![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
133 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is it called when the male urethra forms on the inferior vs superior surface?
mnemonic? |
inferior- hypospadias
superior- epispadia hypo= below, epi= above spadias- like a spade digging a hole |
|
|
show pics of the spadias. is the regular urethra missing?
|
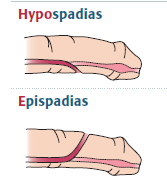
yes, disregard 1st aid
|
|
|
how does hypospadias come about?
|
failure of the urethral folds to seal during development
|
|
|
draw what the sealing of the urethral fold look like? where is the genital tubercle?
|
|
|
|
how does the genital tubercle move as the urethral folds colse up?
|
it goes up and out to extend to be te penis
|
|
|
what goes wrong in epispadias embryologically?
what other presentation of the penis is often associated with epispadias? |
the genital tubercle goes down below the urethral folds and they close up top
incomplete urethral fold closure (from the gential tubercle splitting it) will cause bifid penis |
|
|
show pic of epispadias
|
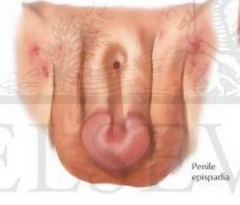
|
|
|
besides te penis, wat else can be malformed in epispadias? ow so?
|
bladder exstrophy- bladder in front is also not sealed properly and you can see it from te outside
|
|
|
sow bladder exstropy
|
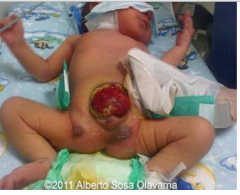
|
|
|
wat would appen if males got HPV 6 or 11? histology?
|
condyloma accuminatas- koilocytic changge
|
|
|
what causes lymphogranuloma verereum?
|
chlamydia trachomatis
|
|
|
where does chlamydia grow? must it?
mnemonic? |
an obligate intracellular bacteria
it clams up inside the cells |
|
|
why does chlamydia have to be inside of cells?
|
it can't make it's own ATP so it must steal it
|
|
|
What are the 3 serotypes of Chlamydia trachomatis?
which one can cause lymphogranuloma verereum? |
A-C
D-K L1-L3 |
|
|
what is a serotype?
|
a different receptor on the surface of the same microorganism
|
|
|
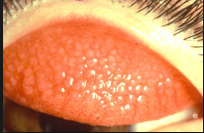
what does lymphogranulosum verereum look like? 2 components
|
swollen inguinal lymph nodes that may ulcerate
ulcers on the genitals |
|
|
dissect lymphogranulosum venereum
|
lympho- affects the lymph nodes
granulosum- will see granulomas verereum- relating to the sexual organs |
|
|
can woemn get lymphogranulosum venereum too?
|
yes
|
|
|
what are the swollen lymph nodes called?
|
buboes
|
|
|
are the genital ulcers and inguinal lymph node enlargements painful.
|
not the genital ulcers, but the nodes are
|
|
|
Mnemonic for aspects of serotypes A-C for Chlamydia trachomatis.
|
A, B, C
Africa Blindness Chronic infection |
|
|
what disease does chlamydia trachomatis A-C cause?
|
trachoma
|
|
|
so what is the pathphysiology of trachomas?
|
the lymphoid follicles and papillae of the inner eyelid start to enlarge and fibrose
the eyelids get so large that the eyelashes double back to the eye and cause corneal abrasions and blindness |
|
|
What does chlamydia trachomatis D-K cause? 3
|
Adults
Urethritis PID- fallopian tube scarring --> ectopic pregnancy Neonatal- pnemonia, trachoma (conjunctivitis) |
|
|
How do infants contract all the things in chlamydia?
|
via passage through the birth canal
|
|
|
what is the presentation of neonatal pneumonia here?
|
staccato cough
|
|
|
what is a staccato? staccato cough?
|
notes played in music that are separate from each other
short bursts of sudden coughing |
|
|
treatment for chlamydia trachomatis?
|
doxycycline
|
|
|
picmonic mnemonic for chlamydia trachomatis/
|

|
|
|
PIC OF THE conjunctivitis trachoma
|
|
|
|
so what is chlamydia trachomatis named for?
