![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
138 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Direct Immunofluorescence is used to detect what?
|
Autoantibodies bound to the patients tissues
|
|
|
Indirect immunofluorescence is used to detect what?
|
antibodies circulating in the patients serum
|
|
|
To maximize diagnosis of dermatologic diseases, what sample should be collected?
|
perilesional tissue
|
|
|
Define "Pemphigus"
|
Group of autoimmune mucocutaneous diseases characterized by intraepithelial blister formation.
|
|
|
In Pemphigus conditions, which ones only involve the oral cavity?
|
Pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus vegetans |
|
|
What is the etiology of PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS?
|
Autoantibodies are directed against components of epithelial desmosomes.
|
|
|
Pemphigus is more common in which peoples?
|
Mediterranean, South Asians, and Jewish heritage
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS?
|
- oral lesions "First to show last to go"
painful, superficial, ragged erosions and ulcerations on the oral mucosa |
|
|
What is a POSITIVE NIKOLSKY SIGN?
|
a characteristic feature of PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS - bulla or vesicle is induced on normal appearing skin if firm lateral pressure is exerted
|
|
|
What is the TREATMENT/DIAGNOSIS modality of PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS?
|
TWO standard biopsies of perilesional tissue. One sent in 10% buffered formalin, the other in Michel's solution.
Treatment with immunosuppresives, usually systemic corticosteroids (prednisone). |
|
|
What are some histopathological features of PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS?
|
intraepithelial clefting
acantholysis |
|
|
What is CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID?
|
group of mucocutaneous chronic diseases in which the autoantibodies are directed against one or more components of the basement membrane. Clinically resembles pemphigus due to blister formation.
|
|
|
What is the most significant aspect of CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID?
|
ocular involvement - can eventually result in blindness
|
|
|
What is BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID?
|
autoimmune condition characterized by production of autoantibodies against basement membrane. Develops in older adults, mostly cutaneous lesions - multiple tense bullae on skin - rupture after several days causing superficial crust and then heals without scarring.
|
|
|
What is LICHEN PLANUS?
|
common chronic dermatologic disease that often affects oral mucosa. Epithelial basal cells are primary target.
Skin lesions are PURPLE, PRURITIC POLYGONAL PAPULES with fine Wickham's striae. |
|
|
ORAL LICHEN PLANUS most commonly occurs on which surfaces?
|
- buccal mucosa
- tongue - gingiva |
|
|
What are the two forms of ORAL LICHEN PLANUS?
|
- Reticular
- erosive |
|
|
Which is the most common type of ORAL LICHEN PLANUS?
|
reticular
|
|
|
Describe the RETICULAR form of LICHEN PLANUS:
|
most common, typically asymptomatic, involves posterior buccal mucosa bilaterally. Interlacing white lines (Wickham's Striae). lesions typically wax and wane over weeks or months.
|
|
|
Describe the EROSIVE form of LICHEN PLANUS:
|
usually symptomatic, atrophic, erythematous areas with central ulcerations of varying degrees and the peripheral of the atrophic areas is bordered by fine white striae. Sometimes ulcerations confined to gingival mucosa (desquamative gingitivis).
|
|
|
What are the immunopathologic features of LICHEN PLANUS?
|
shaggy band of fibrinogen at the basement membrane zone
|
|
|
What are the managements for the two types of LICHEN PLANUS?
|
reticular - no treatment required, annual re-evaluation recommended
erosive - treated with one of the stronger topical steroids. Every 3-6 months checkup |
|
|
What are the conditions that mimic ORAL LICHEN PLANUS?
|
- lichenoid drug reactions
- lichenoid amalgam reaction - oral mucosal cinammon reaction - lichenoid foreign body gingivitis - oral lesions of GVHD - oral lesions of LE - some epithelial dysplasias - chronic ulcerative stomatitis |
|
|
What is CHRONIC ULCERATIVE STOMATITIS?
|
(adult women) Erosions and ulcerations of gingivae, tongue and buccal mucosa. White lichenoid striae are usually present
|
|
|
DIagnosis of CHRONIC ULCERATIVE STOMATITIS is made how?
|
immunopathologic pattern. Direct IF studies show presence of IgG in the basal and parabasal epithelial nuclei.
|
|
|
What is the MOST COMMON OF THE SIGNIFICANT IMMUNE-MEDIATED SYSTEMIC DISEASES?
|
Systemic lupus erythematosus
|
|
|
What is a significant complication of LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS?
|
renal involvement, may lead to kidney failure.
|
|
|
Describe the oral lesions of LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS?
|
non-specific, lichenoid or somewhat granulomatous. Affect palate, buccal mucosa and gingiva. Respond well to topical corticosteroids
|
|
|
What is the treatment of LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS?
|
Decreasing exposure to UV light.
