![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pitch is primarily determined by the ____ of the soundwave
|
Frequency
|
|
|
What do we perceive amplitude as?
|
Loudness
|
|
|
What type of scale is a decibel scale? Why do we use it?
|
Auditory scale. It converts the large range of sound pressure into a more manageable scale.
|
|
|
How do we perceive frequency?
|
Pitch
|
|
|
What is the unit of measurement of frequency?
|
1 Hertz-1 cycle per second
|
|
|
What is the audibility curve?
|
Shows our sensitivity to sounds of differing amplitudes and frequency
|
|
|
Do we perceive sounds played at same amp but diff freq the same?
|
NO-we are more sensitive to frequency and higher frequencies sound louder
|
|
|
What is the human range of hearing?
|
20-20,000 hz
|
|
|
Elephants hearing range compared to ours
|
Elephants can hear lower tones than us, as low as 0 hz
|
|
|
Bats hearing range compared to ours
|
Bats can hear higher tones than us
|
|
|
Dogs hearing range compared to ours
|
Dogs can hear up to 40,000 hz, that's 10,00 hz higher than us
|
|
|
Cats hearing range compared to ours
|
Cats can hear higher and lower tones than dogs and us
|
|
|
Mice hearing range compared to ours
|
Mice can hear high tones than all of these species, up to 100,000 hz
|
|
|
What auditory range are we most sensitive to?
|
2,000-4,000 hz- range of conversational speech
|
|
|
The 3 parts of the outer ear
|
Pinnae
Auditory canal Tympanic membrane |
|
|
What is the function of the pinnae?
|
The part of the ear than we pierce, helps us funnel sound and localize where sound is coming from
|
|
|
Where is the auditory canal and what does it do?
|
Where I got that popcorn kernel stuck-the canal protects the inner structures of the ear
Has ear wax |
|
|
What is resonance?
|
It enhances the intensity of certain frequencies
In humans, the resonant freq is 2,000-5,000 hz |
|
|
What does the tympanic membrane do?
|
Transmits audio vibrations to the inner ear
Lower pitch produce a slower vibration Lower amplitude produce less dramatic vibration Higher freq produce faster vibrations |
|
|
What are the parts of the middle ear?
|
Ossicles
Oval window Middle ear muscles |
|
|
What are ossicles?
|
The 3 smallest bones in the body
Concentrates vibrations from the large tympanic membrane into a smaller area by being hinged to the membrane and creating a lever action in the stapes |
|
|
Why is it important that ossicles amplify sound?
|
Because pressure changes in the air of the outer and middle ear transmit poorly to the dense liquid of the inner ear.
|
|
|
What is the oval window?
|
Receives vibrations from the stapes
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the middle ear muscles?
|
To protect the inner ear against potentially painful and damaging stimuli
|
|
|
What is the cochlea?
|
Fluid filled snail like structure that contains the vestibular and tympanic canal
|
|
|
What is a tonotopic map?
|
Different freq of different sounds stimulate different parts of the membrane, transforming the way sound stimulates different areas of the organ of corti
|
|
|
What are 2 theories on how we hear frequency?
|
Bekesy's place theory
Phase locking theory |
|
|
What is Bekesy's place theory?
|
The frequency of sound is indicated by the place with the highest firing rate
|
|
|
How did Bekesy do his research?
|
Used cadavers
Made physical models |
|
|
What are the structures of the organ of Corti?
|
Basilar membrane-supports organ of corti
Inner and outer hair cells-receptors Tectorial membrane-on top of hair cells |
|
|
Difference between base and apex of the basilar membrane
|
Base is skinnier and stiffer than the apex
Apex responds best to low freq Base responds best to high freq |
|
|
If a tree falls in a forest, and no one is around to hear it, would it make a sound-is useful because it highlights that sound can be ____
|
Both perceptual and physical stimulus
|
|
|
If Daria wants a dog whistle that she can't hear, but her dog can, what range should it be in?
|
30,000-40,000 hz
|
|
|
Helen Keller felt that being ____ was worse because _____
|
Deaf: it isolated her from people
|
|
|
What were Bekesy's basic findings of place theory?
|
Traveling waves in the basilar membrane
Diff freq have diff peaks and it's the way the peaks hit the tectorial membrane, which stimulate the hair cells, that we distinguish frequency |
|
|
Evidence for place theory
|
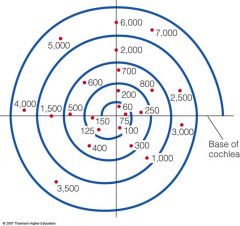
Guinea pig tonotopic map
|
|
|
Why was it necessary to update Bekesy's place theory?
|
Bekesy based his theory on cadavers and their membranes were different from living people
|
|
|
What is motile response and how is it related to the organ of Corti?
|
Outer haircells change the shape of the basilar membrane as it moves, which gives the membrane more a peak with the organ of Corti
|
|
|
How is the basilar membrane a frequency analyzer?
|
Basilar membrane breaks down the sounds that we're hearing and analyzes the diff freq for us
|
|
|
What is phase locking?
|
Frequency processing theory
Nerve fibers fire in bursts at the peak of the wave Good for up to 4,000 hz |
|
|
What are 3 causes of hearing loss?
|
Obstruction
Conductive hearing loss (middle ear bad osicles) Sensorineural (loud noises) |
|
|
What is a cochlear implant?
|
Electronic means of artificially processing sounds by directly stimulating the auditory nerve
|
|
|
Why is it so hard to assess infant perception?
