![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
184 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What term best describes a situation in which an employee is given additional tasks to accomplish in the same job? |
Job enlargement |
|
|
What is job enrichment? |
Increases the depth of the job by adding related responsibilities such as planning, organizing, controlling, and evaluating that add value to the work. |
|
|
Which of the following evaluation methods provides the most valuable measurement information? |
Results |
|
|
Which quality control tool prioritizes categories from most frequent to least frequent? |
Pareto chart |
|
|
Management and leadership differ in that: |
Management directs people; leadership motivates people |
|
|
What law covers both whistleblower protection and notice requirements for defined contribution plans? |
Sarbanes-Oxley Act |
|
|
What action to lower budgets that is legal in the United States that would most likely violate compensation laws in other countries? |
Reduce base salary levels |
|
|
What is the purpose of a balance scorecard? |
Achieve balance between financial and non financial indicators of success |
|
|
Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory |
Employees have two different categories of needs that are essentially independent of each other and affect behavior in different ways. Hygiene-extrinsic: factors that surround the job like working conditions, supervision and relations with coworkers Motivation-intrinsic: factors that are present in the job like achievement and personal growth |
|
|
ADDIE model |
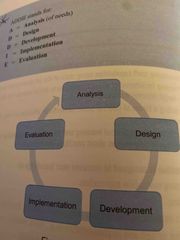
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Employee lifecycle |
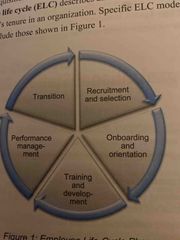
Back (Definition) |
|
|
A company operating internationally: |
Can choose a local responsiveness strategy in addition to a global integration approach |
|
|
Employee branding...it answers the question as to why a talented person would want to work for an organization |
Employee value proposition |
|
|
Examples of an internal recruiting source |
Job bidding Employee referral Inside moonlighting Job posting Nominations Succession planning Skill bank |
|
|
Examples of external recruiting sources |
Advertising Agencies Community awareness Educational institutions Former employees Internships |
|
|
Attitude survey |
Quality of management and organizational issues |
|
|
Opinion survey |
Seeks to gain opinions of specific processes |
|
|
Engagement survey |
Focuses on matters that affect employee satisfaction |
|
|
What is the 1st federal law to require employers to record and retain race and sex data on employees? |
The Fair Labor Standards Act 1938 |
|
|
A supportive leader attempts to: |
Reduce employee stress and frustration in the workplace |
|
|
When workers are judging additional work responsibilities, working longer hours, and performing jobs that are above or below their pay grade, this is known as what in organizational effectiveness and development? |
Declining workforce engagement |
|
|
What is the lifeblood of employment relationship between the worker and the employer based on? |
Compensation and benefits |
|
|
SA8000 social accountability has 9 key areas |
Human rights and labor relations Child labor Forced or compulsory labor Health and safety Freedom of association and right to collective bargaining Discrimination Disciplinary practices Working hours Remuneration Management systems |
|
|
Low context culture |
A communication style that relies heavily on explicit and direct language. Behavior needs to be spelled out explicitly. |
|
|
High context culture |
A culture of people that emphasizes interpersonal relationships and close connections over a long period of time. |
|
|
Building a diverse and inclusive organization in countries outside the U.S. can be influenced heavily by? |
Applying the four Ts: travel, teams, training and transfers Immersion in the culture of a host country can help employees and leaders understand those influences impacting profitability. |
|
|
In HR terms, what does risk management mean? |
Having employee health insurance, discrimination prevention, workplace safety, and asset security. |
|
|
Caux Principles |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Marlow’s Hierarchy of Needs |
Physiological needs |
|
|
3 categories of risk by Kaplan and Mikes |
Preventable risks, strategic risks, and external risks |
|
|
Foreign corrupt practices act of 1997 |
Prohibits American companies from making bribery payments to foreign officials for the purpose of obtaining or keeping business |
|
|
4 global engagement drivers |
The work itself as well as development opportunities the work provides Stability and the confidence that is placed in an organization’s leadership Rewards and recognition The upward and downward flow of communication |