NSAIDs. Systemic corticosteroids for severe cases |
|
|
What is ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME?
|
an acute self limiting ulcerative disorder
|
|
|
What is the etiology of ERYTHEMA MULTIFORM?
|
- 50% unknown
- 25% HSV, mycoplasma pneumoniae - 25% medication related (Abx, analgesics) |
|
|
What are the clinical features of ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME?
|
- male predilection
- hemmorhagic crusting of lips - widespread oral ulcers with ragged margins - "target" lesions of skin |
|
|
What are the three spectrums of ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME?
|
- EM minor (skin or mucosa only)
- EM major [Stevens-Johnson syndrome] - two mucosal sites plus skin involvement - Toxic epidermal necrolysis - diffuse bullous involvement of skin and mucosa |
|
|
What is the treatment of ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME?
|
- mild - supportive care (analgesics, soft diet, hydrations)
- major - corticosteroids , IV pooled human immunoglobulin shows promise |
|
|
What is SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS (scleroderma):
|
rare condition characterized by inappropriate deposition of dense collagen.
|
|
|
What are the two forms of SCLERODERMAN?
|
1) diffuse
2) localized: one area affected looks like coup de sabre (strike of sword) 3) part of CREST syndrome- mild variant |
|
|
What is RAYNAUD's PHENOMENON?
|
vasoconstrictive event triggered by emotional distress or exposure to cold.
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of SCLERODERMA?
|
Raynaud's phenomenon, claw-like deformity of fingers, acro-osteolysis, resorption of the terminal phalanges, ulceration of fingertips.
Mouse faces. |
|
|
What is CREST SYNDROME?
|
mild variant of systemic sclerosis
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of CREST?
|
- Calcinosis cutis
- Raynaud's phenom - Esophageal dysfunction - sclerodactyly - telangiectasia |
|
|
What is the treatment of CREST SYNDROME?
|
symptomatic care, similar to systemic sclerosis
|
|
|
What is the treatmetn of SCLERODERMA?
|
supportive care: esophageal dilation, calcium channel blockers for Raynaud's, ACE inhibitors to control hypertension, problems with oral hygeine/prostheses. PROGNOSIS IS POOR. Most patients die of pulmonary involvement.
|
|
|
What is ERYTHEMA MIGRANS?
|
geographic tongue, common benign condition
|
|
|
What is the etiology of ERYTHEMA MIGRANS?
|
hypersensitivity to an environmental factor
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of ERYTHEMA MIGRANS?
|
anterior two thirds of tongue
- lesions are multiple, well-demarcated zones of erythema (due to atrophy of filiform papillae) concentrated on tip and lateral borders of the tongue and are surrounded by yellowish white serpentine border. |
|
|
What is STOMATITIS AREATA MIGRANS?
|
when geographic tongue type lesions occur in sites such as buccal mucosa, labial mucosa, and soft palate
|
|
|
What is the treatment for ERYTHEMA MIGRANS?
|
no treatment necessary
|
|
|
What is ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA?
|
group of inherited disorders in which two or more ectodermally derived structures are altered: hair, skin, nails, teeth, or sweat glands
|
|
|
What is HYPOHIDROTIC ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA?
|
one of the best known forms of Ectodermal dysplasia. Heat intolerance due to reduced sweat glands. fine sparse blonde hair. periocular hyperpigmentation and wrinkling. nails appear dystrophic and brittle. oligodontia, with conical teeth. xerostomia: varying degrees.
|
|
|
What is WHITE SPONGE NEVUS?
|
Rare genodermatosis (a genetically determined skin disorder) that is inherited as autosomal dominant trait displaying high degree of penetrance and variable expressivitiy. Condition is due to a defect in normal keratinization of the mucosa.
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of WHITE SPONGE NEVUS?
|
symmetric, thickened, white, corrugated, velvety diffuse plaques that primarily affect the buccal mucosa bilaterally. Patients usually asymptomatic
|
|
|
What is the treatment of WHITE SPONGE NEVUS?
|
- no treatment, good prognosis
|
|
|
What is HEREDITARY BENIGN INTRAEPITHELIAL DYSKERATOSIS?
|
rare autosomal dominant genodermatosis primarily affecting descendants of a triracial isolate (native american, african american, and white) of people who originally lived in North Carolina
|
|
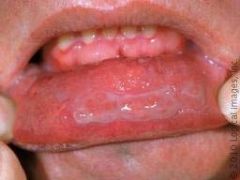
Identify the lesion:
|
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
|
|
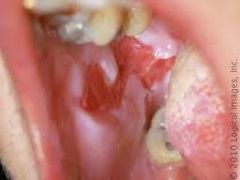
Describe this lesion and identify:
What is your management? |
Description: Superficial, ragged erosions and ulcerations distributed haphazardly on the oral mucosa.