|
They can't understand or respond to instructions from the tester
And they cry, sleep and don't pay attention |
|
|
Preferential looking technique?
|
Babies are more interested in novel stimuli so they measure what the baby prefers to look at
|
|
|
VEP
|
Visual Evoked Potential
Measure neural response to visual stimulus |
|
|
Difference between preferential looking technique and VEP
|
VEP is more precise because it can pick up on the firing of neurons
|
|
|
Habituation Technique
|
Measures how long it takes for an infant to become bored with a stimuli
Infants more likely to look at novel stimuli |
|
|
3 factors that contribute to babies' poor visual acuity
|
Focusing issues (weak ciliary muscles)
Developing visual cortex(dev by 3-6 mo) Cones in fovea (shorter&fatter than adults) |
|
|
Smooth tracking and how does it change with age
|
Doesn't develop until 7 weeks, and is done developing at 8 mo
|
|
|
Smooth tracking the same thing as a saccade?
|
NO
Saccades are jerky eye movements whereas smooth tracking is smooth tracking of a moving object |
|
|
When do infants experience increased color vision?
|
Some as early as 2 weeks
|
|
|
Borstein et al study
|
Habituated 4 mo to 510-nm light(green) then showed them either 480-nm(blue) or 540-nm(greenish). Dishabituated to 480-nm but not 540-nm.
Suggests that 4 mo categorize colors like adults do |
|
|
Binocular disparity
|
The difference in the left and right eye sees
Use binocular cues by 3 mo, few months later can use pictorial cue |
|
|
Visual cliff
|
Experiment where babies sit on plexiglass and underneath looks like the bottom dropped out
This experiment indicates depth perception |
|
|
Monocular cues (and pictorial cues)
|
Accommodation(squinting or widening your eyes
Movement based cues Pictorial cues (sources of depth info from 2-D images) |
|
|
Granrud experiment
|
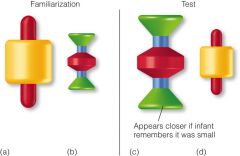
Using 5-7 mos, showed them large&small objects for 10min, then showed, at the same distance, similar objects w/ opposite size
7 mo reached for large object(that used to be small), but 5 mo did not Indicates monocular cues don't develop until 7 mo |
|
|
When do babies develop face perception skills?
|
Within minutes after birth, thanks to fusiform face area
|
|
|
When do babies show a preference for mom's face? What are they paying attention to?
|
2 days old-looked at mom's face 63% of the time
The contrast between forehead and hair line |
|
|
Special mechanism for perceiving faces-YES
|
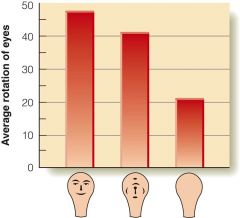
Morton&Johnson study-newborns preferred face-like moving stimuli over other moving stimuli
Farah et al-newborn contracted meningitis at 1 day old, developed prosopagnosia |
|
|
Special mechanism for perceiving faces-NO
|
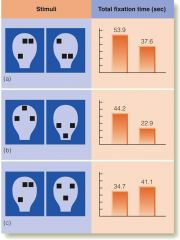
Turati study-infants preferred displays with top-heavy elements cause faces tend to be top-heavy
Develop special mechanism later |
|
|
Kellman & Spelke study
|
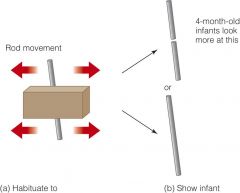
Showed 4 mo a rod with a block moving side to side in front of the rod until baby was habituated. Then showed a full rod or two separated rods. They liked the two rods cause it was unexpected suggesting they have object unity, and movement helped perceive object unity
|
|
|
Johnson et al Object Unity
|
Tested 2 mo and recorded eye movement when looking at the rod/block stimuli
Perceivers focused on the rod, nonperceivers focused on the block Infant perception of object unity depends on development of looking behavior |
|
|
Why is infant color vision poor at birth?
|
Their cones in their eyes are not yet fully developed
|
|
|
As you increase the decibel level from 80 dB to 100 dB, the sound pressure ratio goes from ____ to ____
|
BLANK
|
|
|
Intermodal/cross modal perception
|
Coordinating info from multiple senses at once into a perceptual whole
Begins from birth |
|
|
When can newborns smell things?
|
28 weeks gestation
|
|
|
When can babies taste things?
|
Can taste sweet, sour and bitter; but can't taste salt until later in life
|
|
|
DeCasper and Fifer study
|
Showed newborns recognize mom's voice
They modified their sucking bursts/pauses to hear mom's voice Put headphones on newborns, their sucking paused longer for mom's voice than a stranger |
|
|
Olsho et al study
|
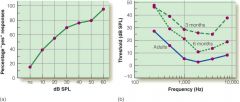
Put baby and mom in room, observer outside watching, baby has headphones, observers watches for changes in baby's face to determine if baby heard the tone
|
|
|
Jaloe is 4 months old, which depth cue is he most likely able to use?
A. Familiar size B. Shading C. Linear perspective D. Binocular disparity |
B. Shading
|
|
|
A human tonotopic map shows that a receptor close to the apex will respond to a tone of ___hz.
A. 60 B. 800 C. 7,000 D. 30,00 |
B. 800
(can't hear anything lower than 100 and the apex is more sensitive to low freq) |
|
|
E.S, a woman with parietal and frontal lobe damage, could___
|
recognize sounds but have difficulty localizing the sound
|
|
|
J.G, a man with damage to the temporal lobe, could____
|
locate sounds but had trouble recognizing sounds
|

