PO qid foran elderly client. The nurse instructs the client about the medication. Whichstatement, if made by the client, indicates further teaching is needed? |
1. "I'll take this pill with meals and before bed."
2. "I may experience mild diarrhea for a while." 3. "My stools may change color while I'm on this medication." 4. "I should call my HCP if I get an acne-like rash." |
Strategy: "Further teaching" indicates incorrect information (1) taking with meals ensures consistent therapeutic effect (2) common side effect, usually subsides (3) correct—no changein stool color (4) side effect seen with medication |
|
|
The teenager comes to the clinic reporting fatigue, a sore throat, andflu-like symptoms for the previous 2 weeks. Physical exam reveals enlargedlymph nodes and temperature of 100.3°F (37.9°C). Which statementby the nurse is best? |
1. "Cover your mouth and nose when you sneeze or cough."
2. "Eat in a separate room away from your family." 3. "Don't share your drinking glass or silverware with anybody." 4. "Stay in your room until all of your symptoms are gone." |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) mononucleosis is spread by direct contact (2) no reason to be isolated (3) correct—symptomsindicate mononucleosis, spread by direct contact; advise family to avoid contactwith cups and silverware for about 3 months (4) clients with mononucleosis are not isolated |
|
|
Which strategy is most therapeuticas the nurse tries to analyze a bulimic client's eating habits and the circumstancesthat precipitate the client's eating problems? |
1. Observe family communication patterns at a "monitored mealtime."
2. Distract the client at mealtime. 3. Assign the client a food/thought/feelings/actions journal. 4. Assign the client to write a "lifeline" in relation to eating behaviors. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Is theassessment appropriate? No. Determine the outcome of each implementation. (1) assessment, should be done after a food/thought/feelings/actionsjournal (2) implementation, should be done after a food/thought/feelings/actionsjournal (3) correct—implementation,nurse is trying to analyze and understand what triggers the client's bingingand purging activities, so therapeutic nursing intervention of assigning athought/feelings/actions (T/F/A) journal relating to client's eating behaviorswill be most helpful to the nurse and therapeutic to the client; after thisinformation is gained and reviewed, collaboration by the nurse and clienton other strategies such as delay and distraction techniques, stress reduction,and developing a "lifeline" in relation to eating behaviors will further benefitthe client (4) implementation, should be done after a food/thought/feelings/actionsjournal |
|
|
The 20-year-old primipara attends a class for women who plan to breastfeed. To prepare for breast feeding, the nurse should encourage the womento perform which implementation? |
1. Apply moisturizer to the breasts every day after bathing.
2. Nurse the infant every 4 to 5 hours after delivery. 3. Wash breasts with water only. 4. Massage the breasts to increase circulation twice daily. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) use of creams not recommended, could cause breast tissues to becometender, sebaceous glands keep skin pliable (2) infant should be nursed immediately after birth and every 2 to 3hours after; will prevent breast engorgment and nipple damage (3) correct—soap avoided to prevent drying (4) could cause breast tissues to become tender |
|
|
The adult client with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes is being seenby the home health nurse. The health care provider placed the client on an1,800-calorie ADA diet, ordered the client to self-administer 15 units ofisophane each day before breakfast, and check the blood glucose qid. Whenthe nurse visits the client at 17:00, the nurse discovers that the clienthas not eaten since noon and has just returned from jogging. The client'svital signs are: BP 110/80, pulse 120/min, respirations 18/min, and temperature98.2°F (36.8°C). The nurse anticipates the client’s blood glucoseto be which value? |
1. 250 mg/dL (13.88 mmol/L).
2. 160 mg/dL (8.88 mmol/L). 3. 90 mg/dL (5 mmol/L). 4. 50 mg/dL (2.78 mmol/L). |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) hyperglycemia symptoms are hot dry skin, rapid, deep respirations(Kussmaul), lethargic, polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, glycosuria, nausea,and vomiting (2) NPH insulin is intermediate-acting, onset 3—4 hours, peak8—16 hours, duration 18—26 hours (3) normal blood glucose 70—110 mg/dL (3.9—6.1 mmol/L) (4) correct—hypoglycemiasymptoms are cool, clammy skin, diaphoresis, nervousness, weakness, hunger,confusion, headache, slurred speech, coma |
|
|
The parent of the 8-month-old infant prepares to take the child homeafter treatment for bacterial meningitis. The parent confides to the nurseof being afraid that the child will have brain damage as a result of the illness.Which statement is the best responseby the nurse? |
1. "Trust your health care provider. They are excellent and will know what to look for."
2. "There is a 20% incidence of residual brain damage after this type of illness, but the odds are in your favor." 3. "It is an unlikely possibility, but if your child doesn't develop normally, your health care provider will help you with any problems." 4. "You feel guilty about your child's illness, and that's understandable. You will feel better after you get home." |
Strategy: Remember therapeutic communication. (1) nontherapeutic, diminishes person's concerns and feelings (2) nontherapeutic to discuss statistics with clients, wrong emphasisfor discussion (3) correct—if treatedearly, good prognosis; may be complications and long-term effects (seizuredisorders, hydrocephalus, impaired intelligence, visual and hearing defects);therapeutic response (4) nontherapeutic, interprets person's feelings |
|
|
The nurse prepares the client for a herniorrhaphy. It is MOST importantfor the nurse to take which action 1 hour before surgery? |
1. Administer an enema.
2. Confirm the consent form has been signed. 3. Perform a preoperative shave and scrub. 4. Evaluate for food or medication allergies. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Is theassessment appropriate 1 hour before surgery? No. Determine the outcome ofeach implementation. (1) should be done earlier than 1 hour before surgery (2) correct—surgicalconsent should be rechecked before going to surgery (3) should be done earlier than 1 hour before surgery (4) assessment; should be done earlier than 1 hour before surgery |
|
|
The nurse cares for the child diagnosed with a fractured right femur.The child is in balanced suspension traction with a Thomas splint and Pearsonattachment. When the nurse checks the client, the nurse finds the weightson the floor, and the child’s feet touching the foot of the bed. Whichaction by the nurse is most appropriate? |
1. Release the traction weights and reposition the child in bed.
2. Pull on the traction weights while two nurse's aides pull the child up in bed. 3. Steady the traction and ask the child to bend the left leg and push up in bed. 4. Assess the child's right leg for proper position and alignment. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Doesthis situation require assessment? No. Determine the outcome of each answerchoice. (1) release of weights would change pull of traction, weight shouldnever be released (2) pulling on traction weights would alter proper pull on fracture (3) correct—permitspatient to reposition self and re-establish pull of traction weights (4) would not re-establish proper pull of traction |
|
|
The nurse makes rounds on the postpartum unit. The nurse notes thata client's uterus is relaxed. The nurse should take which actions? |
1. Encourage the client to drink warm oral fluids.
2. Check the client's pulse and respirations. 3. Massage the fundus until firm. 4. Put the infant to the client's breast. 5. Assess the bladder for fullness. 6. Continue to monitor the fundal height. |
Strategy: Identify all of the actions to help contract the uterus. 1) Drinking any kind of fluids will not help contract the uterus. 2) Checking the pulse and respirations will not help contract the uterus. 3) CORRECT— Massageis the first action to contract the uterus. 4) CORRECT— Having theinfant nurse will cause oxytocin to be produced which will contract the uterus. 5) CORRECT— A full bladderwill cause the uterus to relax and needs to be emptied. 6) Monitoring fundal height is routine and will not help the uterusto contract. |
|
|
The client diagnosed with Addison's disease is admitted with pneumonia.The nurse suggests salted broth for lunch. The appropriateness of this decisionis based on which statement about Addison's disease? |
1. The client requires increased sodium intake to prevent hypotension.
2. A decrease in sodium intake may lead to seizures. 3. Steroid replacement causes rapid loss of sodium. 4. Sodium intake should be increased during periods of stress. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) not as important as answer choice 4 (2) not a correct statement for this condition (3) steroid replacement increases sodium retention (4) correct—with decreasein aldosterone, there is an increased excretion of sodium; sodium intake shouldbe increased |
|
|
The nurse performs screening at the local senior citizen facility. Thenurse is most concerned if whichfinding is observed? |
1. A 69-year-old client has a slightly elevated systolic blood pressure.
2. The nurse has difficulty palpating an apical pulse on a 74-year-old client. 3. The nurse auscultates an S3 ventricular gallop on a 78-year-old client. 4. An 81-year-old man has a temperature of 98.2°F (36.7°C). |
Strategy: Determine how each assessment relates to an older adult. (1) usual finding for the older adult (2) usual finding for the older adult (3) correct—ventriculargallop is the earliest sign of HF (4) may be normal in all age groups |
|
|
The nurse cares for a client diagnosed with sickling crisis. The nurseinstructs the client about how to use patient-controlled analgesia (PCA).The nurse determines teaching is effective if the client makes which statement? |
1. "If I start feeling drowsy, I should notify the nurse."
