![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
139 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
_____ and ____ of atoms provide the theoretical foundation for the periodic classification |
Aufbau principle, electronic configuration |
|
|
The elements in ____ exhibit similar ____ behaviour. |
Group, chemical |
|
|
The similarity arises because the elements have the ______ and ______ of electrons in their outermost orbitals |
Same number, same distribution |
|
|
Helium belongs to ______ block but is positioned in the ______ . |
S, p |
|
|
On what basis hydrogen is similar to alkali metals |
Has only one s electron |
|
|
On what basis hydrogen is similar to group 17 family |
To achieve noble gas arrangement can gain an electron |
|
|
Give the atomic number of rubidium |
37 |
|
|
Give the atomic number of caesium |
55 |
|
|
Give the atomic number of francium |
87 |
|
|
S block elements are all ____ with _____ ionization enthalpy |
Reactive metals, low |
|
|
The reactivity _____ as we go down the group |
Increases |
|
|
S block elements are never found in ____ owing to their _____ . |
Pure state, high reactivity |
|
|
S and p block elements together constitute _____ elements or _____ elements |
Representative , main group |
|
|
In p block the non metallic character ____ as we move from left to right across a period |
Increases |
|
|
The D Block Elements have general electronic configuration of _____ |
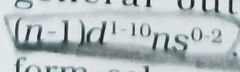
|
|
|
All D block elements are _____ |
Metals |
|
|
The lanthanoids starts from _____(____) to ___ ( ____) |
Ce(Z=58), Lu(Z= 71) |
|
|
The actinoids start from _____ ( ___) to ____(___) . |
Th(Z=90), Lr( Z= 103) |
|
|
The electronic configuration of f block elements are |
(n-2) f1-14(n-1) d0-1 ns2 |
|
|
The last electron in F block elements added to each element is filled in |
F orbital |
|
|
F block elements are all |
Metals |
|
|
The chemistry of _____ is more complicated than the corresponding lanthanoids, due to the large number of oxidation States possible |
Early actinoids |
|
|
Many of the actinoid elements have been made only in _____ quantities or even less by nuclear reactions and their chemistry is _____ fully studied |
Nanogram, not |
|
|
Elements after uranium are called |
Trans uranium elements |
|
|
The electronic configuration of Z =117 |
(Rn) 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p5 |
|
|
Electronic configuration of Z = 120 |
(Uuo) 8s2 |
|
|
Metals comprise more than ____ of all known elements and appear on the ____ side of periodic table |
78%, left |
|
|
______ And ____ also have very low melting points |
Gallium, caesium |
|
|
By ____ property metals can be flattened into thin sheets by hammering |
Malleable |
|
|
By _____ property metals can be drawn into wires |
Ductile |
|
|
Non metals are usually solids or gases at room temperature with ____ melting and boiling points |
Low |
|
|
Non metals are _____conductors of heat and electricity |
Poor |
|
|
Most non metallic solids are ___ and are neither malleable nor ductile |
Brittle |
|
|
The change from metallic to non metallic character is not ____ |
Abrupt |
|
|
Give example of semi metals |
Silicon , Germanium , arsenic, antimony , tellurium |
|
|
Si, Be, Mg, Na, P : Order of metallic character is |
Na>Mg>Be>Si>P |
|
|
In non metals the reactivity ____ down the group |
Decreases |
|
|
The measurement of the distance between two atoms when they are bound Together by a _____ bond in _____ molecule forms the covalent radius. |
Single, covalent |
|
|
______ Is taken as half the inter nuclear distance separating the cores |
Metallic radius |
|
|
Noble gases are ____ . |
Monoatomic |
|
|
Noble gases have ____ radii. |
Van der waal |
|
|
Noble gases have _____ radii |
Non bonded |
|
|
The ionic radii can be estimated by measuring the distance between cations and anions. T/F. |
T |
|
|
The Ionic radius of fluoride ion is ____ where as the atomic radius of fluorine is only _____ . |
136 pm, 64 pm |
|
|
In the ionic form the radius of the metals or nonmetals generally decreases or increases by a factor of |
2 |
|
|
In isoelectronic Species the radii would be ____ |
Different |
|
|
The energy required to remove an electron from an isolated gaseous atom in its ground state is |
Ionization enthalpy |
|
|
Energy is always required to ____ electrons from an atom and hence ionization enthalpy are always _____ . |
Remove, positive |
|
|
In the graph of ionization enthalpy ____ occupy the maxima and _____ occupy the minima |
Noble gases, alkali metals |
|
|
Why alkali metals occupy the minimum position in the ionization enthalpy graph |
Due to their low ionization enthalpy |
|
|
Shielding is effective when the orbitals in the inner shells are ____ . |
Completely Filled |
|
|
Down the group increase in ____ outweighs the increasing _____ so removal of outermost electron requires ______ energy down the group |
Shielding, nuclear charge, less |
|
|
The penetration of ____ electron to the nucleus is more than that of ____ electron. |
2s, 2p |
|
|
In oxygen atom ____:of the four ____ electrons must occupy the same ____ orbital resulting in an increased ___ repulsion |
2, 2p, 2p, electron - electron |
|
|
Due to ______ it is ___ to remove the fourth 2p electron from oxygen in comparison to nitrogen |
Electron electron repulsion, easier |
|