|
|
At a regional level, the U.S. and Canada have the ___________ proportion of workers who are engaged in their jobs. |
Highest |
|
|
OECD |
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development |
|
|
Extraterritorial jurisdiction |
Authority beyond a country’s normal boundaries |
|
|
3 risks criteria according to ISO 31000 |
Moral hazard, principal agent problem, conflict of interest |
|
|
ANSI has published standards for: |
Measuring the cost per hires |
|
|
Marlow’s Hierarchy of Needs |
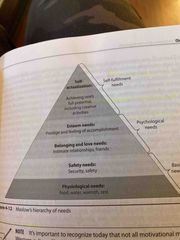
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Theory X, Y, and Z |
X: an authoritative management style because it assumes that employees inherently do not like to work and must be controlled and closed monitored Y: participative style of management, under the belief that employees dislike controls and inherently want to do their best. Z: management tends to promote stable employment, high productivity, and high employee morale and satisfaction. Japanese’s management style. |
|
|
Skinner’s behavioral reinforcement theory |
Positive reinforcement Negative reinforcement Punishment Extinction |
|
|
On a global basis, some countries __________. |
Require fixed % of disability representation |
|
|
3 types of professional HR engagement |
Trait, state, and behavioral |
|
|
Total compensation packages, including direct and indirect compensation, are often designed to help _________ employees. |
Retain |
|
|
Michael Porter’s value chain model? |
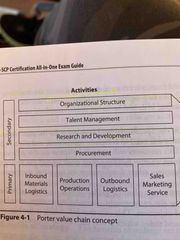
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is an INEFFECTIVE approach for a supervisor to deliver feedback to a struggling employee? |
The supervisor should list each area of deficiency and how it impacts the team. When providing feedback, a supervisor should limit the focus to one or two areas of deficiency. Otherwise, it tends to make the employee feel defensive. |
|
|
Which type of employee must be excluded from bargaining units as per the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA)? |
Supervisors |
|
|
In assessing HR technology programs, what is an example of a “best of breed” concept? |
Selecting an HR payroll system and a separate 3rd party LMS with better features. Best of breed is the process of selecting only the best software system for a specific need of the organization, which often means not choosing an all in one system. |
|
|
FLSA mandates that most employees be paid overtime for more than 40 hours in a week unless they fall under what criteria? |
Exceptions apply only to white collar type employees who fall under the salary and duties: Executive Administrative Professional learned and creative Computer Outside sales Highly compensated employees |
|
|
What types of organizations are required to maintain an affirmative action program (AAP)? |
Federal government contractors or subcontractors, as mandated by the Office of Federal Contract Compliance (OFCCP) |
|
|
In selecting a new HRIS, what is the 1st step in the process? |
Determine if the selection process will be conducted by a consultant or internal resources |
|
|
What would be the 1st step in helping an office in a different country hire a HR person there? |
Conduct a PEST analysis through a HR lens |
|
|
How would you appeal to a senior finance leadership focused in finance and convince them of the importance of a new program? |
Put together a succinct, finance centered document with the budget needed, how the budget will be spent, the expected impacts on employee retention, and in turn, cost savings |
|
|
What’s the biggest concern with using personality assessments as part of the hiring process? |
Assessments can pigeonhole applicants based solely on personality traits. Great applicants might be eliminated from the process based solely on their personality type. |
|
|
In which domain is workforce planning and employment a focus? |
HR operations |
|
|
Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, an employer may utilize the look back measurement method to determine: |
If an employee will be expected to work more than 30 hours per week |
|
|
What style of negotiation aims to meet the needs of both parties and leverage collaboration to come to an agreement called? |
Principled bargaining. It’s an interest based bargaining technique that aims to identify a mutually beneficial agreement , also know as win-win. |
|
|
Under the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), what do Canadians professionals need to work in the U.S.? |
The appropriate documentation (proof of Canadian citizenship) presented at the U.S. border |
|
|
For an employer to hire an unpaid intern, the internship must meet several criteria EXCEPT for: |