2. "This button will give me enough to kill the pain whenever I want it." 3. "If I start itching, I need to call you." 4. "This medicine will help me feel no pain." |
Strategy: Think about what the words mean. (1) may feel sleepy due to medication (2) preset dose administered with preset lock-out times (3) correct—itchingis a common side effect of narcotics used in PCA pain management (4) indicates a need for further teaching or clarification |
|
|
The client taking chlorpromazine should be instructed to notify thenurse immediately if the client experiences which sign or symptom? |
1. Dry mouth and nasal stuffiness.
2. Increased sensitivity to heat. 3. Difficulty urinating. 4. Weight gain and constipation. |
Strategy: Determine the cause of each answer choice and how it relatesto chlorpromazine (1) possible side effect of antipsychotic medications, but client canbe instructed on measures to take at home to resolve this problem (2) possible side effect of antipsychotic medications, but client canbe instructed on measures to take at home to resolve this problem (3) correct—is an anticholinergicreaction that may become a severe health problem unless treated (4) possible side effect of antipsychotic medications, but client canbe instructed on measures to take at home to resolve this problem |
|
|
The charge nurse develops assignments for the evening shift. The nursenotes that the client with a tracheostomy with purulent drainage and a pendingculture and sensitivity (C&S;) is sharing a room with the client diagnosedwith neutropenia. Which action by the charge nurse is most appropriate? |
1. Assign an experienced nurse to care for both clients in the same room.
2. Assign each client a separate nurse. 3. Place the client diagnosed with neutropenia in a private room and assign the same nurse to care for both clients. 4. Place the client diagnosed with neutropenia in a private room and assign different nurses to care for each client. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer. Is it desired? (1) should be in a private room away from roommate with infection (2) should be in a private room away from roommate with infection (3) should be cared for by different nurses (4) correct—infectionin a neutropenic individual may cause morbidity and fatality; place the neutropenicclient in a private room; limit and screen visitors and hospital staff withpotentially communicable illnesses |
|
|
An older client has an order for digoxin 0.25 mg PO daily. Which informationwould cause the nurse to withhold the medication and contact the health careprovider? |
1. Apical pulse of 55 bpm.
2. Respirations of 16 per min. 3. Plasma digoxin level of 2.1 ng/mL(2.7 nmol/L). 4. Blood pressure of 122/62. 5. Apical rhythm has 20 skipped beats in 1 minute. 6. Temperature 100.5° F. |
1) CORRECT— Pulse below60 bpm. 2) Respirations are not related to digoxin. 3) CORRECT— Normal digoxinplasma levels are 0.8-2 ng/mL (1.03 - 2.56 nmol/L). 4) Normal blood pressure, not related to digoxin. 5) CORRECT— Dysrhythmiasmay be caused by the digoxin. 6) Temperature is not significantly elevated. |
|
|
The nurse changes the dressing on the client who had a mastectomy 2days ago. After the nurse removes the old dressing, the client turns theirhead away. Which statement is the best responseby the nurse? |
1. "I notice that you turn your head away as if you don't want to look at your incision."
2. "It's good that you turn your head away while I am doing this sterile procedure." 3. "Your incision looks like it's healing nicely." 4. "Why don't you look at the incision while I have the old dressing off?" |
Strategy: Remember therapeutic communication. (1) correct—states observation (2) doesn't help client confront feelings (3) doesn't deal with avoidance behavior (4) nontherapeutic to ask why, causes client to be defensive |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client with a three-chamber water-seal drainagesystem (Pleur-evac). When the nurse checks the client, the nurse notices thefluid in the water-seal chamber does not fluctuate. Which action by the nurseis best? |
1. Milk the tube gently toward the collection chamber.
2. Anticipate the need for a chest x-ray. 3. Add water to the water seal chamber to re-establish the system. 4. Clamp the chest tube and call the health care provider. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) milking is done only with order of health care provider to clearobstruction due to clots, fluid is clear (2) correct—fluctuationsstop with re-expansion of lung, x-ray will confirm (3) should be kept at level of 2 mL to maintain negative pressure (4) only clamp tube when checking for air leaks or changing equipment |
|
|
*The 10-year-old child weighing 50 lb (23.6 kg) returns from surgeryfor a skin graft to the left leg. The child has an IV of D5Winfusing into the left arm. The health care provider’s orders read:"D5W 2,000 cc/24 h." It is most importantfor the nurse to take which action? |
1. Call the health care provider to clarify the IV fluid order.
2. Keep accurate records of the child's intake and output. 3. Set the controller on the IV pump to infuse at 84 gtt/min. 4. Monitor the child for fluid and electrolyte balance. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Doesthis situation require validation? No. Determine the outcome of each implementation.Is it desired? (1) correct—implementation,amount is excessive for child and there are no electrolytes in fluid (2) implementation, may have serious electrolyte disturbances beforediscrepancies are seen in I and O (3) implementation, rate is correct for amount of fluid ordered, butamount is excessive for child and fluid is inappropriate (4) assessment, should not administer fluids as ordered because theyare inappropriate in amount and content |
|
|
The nursing team consists of an RN, two LPN/LVNs, and a nursing assistivepersonel(NAP). The RN should care for which client? |
1. The infant 2 days postoperative after repair of cleft lip requiring a tube feeding.
2. The preschool child 3 days postoperative after surgical removal of Wilms tumor requiring a bath. 3. The school-aged child diagnosed with osteomyelitis requiring a dressing change. 4. The teenager with a head injury, Glasgow coma scale is 5, requiring personal care. |
Strategy: RNs care for clients who require assessment, teaching, andnursing judgment. (1) stable client with an expected outcome, assigned to the LPN/LVN (2) standard, unchanging procedure, assign to the NAP (3) stable client with an expected outcome, assign to the LPN/LVN (4) correct—Glasgowcoma scale of 5 indicates coma, client requires frequent assessment |
|
|
The elderly client is frantically yelling for the nurse to come intothe room. The nurse enters the room as the client states, "See it? It's thedevil!" Which response by the nurse is best? |
1. "The devil is here?"
2. "Show me where the devil appeared to you." 3. "I don't see the devil, but I understand that it is real to you." 4. "The devil is not here; your mind is playing tricks on you." |
Strategy: Remember therapeutic communication. (1) yes/no question, attempt to reason or argue with the client willonly entrench more firmly into this distortion (2) attempt to reason or argue with the client will only entrench morefirmly into this distortion (3) correct—nurse shouldnot reinforce client's hallucinatory experiences; direct challenge to client'sbelief about sensory-perceptual intake will only increase mistrust and conflictbetween nurse and client (4) argumentative, attempt to reason or argue with the client will onlyentrench more firmly into this distortion |
|
|
The nurse talks to the parent in the emergency department (ED) immediatelyafter the child's death from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Which action by the nurse is best? |
1. Ask the parent if they have other children at home.
2. Explain the cause of SIDS. 3. Allow the parent to cry and talk about the child. 4. Determine how the child was positioned in bed. |
Strategy: The question is unstated. Read the answers to determine thetopic of the question. Answers contain both assessments and implementations.Is assessment required at this time? No. Determine the outcome of each implementation. (1) assessment, does not help with current loss (2) implementation, too soon, should allow to vent feelings and experiencegrief (3) correct—implementation,needs to go through the grieving process (4) assessment, may make parent feel guiltier, inappropriate at thistime |
|
|
The client is returned to the room at 10:00 following a laparoscopicgall bladder surgery. The nurse plans to get the client out of bed for thefirst time at 18:00. In preparation for this activity, the nurse should takewhich action? |