|
the type of bacteria and then then conjunctival condition of trachoma
|
|
|
which types are capable of cuaseing trchoma?
|
A-C and D-K (neonatal)
|
|
|
What should you think is happening if you find vaginall bleeding early in pregnancy 1 vs later on 2?
|
early- spontaneous abortion
late- placenta previa, placenta abruption |
|
|
how does chlamydia spread in youir body? mnemonic?
|
enters mucosa as elementary bodies (young and entering elementary school)
enters endosome once taken in by cells and germinates into reticulate bodies |
|
|
what forms when the lymphogranuloma venereum heals?
|
fibrosis
|
|
|
where else can lymphogranuloma venereums spread? why here?
|
it is in the superficial perineal pouch (superficial iguinal node domaiin) which has no separation from the perianal area
|
|
|
so what can happen when the perianal area heals from the ulcers and inflmmation of lymphogranuloma venereum?
|
perianal strictures
|
|
|
what is the leading cause of penile squamous cell carcinoma?
how often? |
high risk HPV- 2/3rd of the time
|
|
|
what is a risk factor for sqamous cell carcinoma and why?
|
lack of circumcision because the foreskin can harbor microorganisms and can be more easily irritated and inflammed.
|
|
|
how many WBC's would you see in a male vs female urinalysis?
|
male- none
female- trace |
|
|
how would you remove the trace WBC's in women?
|
pee, stop mid stream, clean with alcohol wipe, collect pee sample
|
|
|
what is the effect of estrogen vs androgens on growth plates?
|
androgen- closes them
estrogen- inhibits closing |
|
|
leading 2 causes of prostatitis?
|
chlamydia and gonorrhea (STD's)
|
|
|
What does BPA function as? how do yyou know?
|
estrogen- they are blamming the earlier and earlier periods on BPA
|
|
|
Back to penile pathology: penile squamous cell carcinoma.
What are the 3 precursor lesions? name as describe appearance of each. |
Bowen disease- leukoplakia on shaft
Erythroplakia of Querat- erythroplakia on glans Bowenoid papulosis- reddish papules |
|
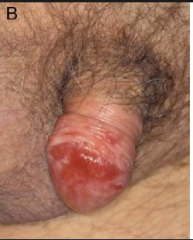
what is this?
|
erythroplakia of Querat
|
|
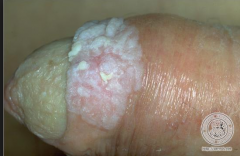
What is this?
|
bowen's disease
|
|
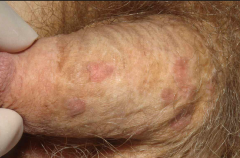
what is this?
|
bowenoid papulosis
|
|
|
So what can cause all these superficial penile lesions?
What do they have in common? |
HPV and chronic irritation from things hding under the foreskin
they can all progress to squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
Comment on the metastatic potential of each of the 3 lesions/
what is their histology classified as |
Bowen and erythroplasia are carcinoma in situ, but will eventually invade the plasma membrane
Bowenoid papulosis is like bowen, but with no capacity to invade |
|
|
So what should you be most alarmed to see on a penis?
|
red on the glands or white on the shaft.
or anything with large plaque lesions ahter than papules. |
|
|
NoW WE TALK ABOUT TESTIULAR PATHOLOGY
WHat is the most common congenital male reproductive abnormality? |
cryptorchidism
|
|
|
When does the testes usually descend?
|
before the 1st year
|
|
|
how prevalent is cryptorrchidism?
|
1% of baby boys
|
|
|
recommended approach to cryptorchismisn? why?
|
wait to see if it will correct itself
if it doesn't y age two, then you need to perform an orchipexy |
|
|
Why must you do it by age 2?
