![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
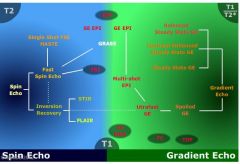
What are 5 different echo types
|
spin echo
gradient echo hahn echo stimulated echo |
|
|
What are the 3 main sequence families
|
spin echo sequences, characterized by the presence of a 180° rephasing RF pulse
gradient echo sequences hybrids |
|
|
Have numerous variations been developed within each of these families, mainly to increase acquisition speed
|
yes
|
|
|
What are some variations of spine echo sequences
3 |
fast spin echo
HASTE single shot FSE |
|
|
What are variations of GRE sequences
|
spoiled gradient echo
ultrafast gradient echo steady state gradient echo balanced steady state gradient echo echoplanar |
|
|
What are 2 examples of hybrid MR sequences
|
GRASE
SE-EPI |
|
|
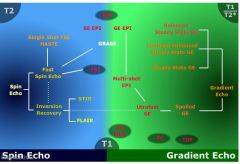
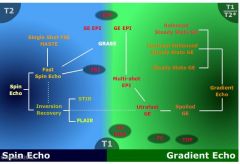
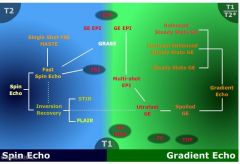
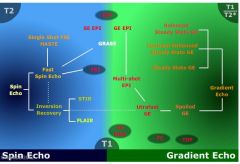
What does the family tree of MR look like
|
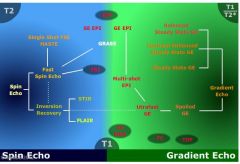
|
|
|
What does the family tree of MR look like
|
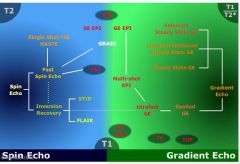
|
|
|
What does the family tree of MR look like
|
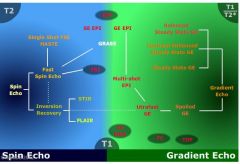
|
|
|
Are flair and stir types of inversion recovery sequences
|
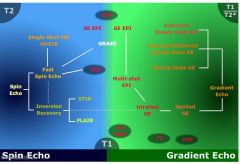
yes
|
|
|
What are the 2 main types of spin echo sequences
|
FSE and inversion recovery
|
|
|
Are spin echo sequences always T2
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the 4 main groups of GRE sequences
|
balanced steady state
contrast enhanced steady state steady state GE spoiled GE |
|
|
Is Ultrafast GE a type of spoiled GE
|
yes
|
|
|
Can GE be both T1 or T2 star
|
yes
|
|
|
Are multi echo spin echo and spin echo sometimes used interchangeably even though they are totally different
|

yes
|
|
|
What are some additional acrynoms for ultra fast SE
|
SSH TSE
SS TSE SS FSE FSE - ADA supper FASE HASTE |
|
|
Is HASTE a type of ultra fast SE
|
yes
|
|
|
What type of SE sequence is HASTE
|
ultra fast SE
|
|
|
What is the GE equivalent of HASTE (ultra fast SE)
|
SS-FSE
|
|
|
What are some acrymomns for STIR
|
STIR TSE
turbor STIR |
|
|
What is TIRM
|
an inversion recovery sequence
|
|
|
What are some acyrnoms of FLAIR
|
FLAIR TSE
Turbo FLAIR Fast FLAIR |
|
|
What are some acrynomns for GE
|
FFE
FE GE GRE |
|
|
What are some acrynomns for ultrafast GE
|