1. Ask the client to cough and deep-breathe at 16:00.
2. Offer pain medication to the client at 17:30 PM. 3. Turn the client from side to side at noon and 16:00. 4. Encourage the client to use the incentive spirometer. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) should turn, cough, and deep-breathe client every 2 hours to preventpostoperative complications, but would not help with ambulation (2) correct—reductionof pain will allow client to cooperate with activities designed to reducepostoperative complications such as ambulation (3) should turn client every 2 hours to prevent postoperative complications,but would not help with ambulation (4) used to promote complete lung expansion and prevent respiratorycomplications following surgery, but would not help with ambulation |
|
|
The nurse enters the room of the 17-year-old mother breast feeding her6-lb, 7-oz infant. Which observation, if made by the nurse, best indicatesthat mother-infant bonding is taking place successfully? |
1. The mother is looking into her infant's eyes as she feeds her.
2. The mother and infant are laying side-by-side in the bed. 3. The mother appears to be relaxed and is reading a book on childcare. 4. The mother interrupts feeding the infant to talk to her roommate. |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to bonding. (1) correct—shows bondingbehavior of eye-to-eye contact, proceeds to touching and holding (2) shows distance between mother and infant (3) doesn't involve communication between mother and infant (4) shows distance between mother and infant |
|
|
The nurse performs discharge teaching for the client after abdominalsurgery. The nurse determines that teaching is effective if the client chooseswhich foods for lunch? |
1. Chicken breast, peas, mashed potatoes, orange, and ice cream.
2. Hamburger, boiled potatoes, corn, pudding, and grapefruit juice. 3. Chicken salad with lettuce, tomatoes, carrots, zucchini, and broccoli, jello, pears, and soda. 4. Shrimp salad with green beans, and broccoli, peaches, cookies, and coffee. 5. Salmon steak, baked potato, lima beans, tangerine, and milk. 6. Ham sandwich, lettuce salad, coleslaw, apple, and low fat milk. |
Strategy: Nutrition following surgery needs to have increased protein,calories, and Vitamin C for wound healing. What meals contain those items? 1) CORRECT— Has highprotein, Vitamin C, and high calories. 2) CORRECT— Has highprotein, Vitamin C, and high calories. 3) Has good protein, low calories and little Vitamin C. 4) Has average protein, low calories, and no Vitamin C. 5) CORRECT— Has highprotein, high calories, and Vitamin C. 6) Has average protein, low calories, and no Vitamin C. |
|
|
The nurse observes the staff member enter the room of the client wearingregular clothing. The nurse determines that the staff member is using theproper precautions if the staff member cares for which client? |
1. A client diagnosed with cancer reporting a sore mouth.
2. A client diagnosed with tuberculosis requiring administration of rifampin. 3. A client diagnosed with rubella requiring an IM injection. 4. A client diagnosed with a draining abscess that is not covered with a dressing. |
Strategy: Determine what type of precautions are needed for each client. (1) correct—indicates Candida, standard precautions required (2) requires airborne precautions (3) requires droplet precautions (4) abscess with no dressing requires contact precaution |
|
|
The nurse cares for a client diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Theplan of care will include which interventions? |
1. Heat.
2. Range-of-motion exercises. 3. A soft mattress on the bed. 4. Weight reduction. 5. Immobilization. 6. Cold packs. |
Strategy: Think of ways to prevent joint pain and stiffness. 1) CORRECT— Heat soothespain and helps joint movement. 2) CORRECT— Keeps jointsmoving and limber. 3) A firm mattress will help keep joints in alignment. 4) CORRECT— Weight reductionwill remove stress from joints. 5) Immobilization will cause joints to freeze. 6) Heat is required. |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client admitted with a diagnosis of myocardialinfarction (MI) 36 hours ago. An appropriate nursing diagnosis is "Alterationin cardiac output" related to which item? |
1. Mitral valve collapse.
2. Endocarditis. 3. Ventricular dysrhythmias. 4. Hypertensive crisis. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) not the most common occurrence (2) not the most common occurrence (3) correct—most commoncomplication following a myocardial infarction is dysrhythmia, with ventriculartypes being the most serious (4) client would most probably experience a decrease rather than anincrease in blood pressure |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client 36 hours after a traditional cholecystectomy.The nurse is most concerned ifwhich finding is observed? |
1. The client reports severe abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant.
2. 500 mL of greenish-brown fluid drained from the T-tube in the last 24 hours. 3. The client has received an antiemetic twice since surgery. 4. Lab tests indicate an Hgb of 14 g/dL, Hct of 44% (0.44 volumn fraction), and WBC of 6,000/mm3 (6x109/L). |
Strategy: "MOST concerned" indicates a complication. (1) correct—could indicateperitonitis or wound infection (2) expected drainage, usually 500-1000 mL/day initially, will graduallydecrease (3) some nausea expected (4) results within normal limits> |
|
|
The client has surgery for cancer of the colon, and a colostomy is established.Before discharge, the client tells the nurse that swimming will no longerbe allowed. Which response by the nurse is correct? |
1. "You should begin looking for other areas of interest."
2. "You will have to wear a watertight dressing over the stoma." 3. "You cannot go into water that covers the stoma area." 4. "You may resume all previous activities." |
Strategy: Determine the outcome of each answer choice. Is it desired? (1) not appropriate for a client after a colostomy (2) not appropriate for a client after a colostomy (3) not appropriate for a client after a colostomy (4) correct—all activitiesthat the client participated in before the colostomy may be resumed afterappropriate healing of the stoma or incisions |
|
|
The nurse prepares the client for a liver biopsy. How should the nurseposition the client? |
1. Prone with the head turned to the side.
2. On the right side with the head slightly elevated. 3. Supine with arms raised above the head. 4. On the left side with the bed flat. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) incorrect positioning for procedure (2) positioned on right side with small pillow under puncture site for3 hours after procedure (3) correct—elevatesthe ribs to allow access to the liver, needle is inserted between two of thelower ribs or below the right rib cage (4) incorrect positioning for procedure |
|
|
To assist the parent to provide appropriate foods for the 3-year-old,the nurse identifies which action as the highest priority? |
1. Provide the child with finger foods.
2. Allow the child to eat only favorite foods. 3. Encourage a diet higher in protein than in other nutrients. 4. Limit the number of snacks during the day. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—child isgoing through autonomy versus shame and doubt stage; finger foods allow childthe necessary independence for this stage (2) child may eat food without appropriate nutrients (3) inappropriate for a 3-year-old child (4) inappropriate for a 3-year-old child |
|
|
The client undergoes peritoneal dialysis. The health care provider orders2 liters to be instilled with a dwell time of 40 minutes. The nurse measuresthe outflow and finds it to be 1,800 mL. During the nurse's shift, the clientdrinks 700 mL of fluids and voids 400 mL. What will the nurse document forthe client’s intake in milliliters.Roundyour answer to a whole number. Enter the mL answer in the box. |
calc |
Inflow and intake are recorded separately. The difference between inflowand outflow is considered intake.