# of hours worked weekly |
|
|
If a sexual harassment complaint is determined to be unfounded what’s the appropriate course of action? |
Disciplinary action should be taken only if the reason was malicious. |
|
|
How would you deliver the feedback to a high performer who made a huge error that would end up costing the organization money? |
Remain neutral and state the facts of the mistake in the report. Ask for feedback on how to avoid these mistakes in the future. Asking for feedback on how to avoid the mistake will make her feel invested in the situation. |
|
|
When preparing to make an offer to a candidate, recruiters must consider several factors before deciding how much to offer within the applicable pay scale. What factors should NOT be considered? |
The candidate’s current compensation |
|
|
A CEO of a company has gained a reputation for berating others in meetings, firing employees, and micromanaging his senior leadership team. How would you describe the likely culture of this company? |
Fear based with minimal contributions from employees |
|
|
When an employee is injured on the job, what’s the 1st thug supervisors should be instructed to do after stabilizing the employee? |
Contact HR |
|
|
HSA finds never expire and employees who leave the organization do not lose access to the funds |
True |
|
|
What should employers NOT do for employees completing Form I-9? |
Provide a comprehensive list of acceptable documentation to an employee |
|
|
What is the best way to deal with workplace conflict between employees? |
Facilitated conversation. It’s best to address the situation before it gets worse |
|
|
What is functional conflict? |
A benefits type of conflict and can actually promote problem solving and creative ideas |
|
|
The Tuckman’s Forming, Storming, Norming, and Performing. Oftentimes, teams may move back and forth between which 2 stages when faced with a new task? |
Storming and Norming Teams often relapse from the Norming stage back into storming when faced with new challenges |
|
|
The expectancy theory of motivation explains that an individual’s choice is driven by: |
How desirable the outcome is |
|
|
Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, what period of time during which an employer must offer coverage to those employees who are considered full time called? |
The stability period. It’s the duration of time that coverage must be offered to full time employees. This period must be at least 6 months and not less than the defined measurement period |
|
|
What’s the most important component of a successful employee recognition program? |
Management buy in |
|
|
How is graded vesting mean in regard to a retirement plan? |
The employee’s ownership of employer contributions grows partially each year of participation |
|
|
On which main concept is the interest based relational approach to conflict resolution based? |
Separate people from problems. Emphasizes a fact based approach to the conversations about conflict; not letting emotions influence the discussion |
|
|
What is the 1st step in the strategic planning process? |
Analyze the applicable data |
|
|
FLSA, what is the minimum age for children to be hired for a non-farm job? |
16 |
|
|
EEO-1 |
Due on or before 30 September Required of private employers with 100 employees Applies to all types of employers except for education |
|
|
ERG theory - Clayton Alderfer |
Looks at levels of existence, relatedness, and growth among employees |
|
|
Hershey Blanchard |
Selling, telling, delegating, participating |
|
|
Sherman Anti Trust Act |
1st piece of legislation to affect the movement for labor rights in the U.S. |
|
|
Drug free workplace act of 1988 apply to federal contracts of a minimum of how much? |
$100,000 |
|
|
The largest number of work related injuries and health problems in the US? |
Poor ergonomics |
|
|
Kurt Lewis’ Change Process Theory includes what stages? |
Unfreezing, moving and refreezing |
|
|
Immigration reform and control act (IRCA) applies to businesses with minimum of how many employees? |
4 |
|
|
Compa-ration |
Method for an employer to judge how an employee’s pay compares to the standard average |
|
|
Graded vesting, how much must be vested after 3 years of employment? |
20% |
|
|
Cliff vesting, 100% must be vested in how many years? |
5 years |
|
|
Employers may choose to discontinue COBRA coverage payments are not received within how many days of being due? |
30 days |
|
|
How much COBRA coverage is allowed after a divorce? |
18 months 60 days after a divorce must an employer be notified to ensure COBRA coverage |
|
|
How much COBRA coverage is allowed after an employee is terminated due to being disabled? |
29 months |
|
|
How much COBRA coverage is allowed for a dependent child who no longer falls under standard health coverage? |