2 possible complications |
because then the increase heat will increase your risk of testicular atrophy and seminoma
|
|
|
What are the bacterial causes of orchitis in younger adults? be specific. why?
|
chlamydia trachomatis D-K
neisseria gonorrhea they are STD's |
|
|
What are the bacterial causes of orchitis in older adults? be specific. why?
|
e. coli and pseudomoas- these are things that hang out there and create UTI's. older adults have less sex and less defenses against these ordinary things.
|
|
|
what virus can cause orchitis?
|
mumps virus
|
|
|
do all males have the capacity to get orchitis?
|
no, only those greater than 10
|
|
|
who is most dangerous to get mumps and why?
|
adolescent boys because this can lead to lifelong inferility
|
|
|
What is the remaining cause of orchitis?
|
autoimmune
|
|
|
What would you see histologically with autoimmune orchitis?
what else does this look like? |
granulomas
also looks like TB |
|
|
What are 2 ways you can differentiate TB from atoimmune granulomatous orchitis?
|
TB will have positive acid-fast baccili stain and have necrotizing granulomas
|
|
|
what goes wrong in testicular torsion?
what is the name of the resulting pathology? |
the spermatic cord twists on itself, clamping down the thin vein, but leaving the artery open.
you get a hemorrhagic infarction as blood keeps coming in, but can't leave. |
|
|
2 reasons why it is a hemorrhagic infarction?
|
blood goes into the tissue and it is a looselyorganized tissue
|
|
|
cause of testicular torsion?
|
congenital failure of testes to attach to the inner lining of the scrotum or some other twisting of the cord
|
|
|
what is supposed to attach the testes to the scrotum?
|
a covering called the tunica vaginalis
|
|
|
I though that was just a closed up flap in front?
what is that? mnemonic? |
no, that is the processes vaginalis
tunica- tunic = covering process- like a digit/finger |
|
|
is it always the fault of the tunica vaginalis not attching? how often is it?
|
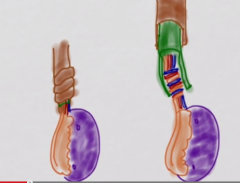
90% it is the tunica's fault, but it can also twist within the tunica
|
|
|
2 presentations of testicular torsion? why for each?
|
testicular pain- sensitive tissue is dying
loss of cremasteric reflex- nerve is cut off |
|
|
how do you test for the cremasteric reflex?
|
scrape a tongue deressor along inner thigh and see if the scrotum lifts up
|
|
|
show what the hemorrhagic infarction of testicular torsion looks like
|
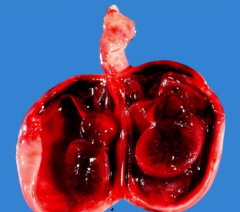
|
|
|
what is the defintiion of a testicular varicocele?
|
when the testicular veins are heavily dilated
|
|
|
what do varicoceles look like and why?
|
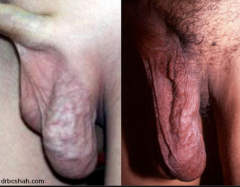
bag of worms because all the superficial veins are dilated
|
|
|
what side is varicocele usually on and why?
|
left because the left testicular vein drains into the renal vein and so has 1 more step to be blocked
|
|
|
most common cause of varicocele?
|
renal cell carcinoma (not nutcracker syndrome)
|
|
|
where does renal cell carcinoma love to invade?
|
the renal veins
|
|
|
what condition is highly associated withvaricoceles? why do we THINK this is?
|
infertility- the heat from all the blood may cause damage to the sperm and the sex cord cells.
|
|
|
which 2 demographics are most prine to testicular torsion and why?
|
anytime the testes is moving aorund a bunch
right after borth- descending puberty- growting |
|
|
describe the diagram of the tunica vaginalis.
does it surround the whole testes? is there a visceral and parietal? how is the process related? |
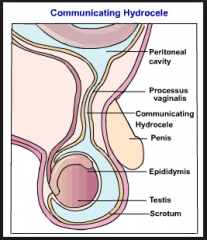
|
|
|
what is the cause of hydrocele in infants vs adults?
|
infants- failure of process vagialis to close
adults- their process has sealed, but if they have impaired lymph drainage then it can fill with fluid |
|
|
is there normally fluid in the tunica vaginalis?
|
nope
|
|
|
how does hydrocele present?
