![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Energy of photon |

|
|
|
|
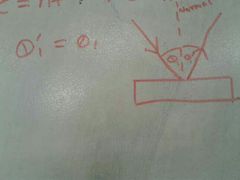
Angle of incidence and reflection |
|
|
|
|
Index of refraction speed of light |

|
|
|
|
Index of refraction wavelength |

|
|
|
|
Snell' s law law of refraction |

|
|
|
|
When enteringa material with higher index this happens |

|
|
|
|
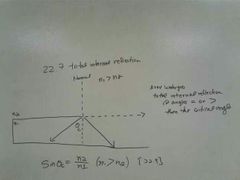
Total internal reflection |
|
|
|
|
Focal length |
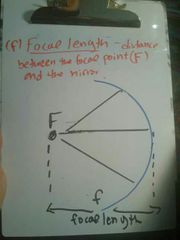
Distance between the focal point and the mirror |
Focal length |
|
|
Connection between radius and focal length |

|

|
|
|
Relationship between four distances |

|
|
|
|
Positive and negative distance |

|
|
|
|
Magnification and meaning of signs |
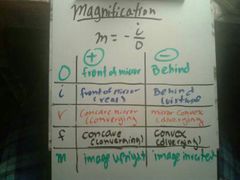
|
|
|
|
Object placed beyond Focal point |

Real, inverted and magnified |
|
|
|
Object is placed at F |

No image formed because reflected light rays parrallel to each other |
|
|
|
Object is placed between Focal point and the mirror |

Image produced virtual, upright, magnified |
|
|
|
Key concepts |

1. Ray parallel to axis-->reflects back through focal point 2. Rays through focal point-reflects back parallel to acids 3. Ray to center of mirror-->reflects back at same angle relative to normal |
|
|
|
Single diverging mirror |

Virtual, upright, and reduced |
|
|
|
UV NO IR |

-Upright images always virtual -No image is formed when the object is a focal length away -Inverted Image are always real |
|
|
|
Focal length concave versus convex mirror |

|
|
|
|
Magnification |

|
|
|
|
Magnification greater than 1 less than 1 for less than one |
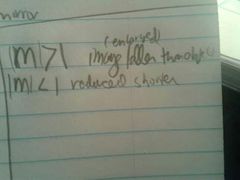
|
|
|
|
Beyond at Centre between Center and focus and focal point |
|
|
|
|
Before focal point |
Virtual and in large is the image produced extend the reflection Rays backwards |
|
|
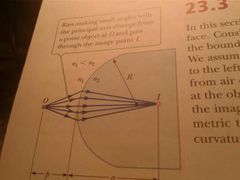
Images formed by refraction |

|
|
|
|
Real images refraction vs mirrors |

|
|
|

Sign conversion for retracting surfaces |

|
|
|

Sign conversion for mirrors |

|

|
|

Flat refracting surfaces |

|
|
|
|
Images formed by refraction |

|

|
|
|
Flat refracting surfaces |

|
|
|
|
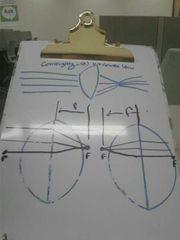
Converging vs diverging lenses |

|
|
|
|
Converging rays |
|
|
|
|
Diverging bioconcave |

|
|
|
|
Signs fire flat, convex, and mirrored |

|
|