|
|
|
The nurse cares for clients in the emergency department. In which orderwill the nurse see these clients? |
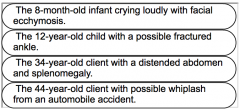
86 |
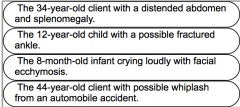
Strategy: Which clients are unstable? Move from the most unstable tothe most stable. Unstable, circulation; Distended abdomen indicates possible bleeding. Unstable: Possible fracture needs to be attended to as soon as possible. Stable, potential airway; Young children need assessment as their problemsmay not be visible. Stable, potential pain; The client with whiplash is stable and noturgent. |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client hospitalized with an acute asthma attack.The nurse is most concerned if whichfinding is observed? |
1. The client becomes more diaphoretic.
2. The client's respirations increase from 14 to 16 per minute. 3. The client's pulse increases from 86 to 100 beats per minute. 4. The client shows increasing pallor. |
Strategy: "MOST concerned" indicates a complication. (1) symptom of acute asthma attack, doesn't indicate deterioration ofstatus (2) expected with acute asthmatic attack, doesn't indicate deteriorationof status (3) correct—pulse increaseis due to decrease in oxygenation of tissues (4) subjective symptom, unreliable indicator of deterioration of status |
|
|
The nurse obtains a history on the client with hyperthyroidism. Thenurse should report which assessment finding to the health care provider? |
1. Anxiety with extreme nervousness.
2. Slow, sluggish pulse. 3. Cool, clammy skin. 4. Husky, slow speech. |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to hyperthyroidism. (1) correct—signs andsymptoms of hyperthyroidism are related to an increased metabolic rate (2) related to a decreased metabolic rate (3) related to a decreased metabolic rate (4) related to a decreased metabolic rate |
|
|
The client with chronic pain due to cancer receives morphine 10 mg POq4h PRN for pain without much relief. Which change in narcotic pain managementis the most valid suggestion forthe nurse to make to the health care provider? |
1. Decrease medication to twice a day.
2. Decrease medication to every 6 h PRN. 3. Administer medication every 4 h around the clock. 4. Administer medication every 2 h PRN. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) decreases the amount of pain medication (2) decreases the amount of pain medication (3) correct—around-the-clock(ATC) administration of analgesics is more effective in maintaining bloodlevels to alleviate the pain associated with cancer (4) might be too frequent an interval to administer the medication |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client recently diagnosed with AIDS. The nurseidentifies the following nursing diagnosis: Risk for Infection. Which interventionby the nurse is best? |
1. Inspect the skin daily for signs of breakdown.
2. Limit the number of health care personnel caring for the client. 3. Use standard precautions when administering parenteral medications. 4. Monitor the client's vital signs q4h. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Doesthis situation require assessment? No. Determine the outcome of each implementation. (1) performed as part of assessment, does not address client's limitedability to respond to possible infection (2) correct—implementation,decreases exposure to microorganisms (3) implementation, done with all clients to protect health care workers (4) performed as part of ongoing assessment |
|
|
Which nursing observation documented in the client's record most clearly indicates the client's mood? |
1. "Client states, 'I see snakes climbing on the walls at alltimes of the day.'"2. "Unable to sustain a train of thought for long periods oftime during history-taking."3. "Clenches fists and shouts in an angry toneof voice when asked about family problems."4. "Is unaware of location, time, day or year."
|
Strategy: Evaluate each answer choice to determine, "What do the wordsmean?" (1) describes hallucinations (2) describes altered thought processes (3) correct—gives datathat reflect client's feelings, tone, and behavior associated with those feelings,as well as content area of conversation that evoked that mood (4) describes disorientation |
|
|
The nurse plans care for the elderly client with dementia. Which actionis a priority for the nurse? |
1. Encourage dependency with activities of daily living.
2. Provide flexibility in schedules due to confusion. 3. Limit reminiscing due to poor memory. 4. Speak slowly in a face-to-face position. |
Strategy: The topic of the question is unstated. Read the answer choicesfor clues. (1) independence should be encouraged (2) schedules need to be routine, reinforced, and repeated; flexibilityleads to confusion (3) reminiscence and life reviews help client resume progression throughgrief process associated with disappointing life events, and increases self-esteem (4) correct—is mosteffective when communicating with an elderly client |
|
|
The 3-month-old infant is experiencing increased intracranial pressure(ICP). Which assessment finding should the nurse report to the health careprovider? |
1. Pinpoint pupils.
2. High-pitched cry. 3. Decrease in blood pressure. 4. Absence of reflexes. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) does not indicate any immediate problem; as pressure increases,pupils may become dilated (2) correct—sign ofincreased intracranial pressure (3) does not reflect complication of increased intracranial pressure (4) does not reflect complication of increased intracranial pressure |
|
|
The nurse reviews histories in the prenatal clinic. The nurse identifieswhich pregnant women is most likelyto have an Rh-incompatibility problem? |
1. The Rh-positive woman pregnant for the third time who conceived with an Rh-negative man. The woman has never received Rho (D) immune globulin.
2. The Rh-negative woman who conceived with an Rh-positive man. The woman has Rh antibodies. 3. The Rh-positive woman who previously aborted a fetus at 12 weeks’ gestation and did not receive Rho (D) immune globulin. The woman currently conceived with an Rh-positive man. 4. The Rh-negative woman who never received Rho (D) immune globulin. The woman currently conceived with an Rh-negative man. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) incompatibility only seen with Rh-negative woman (2) correct—Rh-positivedominant, fetus will be Rh-positive, Rh antibodies from the mother will breakdown fetus's blood cells (3) incompatibility only seen with Rh-negative woman (4) infant would be Rh-negative like parents, so there would be no incompatibility |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client receiving atorvastatin. It is MOST importantfor the nurse to report which client statement to the health care provider? |
1. "I no longer drink grapefruit juice."
2. "I have my liver enzymes checked regularly." 3. "I take a daily multivitamin." 4. "I take propranolol." |
Strategy: Think about what the client’s words mean. (1) appropriate action; grapefruit juice decreases the enzyme that breaksdown atorvastatin (2) appropriate action (3) not contraindicated (4) correct—propranololdecreases the effectiveness of atorvastatin |
|
|
The charge nurse cares for young children in the hospital. Which clientrequires the nurse to use droplet precautions? |
1. The child with cystic fibrosis.
2. The child with tonsillitis. 3. The child with bronchitis. 4. The child with pertussis. |
Strategy: Think about the communicability of each disease. (1) hereditary dysfunction of exocrine glands causing obstruction becauseof flow of thick mucus, standard precautions (2) inflammation of tonsils, standard precautions (3) inflammation of large airway, standard precautions (4) correct—dropletprecautions required, private room, maintain spatial separation of 3 feetbetween child and visitors |
|
|
The elderly client is admitted to an inpatient psychiatric unit withan initial diagnosis of psychotic depression. Which is the priorityinitial nursing action? |
1. Clarify perceptual distortions.
2. Establish reality orientation. 3. Ensure client and milieu safety. 4. Increase self-esteem. |
Strategy: Think Maslow. (1) important, but secondary to safety issues (2) important, but secondary to safety issues (3) correct—initialnursing priority for all psychiatric clients is to ensure their safety andthe safety of all members of the milieu (4) important, but secondary to safety issues |
|
|
A nurse begins a therapeutic relationship with the client diagnosedwith generalized anxiety disorder. It is most importantfor the nurse to obtain which information? |
1. What the client’s priorities are.
2. How the client views self. 3. In what situations the client gets anxious. 4. Any family history of mental issues. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) helpful data; priority is to determine in what situations the clientbecomes anxious (2) helpful data; priority is to determine in what situations the clientbecomes anxious (3) correct—will providenecessary information in baseline assessment of client's anxiety (4) helpful data but not priority |
|
|
The client has a right total hip replacement. The client returns fromsurgery with an IV of 0.45% NaCl infusing into the left forearm at 100 mL/h.It is most important for the nurseto take which action? |
1. Massage the client's legs to increase circulation.
2. Elevate the knee gatch to reduce stress on the suture line. 3. Apply thigh-high TED hose to promote venous return. 4. Decrease fluid intake to 1,200 mL to prevent circulatory overload. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) massage may cause emboli (2) would cause external pressure on the popliteal space, hip shouldnot be flexed beyond 90° (3) correct—use of antiembolichose and/or sequential compression devices decreases venous stasis and reducesrisk of thrombus formation (4) adequate fluid intake (1,500 mL) prevents dehydration |
|
|
The nurse plans care for the client immediately after a cesarean birth.Which nursing goal is most important? |
1. Prevent infection.
2. Prevent fluid and electrolyte imbalances. 3. Provide for pain management. 4. Prevent hazards of immobility. |
Strategy: "MOST important" indicates that this is a priority question.Remember the ABCs. (1) not highest priority initially, usually not seen until 48-72 hoursafter surgery (2) correct—hemorrhageand shock are the most life-threatening conditions that occur after surgery (3) not highest priority initially, not life-threatening (4) not highest priority initially, not life-threatening |
|
|
The client is admitted with a diagnosis of a fractured right hip. Thehealth care provider writes an order for Buck's traction. Which action, iftaken by the nurse, is most important? |