|

|
|
|
Ionization enthalpy _____ across the period |
Increases |
|
|
Electron gain enthalpy provides a measure of the ease with which an atom ____ an electron to form _____ . |
Adds, anion |
|
|
For many elements energy is _____ when an electron is added to the atom and the electron gain enthalpy is ______ . |
Released, negative |
|
|
Halogens have ______ electron gain enthalpy because they can attain stable electronic configuration by _____ electron. |
High negative, adding one |
|
|
Noble gases have _____ electron gain enthalpy because the electron has to enter the next higher _____ level leading to very unstable electronic configuration |
Large positive, principle Quantum, |
|
|
The electron gain enthalpies have ________ values toward the upper right of the periodic table preceding the noble gases |
Large negative, |
|
|
As a general rule electron gain enthalpy becomes _____ with increase in atomic number across a period |
More negative |
|
|
Cl has -349 ∆Hege . What does negative sign means |
When an electron is added to the atom enthalpy is negative |
|
|
Cl has -349 ∆Hege. What does the magnitude represent |
The high magnitude represents the tendency to gain electron |
|
|
What is the general rule which can be applied for electron gain enthalpy |
Enthalpy is negative when an electron is added |
|
|
When does an atom has positive electron gain enthalpy |
When it does not want to add electron , eg: noble gas |
|
|
The positive and electron gain enthalpy indicates |
The tendency with which an electron is repelled |
|
|
The high value of electron gain enthalpy indicates |
Height of Desire |
|
|
The effective nuclear charge ____ from left to right across a period |
Increases |
|
|
Due to increased effective nuclear charge it will be ____ to add an electron to _____ atom because the added electron on an average would be closer to the positively charged _____ |
Easier, smaller, nucleus |
|
|
Electron gain enthalpy becomes _____ as we go down a group |
Less negative |
|
|
The electron gain enthalpy of oxygen or fluorine is ______ than that of the succeeding element because of significant ____ . |
Less negative, repulsion |
|
|
The negative of electron gain enthalpy is defined as |
Electron affinity |
|
|
Electron affinity is defined as |
Absolute zero |
|
|
Give the relation between electron gain enthalpy and electron affinity |
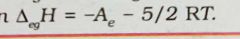
|
|

|

|
|
|
Electronegativity is a _____ measure |
Qualitative |
|
|
Electronegativity is a measurable quantity. T/F |
F. Electronegativity is not a measurable quantity |
|
|
Mulliken-Jaffe scale is applicable to _____ |
Electronegativity |
|
|
Allred - Rochow scale is related to |
Electronegativity |
|
|
Why does the magnitude of electron gain enthalpy decreases down the group |
Because down the group the size of the atom increase and the added electrons would be farther from the nucleus |
|
|
The magnitude of electron gain enthalpy ______ down the group |
Decreases |
|
|
The electronegativity of any given element is _____ . |
Not constant |
|
|
Electronegativity depends on the ____ to which it is bound |
Element |
|
|
Elements have constant electronegativity |
False |
|
|
Electronegativity is a measurable quantity |
False |
|
|
Electronegativity is not a _____ quantity |
Measurable |
|
|
_____ provides a mean of predicting the nature of force that holds a pair of atoms together |
Electronegativity |
|
|
The electronegativity of any given element is |
Variable |
|
|
Electronegativity generally increases across a period from |
Left to right |
|
|
Electronegativity value _____ with the increase in atomic radii down a group. |
Decreases |
|
|
The trend of electronegativity is similar to |
Ionization enthalpy |
|
|
Electronegativity is directly related to _____ property of the element |
Non metallic |
|
|
Electronegativity is ______ related to the metallic properties of elements |
Inversely |
|
|
Increase in electronegativities across a period is accompanied by _______ in non metallic properties |
Increase |
|
|
Decrease in electronegativities down a group is accompanied by |
Increase in metallic properties |
|