|
|
|
What are some acrynomns for spoiled GE
|

|
|
|
go back for GE stuff
|
http://www.imaios.com/en/e-Courses/e-MRI/MRI-Sequences/Sequences-acronyms
|
|
|
When does the rephasing pulse (180degree) occur in spin echo
|
TE/2
|
|
|
How much K-space is filled with each TR in a spin echo sequence
|
With each repetition, a k-space line is filled, thanks to a different phase encoding.
|
|
|
Does the 180 degree pulse require a rephasing lobe
|
no
|
|
|
What heppens when the TR is really long
|
The longer the TR, the more complete the longitudinal magnetization regrowth (decrease T1).
|
|
|
What is aquired after 1 TR r
|
single K space line is filled
|
|
|
What happens to the T2 when the TR is long
|
hen the TR is long (over 2000 milliseconds), longitudinal magnetization recovery is complete and on the following flip, the influence of T1 on signal magnitude will be minimized
|
|
|
What is a long TE
|
80-140 msec
|
|
|
What is the TE/TR timing of a proton density image
|
10-20msec
over 20000msec |
|
|
What happens to the T2 when the TR is long
|
hen the TR is long (over 2000 milliseconds), longitudinal magnetization recovery is complete and on the following flip, the influence of T1 on signal magnitude will be minimized
|
|
|
Can Spin echo sequences be used to get T1 images
|
yes, but it is time prohibitive and not used (long TR intervals)
|
|
|
What is a long TE
|
80-140 msec
|
|
|
What is the TE/TR timing of a proton density image
|
10-20msec
over 20000msec |
|
|
What is the major disadvantatge of spin echo
|
it takes forever
|
|
|
Can Spin echo sequences be used to get T1 images
|
yes, but it is time prohibitive and not used (long TR intervals)
|
|
|
What is the major disadvantatge of spin echo
|
it takes forever
|
|
|
What are 2 types of FSE
|
multi echo SE
Fast SE |
|
|
What is FSE also known as
|
Turbo spin echo
|
|
|
Is fse used as a generic term referring to both multi spin echo and FSE (turbo) and is very confusing bc it has the same name as one of the things it is referring
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the princible behind FSE
|
In fast spin echo sequences, the interval of time after the first echo, is used to receive the echo train, to fill the other k-space lines in the same slice
|
|
|
What are 2 types of FSE
|
multi echo SE
Fast SE |
|
|
Why is FSE so fast
|
Because of the reduced number of repetitions (TR) required, the k-space is filled faster and slice acquisition time is reduced.
|
|
|
What is FSE also known as
|
Turbo spin echo
|
|
|
What happens to the T2 when the TR is long
|
hen the TR is long (over 2000 milliseconds), longitudinal magnetization recovery is complete and on the following flip, the influence of T1 on signal magnitude will be minimized
|
|
|
What is a long TE
|
80-140 msec
|
|
|
What is the TE/TR timing of a proton density image
|
10-20msec
over 20000msec |
|
|
Is fse used as a generic term referring to both multi spin echo and FSE (turbo) and is very confusing bc it has the same name as one of the things it is referring
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the princible behind FSE
|
In fast spin echo sequences, the interval of time after the first echo, is used to receive the echo train, to fill the other k-space lines in the same slice
|
|
|
Can Spin echo sequences be used to get T1 images
|
yes, but it is time prohibitive and not used (long TR intervals)
|
|
|
Why is FSE so fast
|
Because of the reduced number of repetitions (TR) required, the k-space is filled faster and slice acquisition time is reduced.
|
|
|
What is the major disadvantatge of spin echo
|
it takes forever
|
|
|
What is HASTE
|
A variation of the (Half Fourier Acquisition Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo) HASTE sequence, whereat half of the image information is aquired after the first excitation pulse, and the half after the second excitation pulse. The acquired data are then interleaved into the raw data matrix. A long time to repetition (TR) is selected to allow the spin system to recover between excitation pulses and the dead time is used for additional slices. The lenght of the echo train is cut in half. Also more than 2 segments are possible.
|
|
|
What does a fast spin echo sequence look like (turbo spin echo)
|
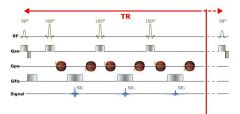
|
|
|
When is the GSS always applied
|
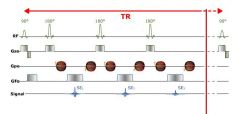
simultaneously with the RF pulse
|
|
|
What is done after each signal
|
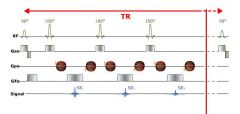
After each echo, the phase-encoding is cancelled and a different phase-encoding is applied to the following echo. (see there are 2 phase encoding symbols per 180 pulse they are in different directions and cancel eachother out)
|
|
|
What is the turbo factor or echo train length
|
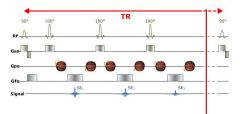
The number of echoes received in the same repetition (during TR time) is called the Turbo Factor or Echo Train Length (ETL).
|
|
|
What is the difference between turbo spin echo and multi echo SE sequences
|
TSE allows multiple K-lines to be filled per TR and MSE allows several images of the same slice position to be obtained with different contrast
|
|
|
When is the second 180 degree RF pulse done in a MSE
|
After the first echo is obtained, there is a free interval until the next TR. By applying a new 180° pulse, a new echo is received, with the same phase encoding, to build the second image
|
|
|
What is the difference between the first and second echo signal
|
The echo time of the 2 images differs and the second image will be more T2 weighted than the first
|
|
|
What is the MSE sequence typically used for
|
ypically, these sequences are used to obtain simultaneously PD- and T2-weighted images.
|
|
|
What does MSE look like
|
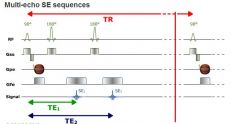
|
|
|
Why does MSE have a different number of phase encoding symbols
|
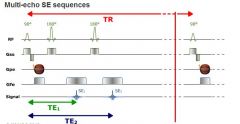
because it is imaging the same row over and over
|