36 months |
|
|
Value stream map |
Step-by-step diagram that shows the purpose of each stage. |
|
|
Risk identification |
A way for HR professionals to mitigate or eliminate all potential setbacks, especially when delivering a solution to a customer. |
|
|
When switching to a cloud database management system what is an important consideration in the contract with the software vendor? |
Security standards for protecting sensitive employee data. |
|
|
Total remuneration survey |
A report of market data on compensation and benefit plans |
|
|
What’s a factor that influences workforce supply? |
Worker attrition |
|
|
What are the factors that influences workforce demand? |
Number of customers Seasonal workload Economic downturn |
|
|
Job enrichment |
Increasing a job’s death by adding new responsibilities to an existing job |
|
|
Job enlargement |
Broadening the scope of a job by adding new tasks. |
|
|
How can you determine ROI on a total rewards package design? |
Analyze relevant performance metrics such as sales per quarter. ROI is determined by taking the vale an employee adds to the organization and comparing it to the amount that is spent to retain the employee. |
|
|
What is a stay interview? |
A structured discussion to determine which factors influence employee retention and how retention efforts can be improved |
|
|
What does the term “mood” refer to in an organization? |
Climate |
|
|
What tool is used to identify an initiative’s value to a stakeholder along with the investment and influence that specific stakeholders have in promoting and supporting the initiative? |
Stakeholder mapping |
|
|
Principles bargaining |
When 2 groups negotiate a contract while being aware and mindful of the key issues to each side. Solutions so both sides gain from the agreement. |
|
|
Multi-employer bargaining |
Bargaining that occurs when a union with multiple employees at multiple companies meets with all of the companies in one negotiation |
|
|
Whipsawing, leapfrogging, and parallel bargaining |
Means the same thing; when a union successfully negotiates an agreement with a company and then uses these results to deal with another company |
|
|
Mini-cultures |
When each site maintains a separate operational structure and aligns their business practices to the customers they serve |
|
|
What can you do to ensure that diversity and inclusion practices are sustainable? |
Auditing |
|
|
Business technology |
Formal term that refers to software, online systems, workplace resources and reporting systems |
|
|
Data advocacy |
One who understands how important data is and uses data to make recommendations or decisions |
|
|
Quality assurance |
Process of establishing a relevant, unbiased system of data collection |
|
|
Umbrella goals |
Gaining buy in for large scale projects that impact the entire organization, which term describes the concept of finding values or interests across multiple departments that would encourage support? |
|
|
HR’s keystone value to an organization? |
Talent acquisition |
|
|
On boarding is also known as? |
Organizational socialization and should last the employee’s 1st year |
|
|
Culture shock |
Occurs after arriving in the new country and upon returning home, resulting in a low level of satisfaction for both stages |
|
|
Workplace diversity |
The differences in employee’s characteristics |
|
|
What are the 2 most common workplace safety risks? |
Blood-borne pathogens and tripping hazards |
|
|
Workforce management |
Understanding an organization’s current talent, anticipating future needs and implementing actionable plans to bridge gap |
|
|
Financial restructuring |
Form of corporate restructuring that is specific to when an organization has experienced significant decreases in profits primarily due to a poor economy |
|
|
Outplacement services |
Provide career counseling, resume writing and interview preparation to assist separated employees with future employment |
|
|
Labor union |
A formally organized group of employees who work together to accomplish goals |
|
|
What are the attributes of being an effective leadership? |
Managing time in a financially responsible manner Solving problems as they arise Strategic thinking |
|
|
Front pay |
Money awarded to an individual in a workplace discrimination case, generally equal to list of earnings |
|
|
External salary data |
The best source of data to review and analyze when determining if a company is paying their employees a salary that is competitive against the industry standard |
|
|
Employers are required to provide an initial COBRA notice within: |
Within 90 days of the individual’s separation |
|
|
When using the empirical-rational strategy to initiate change, what is the best way to accomplish the change successfully? |