Give the electronegativity of |

|
|

Give the electronegativity of |

|
|
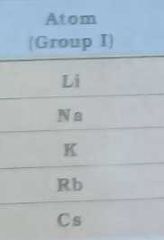
Give electronegativity of |
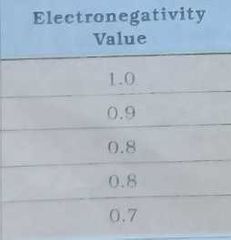
|
|
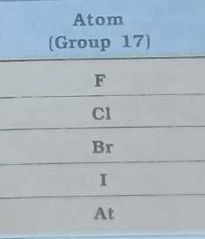
Give electronegativity of |
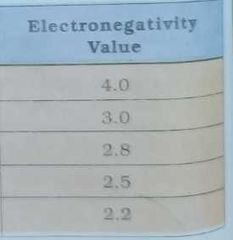
|
|
|
The _____ is the most characteristic property of the element |
Valence |
|
|
In OF2 molecule oxygen ____ two electrons with fluorine atoms |
Shares |
|
|
Oxidation state is defined as the charge acquired by its atom on the basis of _____ consideration from other atoms in the molecule |
Electronegative |
|

|

|
|

Give the number of valence electron |

|
|

Give the valence of |

|
|
|
There are many elements which exhibit variable valence. This is particularly characteristic of _____ elements and _____ . |
Transition, actinoides |
|
|
Lithium shows diagonal relationship with |
Magnesium |
|
|
Beryllium shows diagonal relationship with |
Aluminium |
|
|
The maximum covalency of the first member of each group is |
4 |
|
|
The first member of p block elements displays greater ability to form _______ multiple bonds to itself and to the other ___ period elements. |
Pπ-pπ, second |
|
|
Give the order of metallic radius of Lithium and magnesium |
Mg>Li |
|
|
Give the order of Ionic radius of Lithium and magnesium ion |
Li+>Mg+ |
|

|

|
|
|
The chemical reactivity at the two _____ is highest and the lowest in the _____ . |
Extremes, centre |
|
|
The metallic character ___ while the non metallic characters ____ while moving from left to right across the period |
Decreases, increases |
|
|
Oxides of elements in the centre are ____ or ____ |
Amphoteric , neutral |
|
|
As2O3 is _____ in nature |
Amphoteric |
|
|
Give example of neutral oxides |
CO NO N2O |
|
|
Give the nature of N2O |
Neutral |
|

|

|
|
|
Transition metals are _____ electropositive than first and second group metals |
Less, |
|
|
Who was the first to consider the idea of trends among properties of elements |
Johann dobereiner |
|
|
Give the group one triad of Dobereiner's triad |
Li Na K |
|
|
Give the group two triad of Dobereiner's triad |
Ca Sr Ba |
|
|
Give the group 17 triad of Dobereiner's triad |
Cl Br I |
|
|
What comment did the dobereiner passed on the triads |
Properties of the middle element was in between those of the other two members |
|
|
Who arranged the then known elements in order of increasing atomic weights |
Chancourtois |
|
|
Who made a cylindrical table of elements to display the periodic reference of properties |
Chancourtois |
|
|
Law of triods was given in |
Early 1800s(1829) |
|
|
Law of octaves was given in |
1865 |
|
|
Who gave law of octaves |
Newland |
|
|
Law of octaves seemed to be true only for elements up to |
Calcium |
|
|
Who was awarded the davy medal in 1887 |
Newland |
|
|
Dimitri mendeleev |
1834 to 1907 |
|
|
Lothar Meyer |
1830- 1895 |
|
|
Who is generally credited with the development of modern periodic table |
Dimitri mendeleev |
|
|
Who plotted various physical properties against atomic weight to obtain a periodically repeated pattern |
Meyer |