physical exam finding? |
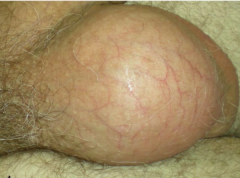
scrotal swelling than cannot be transilluminated
|
|
|
NOW WE DO TESTICULAR TUMORS
what categor of ovarian tumor is absent in testicular tumors and why? |
surface epithelial tumors because this layer doesn't exist in men
|
|
|
what will you find on PE of testicular tumors?
texture? pain? |
firm, painless mass that cannot be transiluminated
|
|
|
how do we treat testicular tumors different than other tumors?
|
we don't biopsy
|
|
|
why don't we biopsy? 2 reasons
|
1. the testicle can leak out stuff afterwards and seed to the scrotum
2. 95% of tumors are germ cell and malignant anyways |
|
|
two risk factors for germ cell tumors?
|
cryptorchidism and Klinefelter syndrome?
|
|
|
what is the usual age demographic for testicular tumors?
mnemonic? |

15-40
think lance armstrong |
|
|
what are the two major divisions of testicular tumors? why? 3
|
seminoma and nonseminoma
seminomas are easily treated and have good prognosis and metastasize late while all the others do the opposite |
|
|
ovarian analog to seminoma?
|
dysgerminoma
|
|
|
histological sign of seminoma?
|
uniform cells that are large with clear cytoplasm and central nuclei
|
|
|
what is a hormone that seminomas can produce? is this common?
|
b-hCG and no it is rare
|
|
|
what kind of cancer treatment should we use for seminoma?
|
radiotherapy
|
|
|
what does seminoma look like grossly? mnemonic?
|
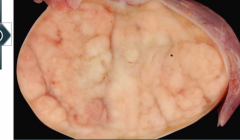
large homgenous mass with no hemorrhage or necrosis - it is the best of the tumors so it looks pretty darn good
|
|
|
decribe what an embryonal carcinoma is
what type of cells are there? 2 is it malignant? |
a malignant tumor of immature, primitive cells that may also form glands
|
|
|
is embryonal carcinoma malignant? how do yoiu know?
mnemonic? |
yes, these are embryo-like cells that are designed to grow really fast because embryos grow really fast
|
|
|
can embryonal carcinoma spread to other areas? readily? ewhat route?
mnemonic? |
yes, quite aggressively because embryos like blood like the placenta and will seek it out right away
|
|
|
What can happen to embryonal carcinoma if you treat with chemotherapy? why?
|
they can differentiate into more mature cells (like a teratoma)
they are pluripotent and use external signals to know when to differentiate |
|
|
what things in the blood may be elevated in embryonal carcinoma? Why? 2
|
AFP- embryos will produce alpha feto protein
b-hCG- it is probably part placenta too (likes to spread hematogenously) |
|
|
what tumor classically secretes AFP? b-hCG?
|
AFP- yolk sac
b-hCG- choriocarcinoma |
|
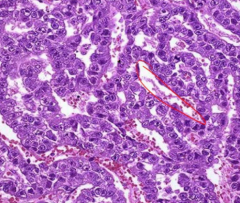
what is this? what is in the red?
|
embronal carcinoma- very purple
red is the glands |
|
|
what does embryonal carcinoma look like grossly?
Why? mnemonic? |
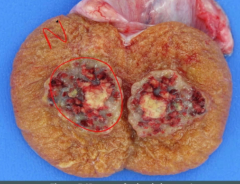
hemorrhagic and necrotic tissue- so agressive that it outgrows blood vessels and breaks them too.
|
|
|
a boy gets a testicular tumor. what is it most likely?
|
yolk sac tumor
|
|
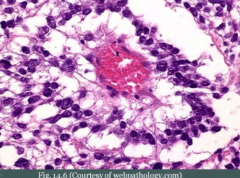
what is this?
what does it look like? |
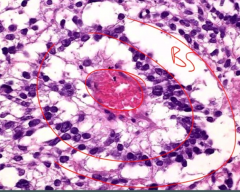
schiller-duval body
looks glomeruloid |
|
|
what two cells are malignant in choriocarcinoma?
which produces b-hCG? |
cytotrophoblasts and synctiotrophoblasts (b-hCG)
|
|
|
what are two other conditions that elevated b-hCG can lead to and why?
|
it is similar in structure to FSH, LH, and TSH
TSH- hyperthyroidism FSH and LH- gynocomastia |
|
|
are there villi in choriocarcinoma?