1. Turn the client every 2 hours to the unaffected side.
2. Maintain the client in a supine position. 3. Encourage the client to use a bedside commode. 4. Place a footboard on the bed. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—immobilityis a leading cause of problems with Buck's traction; important to turn clientto unaffected side (2) head of the bed should be elevated 15-20° because the supineposition can increase problems with immobility (3) client is on strict bedrest (4) would interfere with the traction |
|
|
The nurse makes client assignments on a medical/surgical unit. The staffincludes one RN, one RN pulled from the pediatric unit, an LPN/LVN, and anursing assistive personel. Which client should be assigned to the RN fromthe pediatric unit? |
1. The client 1 day postoperative after an appendectomy.
2. The client who had a detached retina surgically repaired 4 hours ago. 3. The client with a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube in place. 4. The client 2 days postoperative after a laminectomy with spinal fusion. |
Strategy: Assign a pulled RN to stable clients with expected outcomes. (1) correct—stable clientwith expected outcome (2) requires frequent assessment for hemorrhage, instruct client toavoid sneezing, coughing, or straining at stool (3) requires frequent monitoring due to hemorrhage (4) requires assessment and teaching |
|
|
The nurse cares for the 2-month-old infant diagnosed with reflux. Which nursing action is most appropriate? |
1. Hold the next feeding.
2. Teach the parent CPR. 3. Maintain a normal feeding schedule. 4. Elevate the head of the bed. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) may not be necessary if positioning is effective (2) inappropriate (3) client's feedings should be changed to small-volume, frequent feedings (4) correct—infant withreflux should be maintained in an upright position; head of the bed shouldbe raised at a 30° angle |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client who delievered an 8 lb, 4 oz newborn. the newborn is diagnosed with talipes equinovarus. The woman confides tothe nurse, "I feel so bad that my baby is abnormal." Which response by thenurse is best? |
1. "It's understandable that you feel this way, but there are treatments to correct your baby's problem."
2. "Your baby is not really abnormal. The feet just look different because of the way the muscles pull." 3. "You have nothing to feel guilty about. The abnormality is not your fault." 4. "Don't feel bad. Your baby's abnormality can be corrected surgically." |
Strategy: Remember therapeutic communication. (1) correct—acceptsfeelings and gives correct information, serial casting is used to treat infant (2) doesn't accept person's feelings, nontherapeutic (3) prematurely interprets person's feelings as guilt, nontherapeutic (4) nontherapeutic to tell person how to feel |
|
|
The client reports pain after an appendectomy. After administering ananalgesic, the nurse should take which action? |
1. Elevate the head of the bed 30-45°.
2. Place a pillow behind the client's knees. 3. Elevate the knee gatch on the bed 30°. 4. Position the client supine with a small pillow under the head. |
Strategy: Answers are all implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—would reducestress on suture line and provide for comfort (2) would put pressure on popliteal space, would restrict circulationand increase risk of thrombophlebitis (3) would put pressure on popliteal space, would restrict circulationand increase risk of thrombophlebitis (4) does not reduce stress on suture line |
|
|
The 5-year-old child is scheduled for a lumbar puncture (LP). Whichnursing action best prepares thechild for the procedure? |
1. Explain the procedure in detail.
2. Show a video of the procedure. 3. Do a mock run-through of the procedure. 4. Answer all questions simply and honestly. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) would be very difficult to prepare a 5-year-old child for a totallyforeign procedure with only words (2) may be frightening without additional preparation (3) correct—excellentmethod to use with a child because it incorporates actually "feeling" manyaspects of the procedure as they are explained (4) child probably doesn't know enough to ask many questions |
|
|
The client is scheduled to have a parathyroidectomy. The nurse is most concerned if the client is observed eatingquantities of food from which food group? |
1. Milk products.
2. Green vegetables. 3. Seafood. 4. Poultry products. |
Strategy: Determine the outcome of each answer choice. (1) correct—low-calciumdiet is recommended preoperatively (2) diet should be high in phosphorus and low in calcium (3) diet should be high in phosphorus and low in calcium (4) poultry is allowed in the diet |
|
|
A client with a spinal cord injury resulting in paraplegia has a reorientationouting with the recreational therapist. Which documented activity indicatesto the nurse the client is ready for discharge? |
1. The client states enjoyment in being outside the hospital environment.
2. The client participated in a structured team sport by keeping score. 3. The client independently ordered a meal and fed self. 4. The client is independent in transfers and wheelchair mobility. |
Strategy: Think Maslow. (1) psychosocial, speaks to his psychosocial status, but is not an indicationfor discharge (2) psychosocial, addresses social skills, but is not an indicationfor discharge (3) physical, not pertinent for a paraplegic (4) correct—physical,these skills are requisite for discharge |
|
|
The nurse instructs the client with newly diagnosed type 1 diabeteshow to treat hypoglycemia at home. The nurse should instruct the client toperform which action if symptoms of hypoglycemia occur? |
1. Eat a candy bar then check blood glucose.
2. Drink 1/2 cup fruit juice followed by peanutbutter crackers. 3. Inject 10 units of regular insulin. 4. Inject glucagon followed by protein snack. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) too concentrated a carbohydrate, will cause hyperglycemia (2) correct—will correcthypoglycemia and stabilize blood glucose (3) treatment for hyperglycemia (4) used if person becomes unconscious |
|
|
The 3-month-old infant is placed in traction for developmental dysplasiaof the hips. Which toy is appropriate for the nurse to offer the infant duringhospitalization? |
1. A rattle.
2. A stuffed animal. 3. Colorful blocks. 4. A tape playing nursery rhymes. |
Strategy: Think growth and development. (1) correct—3-month-oldinfant can grasp a rattle (2) not as good as answer choice (1) (3) designed for an older child (4) not as good as answer choice (1) |
|
|
The nurse instructs the client about a low-sodium, low-cholesterol diet.The nurse determines the client teaching is effective if the client selectswhich menu? |
1. Canned vegetable soup, applesauce, and hot chocolate.
2. Cheeseburger, french fries, and skim milk. 3. Tomato and lettuce salad, roasted chicken, and lemonade. 4. Tuna fish sandwich, cottage cheese, and a cola. |
Strategy: Evaluate each of the foods. (1) canned foods contain increased salt, and milk contains cholesterol (2) breads contain sodium, and dairy products and beef contain cholesterol (3) correct—fresh fruitsand vegetables are low sodium, roasted chicken is low cholesterol (4) bread and carbonated beverages contain sodium |
|
|
The adult child of the client diagnosed with cancer asks the nurse,"Do you believe in euthanasia?" Which response by the nurse is best?
|
1. "I think this is a decision each person needs to make."
2. "My religion is opposed to euthanasia." 3. "What are your thoughts about euthanasia?" 4. "Did you see the TV program about euthanasia last night?" |
Strategy: Remember therapeutic communication. (1) closed statement, focus is on the nurse and not the client (2) focus is on the nurse and not the client (3) correct—open-endedquestion, allows client to verbalize (4) yes/no question |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client who experienced a thermal injury 2 weeksago. The nurse is most concernedif which finding is observed? |
1. Increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure.
2. Temperature of 100.6°F (38.1°C) and decreased respiratory rate. 3. Increased heart rate and decreased respiratory rate. 4. Increased respiratory rate and decreased blood pressure. |
Strategy: Determine the significance of each assessment and how it relatesto burns. (1) should be investigated further, but alone do not represent significantcompromise (2) should be investigated further, but alone do not represent significantcompromise (3) should be investigated further, but alone do not represent significantcompromise (4) correct—may indicateburn wound sepsis, a life-threatening complication of thermal injury |
|
|
The older client comes to the outpatient clinic for a routine healthscreening. The nurse learns the client is a retired teacher who lives aloneon a limited income. A history indicates the client drinks about 1,500 mLa day and the client’s diet consists primarily of starches. It is most important for the nurse to encouragethe client to take which action? |