Incentivize the change to relay the benefit employees will experience |
|
|
What are the 2 primary methods to examine HR programs, practices, and objectively for effectiveness and sustainability? |
Program and process evaluation |
|
|
COBRA |
Former employee pays the full cost of coverage Employers may impose 2% fee to cover costs Employers may face civil and criminal penalties for not complying with the COBRA requirements |
|
|
FMLA |
Employers are required to maintain employees’ group health insurance coverage while they are out on FMLA leave |
|
|
How long must an employee work to qualify for the Old Age, Survivor, and Disability Insurance Program? |
5 years, or 20 quarters |
|
|
Medical Part D |
Prescription drug coverage |
|
|
Job specification |
A detailed statement of the essential parts of a particular class of jobs. It includes a summary of the duties to be performed and responsibilities and qualifications necessary to do the job |
|
|
Non-quantitative job evaluation method |
Job ranking, paired comparison, and job classification |
|
|
Strong Employee Value Proposition (EVP) |
A strong EVP allows an organization to proactively attract and retain top talent by ensuring an understanding of the benefits offered |
|
|
Purpose of performance management |
The purpose is to foster a culture of constant improvement and development |
|
|
Bureau of Labor Statistics |
Division of the DoL that measures and collates nationwide employment data |
|
|
What are the 4 areas that must be equal to establish whether jobs are equivalent to each other under the Equal Pay Act? |
Skill, working conditions, effort, responsibility |
|
|
Sustainability |
When an organization’s current needs do not compromise the needs of their stakeholders |
|
|
Quantitative Benefits of corporate social responsibility (CSR) program |
Reduction of legal liabilities CSR also has a positive impact on employee recruiting, retention, and overall satisfaction |
|
|
Cross-cultural training |
Allows employees to engage in opportunities that broaden their experience |
|
|
Deauthorization |
The official process to remove a union’s security clause and negotiating authority. Removes the requirement that employees must join the union |
|
|
Constructive confrontation |
Next step after mediation that is used in specific circumstances, such as when neither side is willing to consider compromise or accept anything other than their specific resolution |
|
|
Employer brand |
Describing the organization’s mission, values, vision, culture and working environment |
|
|
The IRS looks for the following factors to evaluate a worker’s classification: |
Behavioral control, financial control and type of relationship If the company directs the workers how to perform their work, the court will label them as employees If the company allows the worker to reach a mutually agreed upon objective, they will be classified as an independent contractor |
|
|
Job analysis |
Includes job competencies, job specifications and job descriptions |
|
|
Time to fill |
Total days elapsed since job posted / # hires |
|
|
Cost per hire |
External costs + Internal costs / # hires |
|
|
Authoritarian culture |
Extremely focused on efficiency and productivity. Employees produce out of fear or anticipation of rewards. Micromanagement |
|
|
Mechanistic culture |
Characterized by organization and strong guidance from leadership. Focused on productivity, employees operate like a well oiled machine. Does not foster collaboration or creativity |
|
|
Participative culture |
Open communication and shared power. Morale is high, but it can be hard to get anything accomplished quickly |
|
|
Learning culture |
Use knowledge, abilities and innovation to adapt to an ever changing business environment. A lot of resources for training and development. Failure is not feared |
|
|
High performance culture |
Promotes goal achievement by setting clear objectives, clearly spelling out employee responsibilities, encouraging continuous development, and fostering trust. |
|
|
Retention rate |
(# employees who were employed for the entire measurement period / # employees at the start of measurement period) x 100 |
|
|
Turnover rate |
(# employees who left during measurement period / average # employees during the measurement period) x 100 |
|
|
3 behaviorally based appraisal methods |
Management by objectives Behaviorally anchored rating scales Behavior observation scales |
|
|
3 common narrative appraisal techniques |
Critical incident method Essay method Field review method |
|
|
Kilpatrick’s 4 level evaluation model |
Reaction - measures how people react to the training Learning- measures what they have learned Behavior- measures how the behavior of the people who took the training Results - analyzes noticeable effects of the training, like production |