|
no
|
|
|
what does choriocarcinoma do that is aaginst regular convention of cancer?
|
there is just a tiny lesion in the testes/ovary, but massive amounts everywhere else
usually it is the opposite |
|
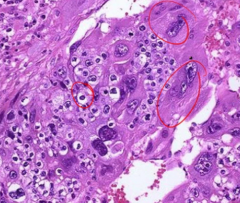
what is this?
|
choriocarcinoma- larger cells are the synctiotrophoblasts
|
|
|
differences 1 and similaities 2 between teratomas in males and females?
|
differences- it is malignant in males
similarities- they are composed of mature fetal tissues and are derivved from 2-3 embryonic layers |
|
|
what things may be raised in the blood with teratomas in males?
|
AFP or b-hCG
|
|
|
do most germ cell tumors fit into nice little boxes of these categories?
|
no, most garm cell tumors are mixed
|
|
|
how do you make a prognosis of a mixed germ cell tumor?
|
you go off of the most malignant tumor type
|
|
|
can seminoas be mixed with non seminomas?
|
yup!
|
|
|
are sex cord tumors usually benign or malignant?
|
benign!
|
|
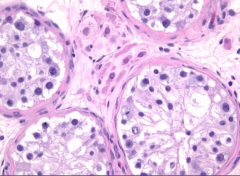
what is this?
|
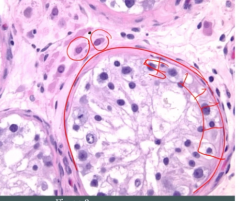
normal testes histology
|
|
|
what is the product of leydig cell tumors?
|
androgens
|
|
|
what is the presentation of leydig cell tumors in children vs adults? why?
|
children- precocious puberyt- too much androgen
adults- gynocomastia - I THINK... adrostenedione --> peripheral conversion to estrogen --> increase sex hormone binding globulin --> decrease testosterone relative to estrogen |
|
|
characteristic histology of some leydig cell tumors?
mnemonic? |
reinke crystals
Reike and crystals are big hoaxes that LIE to people. |
|
|
what happens histologically to the testes in sertoli cell tumors? why?
|
tumors increase in side and number because sertoli cells are the lining of the tubules essentially
|
|
|
usual presentation of sertoli cells? why do you think this is?
|
clinically silent because it is benign and also doesn't produce any hormones
|
|
|
the 15-40 age range is for what kind of testicular tumor?
mnemonic? how do you figure this? |
lance armstrong was in this range- and the most common type is germ cell
|
|
|
what should you think of when you find a testicular mass in a man greater than 60 years old?
|
lymphoma
|
|
|
are germ cell tumors and lymphomas each usually bilateral or iunivlareral? why?
|
lymphoma- bilateral because the lymph is everywhere
germ cell tumor- unilalteral like most primary cancers |
|
|
what kind of lymphoma is it usually in the testicles?
|
B cell
|
|
|
Let's sum it up!
What are the penile pathologies? 5 count thing separately |
1. epispadias
2. hypospadias 3. condyloma accuminatas 4. squamous cell carcinoma 5. Lymphogranuloma Venereum |
|
|
3 precursor lesions to squamous cell carcinoma of the penis?
|
bowen disease
erythroplakia of Querat bowenoid papulosis |
|
|
mnemonic for bowen and querat?
|
White Bowflex, Red Quaran
Imagine a penis with cancer that just watched "sexy crazy cancer" who is now working out on a white bowflex and adpting religion bby dipping it's tip into a red quaran |
|
|
What are the testicular pathologies (non tumor) 5
|
1. orchitis
2. testicular torsion 3. varicocele 4. hydrocele 5. cryptorchidism |
|
|
What are the testicular tumors? divide into 2 types
5 for germ cell 2 for sex cord |
Germ cell
1. seminoma nonseminoma 2. embryonal carcinoma 3. teratoma 4. choriocarcinoma 5. yolk sac tumor Sex Cord 1. Leydig cell tumor 2. Sertoli cell tumor |
|
|
what other testicular mass can be present that isn't a tumor?
|
lymphoma
|

