![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cell |
The smallest living unit and the basic unit of function and structure for all living matter |
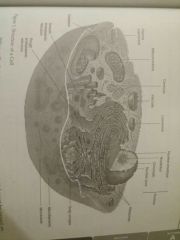
|
|
|
what is the nucleus? |
The part of the cell that contains the genetic information or DNA and controls all protein synthesis and activities of the cell. most adult cells have one nucleus |
The brain of the cell |
|
|
why are RBC shaped like a Frisbee? |
to be able to bend and squeeze through tiny blood vessels and deliver oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. |
|
|
|
what is microvilli? |
a membrane that forms accordion-like folds, the folding of the cell increases surface area so it increases fluid absorption
for example the digestive tract has millions of microvilli to absorb water and end products of digested food. |
|
|
|
Interstitial fluid |
Works as a lubricant for organs, it is a fluid that fills the empty spaces in the body. it contains substances such as amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, hormones, near transmitters, and salt. |
|
|
|
Selective permeable (semipermeable) |
Refers to select a feature of the plasma membrane. It contains pores, some channels but it will only allow particles of the right size and right chemical nature to pass through the cell |
|
|
|
what is the cytoplasm and what does it contain? |
the cytoplasm in the gel in the cell, it is found inside the cell but outside the nucleus it contains the cytosol and organelles |
|
|
|
what are organelles?
|
Also known as little organs, are specialized units in the cell that perform certain functions. |
|
|
|
what is the mitochondria? |
a tiny slipper shape oragnells that does cellular respiration, that is, the conversion of food to energy at the cellular level (ATP) this organelles is also known as the powerhouse |
|
|
|
ATP ( adenosine triphosphate) |
The chemical the cell uses to transfer energy within the cell |
|
|
|
what are ribosomes? |
cytoplasmic organelles involved with protein synthesis in the cells
|
|
|
|
what is endoplasmic reticulum (ER)? |
The endoplasmic reticulum serves as a means for transport within the cell its just made up of many channels (network of membranes) |
|
|
|
what is the golgi apparatus? |
An organelle that puts the finishing touches and packages proteins. |
|
|
|
what are lysosomes? |
An organelle shaped as a sac that contains strong digestive enzymes. These sacks are responsible for digesting cell structures that are no longer living or that are malfunctioning, and for digesting waste. "clean house" |
|
|
|
what are the centrioles? |
are cells that are not capable of cell division
such as: neurons, mature RBCs, skeletal muscle cells, and cardiac muscle cells. |
|
|
|
what is cilia? |
short hairlike projections on the outer surface of the cell membrane. cilia move wavelike motions to move substances of the cell
|
|
|
|
Chromatin |
When a cell is not dividing, DNA is found in the form of loosely structured chromatin |
|
|
|
chromosomes |
cell is dividing, the DNA is seen in condensed rod shaped bodies called chromosomes |
|
|
|
Mitosis |
It is a type of cell division for non reproductive cells, it is when you cells are identical copies of the parent cells. it is achieved by a doubling of the chromosomes prior to division. this type of cell division is very useful in the growth and repair of our bodies |
|
|
|
Zygote |
The cell created by the union of a sperm and egg |
|
|
|
Meiosis |
It is a cell division that occurs for the for the zygote cell, these reproductive cells contain half of the normal number of chromosomes so that the zygote, contains a full set of chromosomes half from each parent |
|
|
|
what do nerve cells resemble? |
they resemble bushes or trees, they can be very long |
|
|
|
what does the nerve cells shape and size enable them to do? |
to conduct electric signals quickly over long distances |
|
|
|
Typical cells |
despite differences, each specialized cell, such as a nerve cell, possesses some or all of the properties of the typical cell |
|
|
|
what are cell membranes? what do they do? |
cell membranes is also called plasma membrane, it encases the cell. cell membranes separate intracellular material from extracellular material |
|
|
|
what is semipermeable? (cell membrane) |
selective permeable which means that it selects the substances allowed to enter or leave the cell. |
|
|
|
what is the cell membrane primarily composed of? |
phospholipids, proteins, and small amounts of carbohydrates. |
|
|
|
what do the protein molecules in the cell membrane do? |
they provide structural support for the membrane act as binding sites for hormones poke holes/pores through the lipid membrane |
|
|
|
what are the two ways that substances move across the semipermeable membrane? (cell membrane) |
they can dissolve in the lipid portion of the membrane (lipid-soluble substances). they can flow through the pores |
|
|
|
what is cytosol? (cytoplasm) |
it is the intracellular fluid of the cell and it is composed of water, electrolytes, proteins, and nutrients. |
|
|
|
what are fixed ribosomes? |
ribosomes attached to the ER, they are concerned with the synthesis of exportable protein. |
|
|
|
what are free ribosomes? |
ribosomes that float freely in the cytoplasm and synthesize proteins that are used within the cell |
|
|
|
what are the two types of ER? |
ROUGH ER: contains ribosomes along its surface; primarily concerned with proteins synthesis which is then transported through the channels and delivered to golgi apparatus. SMOOTH ER: is er that does not contain ribosomes on its surface;it is primarily involved with the synthesis of lipids, steroids, glycerides, and glycogen in the skeletal muscle and liver cells. |
|
|
|
what is phagocytosis? |
a process in which lysosomes participate in the destruction of ingested bacteria. |
|
|
|
what is the cytoskeleton? |
it is composed of threadlike structures called microfilaments and microtubules it helps maintain the shape of the cell and assists the cell with movement |
|
|
|
why is cilia important for the respiratory passages? |
because cilia line the respiratory passages and help move mucus and trapped dust/dirt toward the toward the throat, away from the lungs. they help clear the respiratory passages. |
|
|
|
what is flagella? |
are similar to cilia in the hairlike projections, they act as tails to the cells and enable cell to swim example: sperm cell |
|
|
|
what is passive transport? |
it is a transport mechanism that doesnt require any extra energy in the form of ATP. it allows water and dissolved substances to move without additional ATP passive transport is like a ball going down hill |
|
|
|
what is active transport?
|
it is a transport mechanism that requires an input of energy in the form of ATP. it is like pushing a ball uphill. |
|
|
|
what are the passive transport mechanisms that move substances across the membrane? |
diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and filtration. |
|
|
|
what is diffusion? |
the most common transport mechanism, it is the movement of a substance from one area of higher concentration to one area of lower concentration |
|
|
|
what is facilitated diffusion? |
facilitates means to help it is when a substance is helped across the membrane by a molecule within the membrane. |
|
|
|
what is osmosis ? |
it is a special case of diffusion , where the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane, during osmosis the water diffuses from an area with area with more water to one with less. because water moves toward the more concentrated solution it appears to be pulled in that direction. |
|