|
|
6 levels of Blooms taxonomy of learning |
Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation |
|
|
Compa-ratio |
Compares a specific employee’s pay with the pay at the middle of the pay range |
|
|
Balanced scorecard |
Reflects the vision and strategy for the organization’s success from the financial outlook, customer perspectives and internal business processes The expectations of the stakeholders must be satisfied for a company to be sustainable and profitable. If a scorecard reports that one of the stakeholders is not being satisfied, the company must attempt to realign expectations |
|
|
Reduction in force |
Select employees for layoff using seniority, performance, job classification, location, or skill Ensure selected employees do not effect a protected class WARN Employees over 40 has the right to review any severance agreements. Consideration period of 21 days if 1 older worker is separated and 45 days when 2 or more are separated. 7 days revocation time |
|
|
Wildcat strike |
When a group of workers walks off the job in violation of valid labor agreements and usually against orders from the labor union |
|
|
Protected strikes |
Economic in nature over terms and conditions of employment or caused by an unfair labor practice |
|
|
High potential development programs |
Offer targeted training and other enrichment opportunities to the organization’s best and brightest employees. |
|
|
Business representative and union steward are: |
Most important positions within local unions. |
|
|
National labor relations board (NLRB) |
Founded by Congress as part of the Wagner Act They resolve unfair labor practices and conduct representative elections |
|
|
International Labour Organization (ILO) |
Address global working conditions. Promote decent working conditions that include eliminating child labor, ending unlawful discrimination, protecting human rights and worker rights |
|
|
Taft Hartley act |
Aka Labor Management Relations Act. Unfair for a union to force an employee to join or take part in a union |
|
|
Sherman Antitrust Act |
Established to oppose oppressive business practices such as court injunctions and yellow dog contracts |
|
|
Multi employer bargaining or coalition bargaining |
Takes place between multiple employers and a single union |
|
|
Coordinated bargaining |
Involves multiple unions and a single employer |
|
|
Sit down strike |
When employees report to work without actually working working or accomplishing anything |
|
|
Reduction in force |
Select employees for layoff using seniority, performance, job classification, location, or skill Ensure selected employees do not effect a protected class WARN Employees over 40 has the right to review any severance agreements. Consideration period of 21 days if 1 older worker is separated and 45 days when 2 or more are separated. 7 days revocation time |
|
|
Wildcat strike |
When a group of workers walks off the job in violation of valid labor agreements and usually against orders from the labor union |
|
|
Protected strikes |
Economic in nature over terms and conditions of employment or caused by an unfair labor practice Economic strikers can be temporarily or permanently replaced Unfair labor practices strikers can be ONLY temporarily replaced |
|
|
High potential development programs |
Offer targeted training and other enrichment opportunities to the organization’s best and brightest employees. |
|
|
Business representative and union steward are: |
Most important positions within local unions. |
|
|
National labor relations board (NLRB) |
Founded by Congress as part of the Wagner Act They resolve unfair labor practices and conduct representative elections |
|
|
International Labour Organization (ILO) |
Address global working conditions. Promote decent working conditions that include eliminating child labor, ending unlawful discrimination, protecting human rights and worker rights |
|
|
Taft Hartley act |
Aka Labor Management Relations Act. Unfair for a union to force an employee to join or take part in a union |
|
|
Sherman Antitrust Act |
Established to oppose oppressive business practices such as court injunctions and yellow dog contracts |
|
|
Multi employer bargaining or coalition bargaining |
Takes place between multiple employers and a single union |
|
|
Coordinated bargaining |
Involves multiple unions and a single employer |
|
|
Sit down strike |
When employees report to work without actually working working or accomplishing anything |
|
|
4 types of risks |
Hazard- fires and workplace accidents Financial- negative impacts to organization’s cash flow Operational- impact the the organization’s ability to function Strategic- involves an organization’s plans becoming outdated due to shifts in the economy |