1. Increase protein intake.
2. Increase intake of vitamins. 3. Reduce caloric intake. 4. Reduce fluid intake. |
Strategy: "MOST important" indicates priority. Each answer choice isan implementation. Determine the outcome of each answer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—proteinneeded to slow down degeneration process of aging (2) necessary, but not most important (3) necessary, but not most important (4) should maintain oral intake |
|
|
The client tested positive for the tuberculosis antibody and was placedon isoniazid 4 weeks ago. The nurse observes the client in the outpatientclinic. The nurse is most concernedif which finding is observed? |
1. Fatigue and dark urine.
2. Malaise and glucosuria. 3. Proteinuria and lethargy. 4. Diluted urine and epigastric distress. |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates isoniazid. (1) correct—initialindications of hepatic dysfunction (2) seen with pancreatic problems (3) seen with kidney problems (4) is not seen with liver problems |
|
|
The preschooler is brought to the emergency department after ingestinga bottle of baby aspirin. The nurse should observe the preschooler for whichsigns and symptoms? |
1. Nausea and vertigo.
2. Epistaxis and paralysis. 3. Dysrhythmia and hypoventilation. 4. Tinnitus and gastric distress. |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice and how it relates to aspirinoverdose. (1) dizziness not seen with aspirin overdose (2) nosebleed may occur, but not paralysis (3) may see hyperventilation with use of aspirin, does not affect heartrhythm (4) correct—symptomsof overdose |
|
|
While performing care for the elderly client, the nurse notices thatthe client has a dry, parched mouth and tongue. The nurse should take whichaction? |
1. Brush the client's teeth with a hard-bristled toothbrush before meals and at bedtime.
2. Use glycerin swabs to perform mouth care every 4 hours. 3. Rinse the client's mouth with room-temperature tap water before and after meals. 4. Use a water pick, then rinse with commercial mouthwash every 8 hours to freshen the mouth. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) should use soft-bristled toothbrush so gums are not injured (2) should be avoided, causes dryness of mucous membranes (3) correct—will hydratethe mucous membranes and keep mouth clean (4) most commercial mouthwashes contain alcohol, would dry mucous membranes |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client diagnosed with schizophrenia who hasbecome increasingly withdrawn to the point of mutism. It is most importantfor the nurse to take which action? |
1. Ignore the client until the client is ready to respond.
2. Sit with the client for brief periods of time. 3. Read to the client in a quiet area of the unit. 4. Encourage the client to play dominos with the group. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) rejects the client (2) correct—nurse shouldmaintain contact with client but not make demands to communicate or participatein activities (3) not going to benefit this client (4) not going to benefit this client |
|
|
The nurse cares for a client after an ileostomy. The nurse is MOST concernedif which finding is observed? |
1. The ileostomy functions without daily irrigations.
2. The stoma appears to be tight, and there is a decreased amount of stool. 3. A small amount of mucus is seen around the anal area. 4. There is weight gain of 5 lb over a 3-week period of time. |
Strategy: "MOST concerned" indicates a complication. (1) normal process, ileostomies are not irrigated (2) correct—importantto report these findings to the health care provider; may indicate an obstructionor stoma stricture (3) anal area is not functional but some mucus may be seen (4) should not concern nurse |
|
|
The home care nurse instructs the spouse of the client about how toperform a wet-to-dry abdominal dressing for the client because of an infectedabdominal incision. The nurse should intervene if which action is observed? |
1. The client’s spouse wets the old dressing with sterile saline before removing it.
2. The client’s spouse covers the wound with wet, sterile 4 × 4s. 3. The client’s spouse irrigates the wound with hydrogen peroxide using a bulb syringe. 4. The client’s spouse uses Montgomery straps to secure the dressing. |
Strategy: "Nurse should intervene" indicates an incorrect action. (1) correct—contraindicated,remove dry so wound debris and necrotic tissue are removed with old dressing (2) purpose of wet-to-dry dressing is to débride incision; wettingdressing before removal defeats purpose of dressing (3) irrigation of wound sometimes used (4) adhesive is attached to skin and laced to secure dressing, usedwhen frequent dressing changes are anticipated |
|
|
The nurse monitors the client in active labor who is receiving oxytocin 1 mU/min IV. The nurse should stop the infusion if which finding is observed? |
1. The contractions occur at 3-minute intervals and last more than 60 seconds.
2. The contractions occur at 2.5-minute intervals and last more than 90 seconds. 3. The contractions occur at 2-minute intervals and last more than 90 seconds. 4. The contractions occur at 2-minute intervals and last more than 60 seconds. |
Strategy: All answers are assessments. Determine the result of eachassessment. (1) normal frequency and duration (2) normal frequency and duration (3) correct—contractionsshould be less frequent (longer than 2-minute intervals) and should be ofshorter duration (less than 90 seconds); allows for longer resting time betweencontractions (4) normal frequency and duration |
|
|
While the 2-day-old infant is in surgery for repair of spina bifida,the infant's parent expresses concern to the nurse because the health careprovider said the infant would be confined to a wheelchair. Which statement,if made by the nurse, is best? |
1. "Physical therapy can restore the function to affected muscles."
2. "Orthopedic devices will allow your child to strengthen lower extremity muscles." 3. "Corrective surgery will return function to the affected muscles." 4. "The corrective surgery will not change your child's physical disability." |
Strategy: Determine the outcome of each answer choice. (1) not appropriate or true regarding this condition (2) not appropriate or true regarding this condition (3) not appropriate or true regarding this condition (4) correct—spinal nervesthat are destroyed by the myelomeningocele cannot be corrected; nothing canreturn function to portions of the body that are innervated by the spinalnerves below the site of the myelomeningocele |
|
|
The nurse receives a bedside report from another nurse. The nurse givingreport begins to talk about another client. Which action by the nurse receiving report is most appropriate? |
1. Ask the nurse to report on this client only.
2. Ask the nurse to lower their voice. 3. Ask the nurse to move to another part of the room. 4. Ask the nurse to clarify which client they are reporting on. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—client confidentialityis being violated, nurse should intervene to protect client (2) does not provide for client confidentiality (3) does not provide for client confidentiality (4) does not provide for client confidentiality |
|
|
A family member of the client who has sustained an electrical burn states,"I don't understand why my sibling has been here a week. The burn does notlook that bad." Which response by the nurse is best? |
1. "Electrical burns are more prone to infection."
2. "Electrical burns are always much worse than they look on the outside." 3. "Cardiac monitoring is important because electrical burns affect cardiac function." 4. "Electrical burns can be deceptive because underlying tissue is also damaged." |
Strategy: Determine which statement correctly states the facts. (1) incorrect regarding electrical burns (2) not the most accurate statement (3) is true in the immediate post-burn phase, not a week later (4) correct—electricalburn injuries are typically more injurious to underlying tissue, such as nerveand vascular tissue, which require complex and timely treatment |
|
|
The nursing care plan for the 5-year-old child with a closed head injuryshould contain which action? |
1. Encourage child to sleep and decrease stimuli in the room.
2. Assess orientation to person, place, and time every hour. 3. Notify the health care provider regarding a negative Babinski reflex. 4. Increase fluid intake to maintain adequate urinary output. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Doesthis situation require assessment? Yes. Is there an appropriate assessment?Yes. (1) an increase in sleep could indicate a complication with intracranialpressure (2) correct—early signsof increased intracranial pressure are alterations in orientation (3) negative Babinski is normal (4) ignores assessment of a potential complication; fluid would notbe increased for a child with a closed head injury |
|
|
The client received morphine 7 mg IM 2 hours ago for report of pain.The client turns on the call light and tells the nurse they have to go tothe bathroom. The health care provider ordered bathroom privileges. The nurseshould take which action? |
1. Obtain a bedside commode for the client's use and provide privacy.
2. Help the client to sit on the side of the bed before proceeding to the bathroom. 3. Provide a bedpan for the client's use and pull the curtains. 4. Ask two nurses to assist the client to the bathroom. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) should ambulate client safely to prevent hazards of immobility (2) correct—side effectsof medication include decreased BP, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia (3) easier for client to use bathroom than to use bedpan (4) an additional nurse not necessary, before ambulating should siton side of bed to allow body to adjust to change in position |
|
|
The client is transferred to the neurology unit after developing right-sidedparalysis and aphasia. The nurse should include which implementation in theclient's plan of care? |
1. Encourage client to shake head in response to questions.
2. Speak in a loud voice during interactions. 3. Speak using phrases and short sentences. 4. Encourage the use of radio to stimulate the client. |
Strategy: Topic of question is unstated. Read the answer choices forclues. (1) does not encourage verbal communication (2) inappropriate for the situation (3) correct—will decreasetension and anxiety; client may understand some of the incoming communicationif it is kept simple; speech may be relearned with appropriate support andinterventions (4) inappropriate for the situation |
|
|
Which statement, if made to the nurse, indicates parental understandingabout the cause of their newborn's diagnosis of cystic fibrosis (CF)? |
1. "The gene came from my husband's side of the family."
2. "The gene came from my wife's side of the family." 3. "There is a 50% chance that our next child will have the disease." 4. "Both of us carry a recessive trait for cystic fibrosis." |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) both parents are carriers of the abnormal gene (2) both parents are carriers of the abnormal gene (3) there is a 25% chance of passing the disease on to any of theiroffspring (4) correct—cystic fibrosisis inherited by an autosomal recessive trait |
|
|
The client has an order for furosemide 40 mg IV push via a heparin lock.Which nursing action is most appropriate? |
1. Use a 16- to 18-gauge 1-inch needle for administration.
2. Administer the medication over 1-2 minutes. 3. One mL of 1:1,000 heparin flush should be administered before the medication. 4. A primary IV should be started prior to medication administration. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) needle gauge is too large (2) correct—furosemide given IV push should be administered slowly over 1-2 minutes (3) lock is flushed with heparin after administration of the medication (4) unnecessary |
|
|
The college student has a Mantoux test performed at the college healthclinic and the result is positive. The clinic nurse should take which action? |
1. Refer the student to an appropriate center for further testing.
2. Restrict the student's activity until the parents can be notified. 3. Notify the local Public Health Department. 4. Place the student in an isolation room in the college infirmary. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—will performchest x-ray (2) premature action, insufficient information (3) true if active disease confirmed, premature action (4) premature action, insufficient information |
|
|
The nurse in the outpatient clinic teaches a young adult with a sprainedright ankle to walk with a cane. While teaching the client to use the cane,how should the nurse be positioned? |
1. Standing on the client's left side and slightly behind the client.
2. Standing on the client's right with one hand on the client's waist. 3. Standing directly in front of the client with both hands on the client's arms. 4. Standing in front of the client on the right side. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer. Is it desired? (1) correct—stand slightlybehind client on strong side (2) incorrect positioning (3) use a gait belt to assist client, don't place hands on client'sarms (4) stand slightly behind client on strong side |
|
|
The nurse prepares to suction the client with a new tracheostomy inthe postanesthesia recovery room. Which action, if performed by the nurse,indicates a break in proper technique? |
1. The nurse sets the suction source at 120 mm Hg and obtains a #14 French suction catheter.
2. The nurse inserts the suction catheter until resistance is met, and then applies intermittent suction as the catheter is withdrawn. 3. The nurse suctions the client's mouth prior to suctioning the tracheostomy to ensure a patent airway. 4. The nurse administers oxygen to the client using an Ambu bag attached to 100% oxygen prior to suctioning. |
Strategy: "Break in proper technique" indicates an incorrect action. (1) use suction 90-120 mm Hg and #12 or #14 suction catheter (2) use a twirling motion to remove catheter while applying suction (3) correct—break insterile procedure, suction mouth after trachea (4) hyperoxygenates client to prevent hypoxia from procedure |
|
|
The 2-year-old child is hospitalized. The nurse assesses the child andasks the parent about the activities the child does at home. Which activitywould the nurse anticipate this child to perform? |
Select all that apply.
1. Plays beside other children, but not with them. 2. Builds 6-7 block towers. 3. Can put toys away alone. 4. Names colors 5. Can retrieve objects when asked to do so. 6. Uses sentences of 4-5 words. |
Strategy: Think of the growth and development of a 2-year-old. 1) CORRECT— Participatesin parallel play. 2) CORRECT— Able tobuild tower this high. 3) More likely at age 3-4. 4) Names colors at age 3-4 years. 5) CORRECT— Can follow simple directions/commands. 6) Occurs at age 4 years. |
|
|
The client has a subclavian triple lumen catheter used for administrationof parenteral nutrition (PN). The health care provider orders all lumensbe flushed with a diluted heparin solution BID. When the nurse attempts toflush the distal lumen, resistance is met. The nurse should take which action? |
1. Clamp off the lumen and label it as "clotted off."
2. Gradually increase the pressure on the irrigating solution. 3. Aspirate blood from the lumen to restore patency. 4. Secure the lumen with a Luer-Lock cap and notify the health care provider. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) should be reported to the health care provider to see if patencycan be re-established before it is labeled as clotted off (2) force should never be used to irrigate the catheter (3) blood should not be aspirated from the catheter (4) correct—streptokinasemay be used to dissolve clot; if unsuccessful, lumen is labeled as clottedoff |
|
|
The nurse prepares the child diagnosed with Addison's disease for discharge.The child’s parent asks how long the child must continue receiving replacementtherapy. Which response by the nurse is best? |
1. "For approximately 6 months."
2. "For approximately 1 year." 3. "Until the child reaches puberty." 4. "For the rest of their life." |
Strategy: Think about each answer choice. (1) needed for lifetime to prevent recurrence of adrenal insufficiency (2) needed for lifetime to prevent recurrence of adrenal insufficiency (3) needed for lifetime to prevent recurrence of adrenal insufficiency (4) correct—diseaseis caused by deficiency in glucocorticoids, will always need corticosteroidsand mineralocorticoids |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client following surgery for a coronary arterybypass graft (CABG). Which symptom would the nurse expect to see if the clientwas in the early stages of circulatory overload? |
1. Change in the character of respirations.
2. Fluctuation in the blood pressure. 3. Reduced tissue turgor. 4. Increase in body temperature. |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to fluid overload. (1) correct—will seedyspnea, cough, edema, hemoptysis (2) will initially increase and then fall due to congestive heart failure,doesn't fluctuate (3) reflects body's general hydration status, mainly shows dramaticchanges with dehydration (4) would indicate infectious, inflammatory process, skin temperaturewill fall with circulatory overload |
|
|
The nurse teaches the group of 12 year-olds how to prevent Lyme disease.Which statement, if made by one of the children to the nurse, indicates thatfurther teaching is necessary? |
1. "When I go on a long hike, I should check any exposed skin for insects every 4 hours."
2. "When I hike in the woods, I should wear long pants, socks, and a long-sleeved shirt." 3. "I should remove any ticks by crushing them firmly against my skin." 4. "I should reapply insect repellant every couple of hours when hiking." |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Is theassessment appropriate? No. Determine the outcome of each of the implementations. (1) assessment, should be done to check for ticks that transmit disease;pay particular attention to arms, legs, and hairline (2) protects exposed skin from ticks (3) correct—should notbe crushed, remove tick with tweezers or fingers and flush down toilet; burninga tick could spread infection (4) protects exposed skin from ticks, avoid heavily wooded areas |
|
|
Which nursing approach is most appropriateto use while administering an oral medication to a 4-month-old infant? |
1. Place the medication in 45 mL of formula.
2. Place the medication in an empty nipple and allow the infant to suck. 3. Place the medication in a full bottle of formula. 4. Place the medication in a plastic syringe and give with the infant in the reclining position. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) medication is never added to the infant's formula feeding (2) correct—is a convenientmethod for administering medications to an infant (3) medication is never added to the infant's formula feeding (4) infant is never placed in a reclining position during proceduredue to potential for aspiration |
|
|
The elderly adult is admitted to a medical unit with shortness of breathand is diagnosed with an upper respiratory infection (URI). The client isplaced on droplet precautions. The nurse administers oral medications to theclient. As the nurse leaves the room, the nurse should take which action? |
1. Wash hands, remove the gown and mask, and throw the trash in a container outside of the room.
2. Remove the mask, wash hands, and throw the trash in a container inside the room. 3. Wash hands, remove the mask, and throw the trash in a container inside the room. 4. Remove the gown and gloves, wash hands, remove the mask, and throw the trash in a container inside the room. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) gown unnecessary, trash should be left inside room (2) wash hands then remove mask, so microbes aren't transferred fromhands to face (3) correct—hands shouldbe washed before removing mask to prevent transfer of microbes to face (4) gown unnecessary |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client diagnosed with schizophrenia. Which statementis most descriptive of the affectof a client with schizophrenia? |
1. The client answers all questions with one word.
2. The client laughs while talking about being raped. 3. The client exhibits no energy or interest in tasks. 4. The client cries while talking about parent's death. |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to schizophrenia. (1) not indicative of schizophrenia (2) correct—inappropriateaffect, expression of feelings bizarre for situation (3) describes depression (4) appropriate response |
|
|
The nurse cares for a postoperative client. Four hours after surgery,the client voids 200 mL of urine with a specific gravity of 1.019. The nurseshould take which action? |
1. Palpate the client's lower abdomen for distention.
2. Encourage an increased intake of oral fluids. 3. Record the time and the amount of urine. 4. Encourage the client to void again in 2 hours. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Doesthis situation require validation? No. Determine the outcome of the implementationanswers. (1) implies bladder distention and urinary retention, 200 mL dividedby 6 hours = more than 30 mL/h (2) doesn't recognize amount and specific gravity as normal in thissituation (3) correct—amount andspecific gravity normal (1.010-1.030) (4) doesn't recognize amount and specific gravity as normal in thissituation |
|
|
The client comes to the clinic reporting severe facial pain. To collectsubjective data from the client, it is most importantfor the nurse to take which action? |
1. Obtain the client's vital signs.
2. Interview the client. 3. Inspect the face for grimacing. 4. Administer pain medication. |
Strategy: Focus on the question. (1) vital signs are objective data (2) correct—subjectivedata is collected in the health history or interview (3) objective data (4) implementation, complete assessment to determine the problem |
|
|
The client receives thrombolytic therapy. The health care provider ordersmorphine IM for pain. Before administering the injection, the nurse shouldtake which action? |
1. Confirm that all lab work has been completed.
2. Verify the order with the health care provider. 3. Check the client's PTT. 4. Determine that all of the thrombolytic agent has infused. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Doesthis situation require assessment? No. Determine the outcome of the implementations.Is it desired? (1) assessment, unnecessary (2) correct—implementation,complications of thrombolytic therapy include bleeding, which can occur withintramuscular injections; nurse should confer with the health care providerabout the appropriateness of the order (3) assessment, PTT should be monitored, but this is not a priorityaction (4) implementation, unnecessary |
|
|
The home care nurse visits the client reporting episodes of vomitingfor 3 days. The client has a low-grade temperature and reports feeling lethargic.Which nursing action is most appropriateto evaluate for fluid volume deficit? |
1. Obtain a urinalysis for casts and specific gravity.
2. Determine client's weight and assess gain or loss. 3. Ask client to provide a 24-hour intake and output record. 4. Determine the quality of the client's skin turgor. |
Strategy: Determine how each answer choice relates to fluid volume deficit. (1) provides information regarding the fluid volume level, but is notthe best action for evaluation (2) correct—daily weightis the best way to evaluate for fluid volume deficit (3) provides information regarding the fluid volume level, but is notthe best action for evaluation (4) provides information regarding the fluid volume level but is notthe best action |
|
|
The 20-year-old woman calls the outpatient clinic to schedule her firstPapanicolaou smear. The nurse should recommend which preparation to the client? |
1. Avoid intercourse for 48 hours before the appointment.
2. Avoid douching for 24 hours before the appointment. 3. Withhold all foods and fluids 12 hours before the appointment. 4. Save first voided urine specimen the morning of the appointment. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Think about the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) sperm doesn't resemble atypical cells that the test is designedto find but intercourse is avoided 24 hours before the examination (2) correct—douchingwould affect appearance of cells in vaginal smear, would make test inaccurateby removing potentially abnormal cells (3) will concentrate urine but won't affect Pap smear (4) part of routine GYN exam, but not related to Pap smear |
|
|
The nurse is the first on the scene of a motor vehicle accident. Thevictim has sucking sounds with respirations at a chest wound site and trachealdeviation toward the uninjured side. Which action should the nurse take first? |
1. Cover the wound loosely, preferably with a sterile dressing.
2. Place a sandbag over the wound. 3. Monitor chest wound drainage. 4. Place a firm, airtight, sterile dressing over the wound. |
Strategy: Answers are a mix of assessments and implementations. Is theassessment appropriate? No. Determine the outcome of each implementation. (1) correct—implementation,in an open pneumothorax, air enters the pleural cavity through an open wound;placing a sterile dressing loosely over the wound allows air to escape butnot re-enter the pleural space (2) implementation, would prevent air from escaping (3) assessment, chest tube has not yet been inserted (4) implementation, would prevent air from escaping |
|
|
The nurse is caring for the elderly client diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.The client is scheduled for cataract surgery under general anesthesia at 9:00. The client usually receives 30 units of NPH and 10 units of regular insulineach morning at 07:00. At 07:00 the morning of surgery, the nurse expcts totake which action? |
1. Hold the morning dose of NPH and regular insulin and monitor the blood glucose.
2. Give half the morning dose of NPH insulin together with the regular insulin and monitor the blood glucose when the client returns from surgery. 3. Give the full dose of NPH and regular insulin and monitor the blood glucose every 2-4 hours. 4. Give the full dose of regular insulin but hold the NPH insulin and monitor the blood glucose until the client goes to surgery. |
Strategy: All answers are implementations. Determine the outcome ofeach answer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—usuallyuse sliding scale with regular insulin based on blood glucose readings (2) may cause hypoglycemia because client will be NPO when NPH peaks,NPH intermediate-acting insulin, onset 1-2 hours, peaks 6-12 hours, duration18-26 hours; regular insulin short-acting, onset 0.5-1 hour, peaks 2-4 hours,duration 6-8 hours (3) client may become hypoglycemic because NPH will peak when clientis NPO (4) may cause hypoglycemia during surgery |
|
|
The nurse cares for the woman completing the first stage of labor. Thewoman's significant other is at her side and has been coaching her accordingto exercises they learned in childbirth classes. Suddenly the woman beginsto shake and screams, "I can't stand this anymore!" The nurse should encouragethe significant other to take which action? |
1. Instruct the women to use shallow respirations during the contractions.
2. Offer the women ice chips or sips of water to distract her from the pain. 3. Stroke the women's abdomen between contractions. 4. Review with the women the breathing pattern needed at each stage of labor. |
Strategy: Answers are implementations. Determine the outcome of eachanswer choice. Is it desired? (1) correct—enteringtransition phase of first stage of labor, rapid shallow breaths needed (pantbreathing) (2) doesn't address issue of breathing pattern needed during transitionphase of labor (3) used in conjunction with controlled breathing for Lamaze (4) needs support and coaching of significant other during transitionphase of labor |
|
|
The nurse cares for the client admitted with low back pain. The historyindicates that the client has hemophilia A. The nurse should question whichorder? |
1. Ketorolac.
2. Codeine phosphate. 3. Oxycodone/aspirin. 4. Hydromorphone hydrochloride. |
Strategy: "Nurse should question order" indicates a contraindication. (1) NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) used for short-termmanagement of pain (2) analgesic used for moderate to severe pain (3) correct—contraindicatedfor persons with bleeding disorders, contains aspirin (4) narcotic analgesic used for moderate to severe pain |
|
|
After receiving report, the nurse is assigned to these clients. In whichorder should the nurse see the clients? |
|
Strategy: Identify the least stable client to see first. 1) The client with a sickle cell crisis is least stable and fluids arecrucial for this client. 2) The sedative is time sensitive and needs to be given about 30 minutesbefore the procedure. 3) Clients receiving blood products need to be assessed about every15 minutes. 4) The leaky colostomy bag is the least important. |