DX: PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS MGMT: Diagnosis should be made as early as possible with DF. Treatment consists of SYSTEMIC CORTICOSTEROIDS (usually prednisone), often in combination with other immunosuppressive drugs. |
|
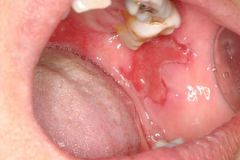
Identify the lesion:
|
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
|
|
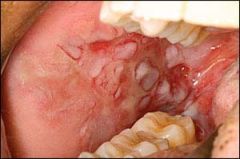
Identify the lesion:
|
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
|
|
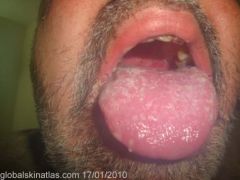
Identify the lesion:
|
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
|
|
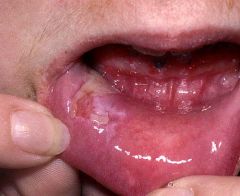
Identify the lesion:
|
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
|
|
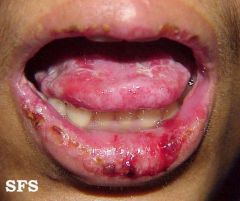
Identify the lesion:
|
CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID
|
|
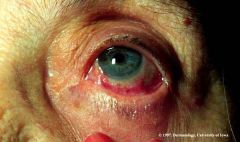
Identify the lesion:
|
Symblepharon associated with CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID
|
|
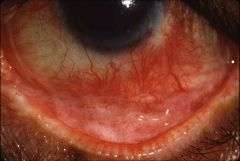
Identify the lesion:
|
Symblepharon associated with CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID
|
|
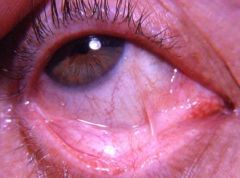
Identify the lesion:
|
CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID
|
|
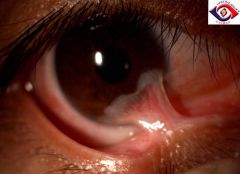
Identify the lesion:
|
Symblepharon associated with CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID
|
|
Identify the lesion:
|
Symblepharon associated with CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID
|
|
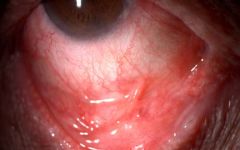
Identify the lesion:
|
Symblepharon associated with CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID
|
|
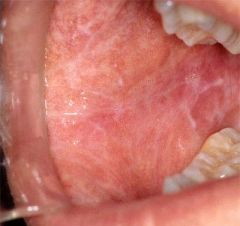
Identify the lesion:
|
LICHEN PLANUS
|
|
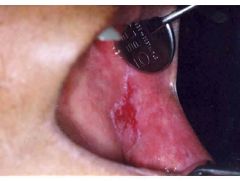
Identify the lesion:
|
LICHEN PLANUS
|
|
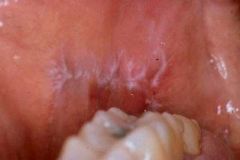
Identify the lesion:
|
LICHEN PLANUS
|
|
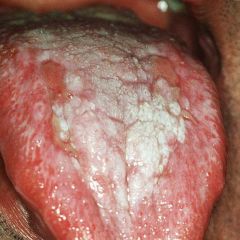
Identify the lesion:
|
LICHEN PLANUS
|
|
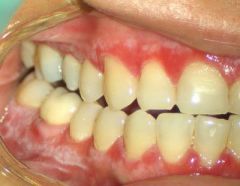
Identify the lesion:
|
LICHEN PLANUS
|
|
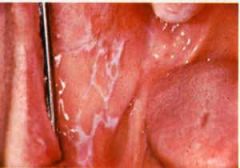
Identify the lesion:
|
LICHEN PLANUS
|
|
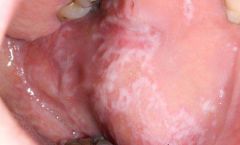
Identify the lesion:
|
LICHEN PLANUS
|
|
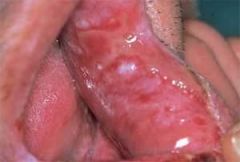
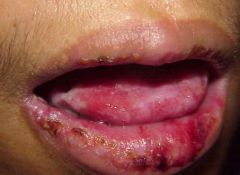
Identify the lesion:
|
CHRONIC ULCERATIVE STOMATITIS
|
|
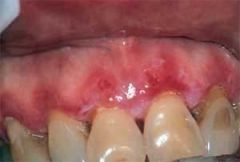
Identify the lesion:
|
CHRONIC ULCERATIVE STOMATITIS
|
|
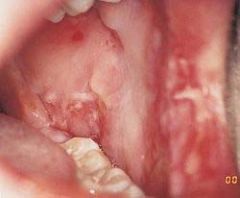
Identify the lesion:
|
CHRONIC ULCERATIVE STOMATITIS
|
|
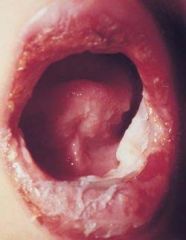
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
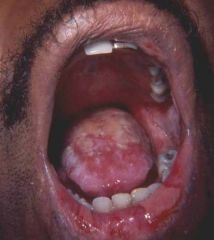
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
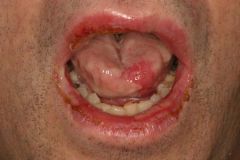
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
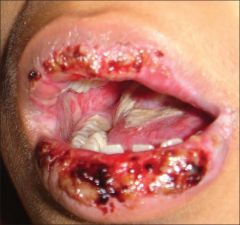
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
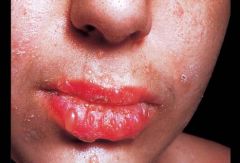
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
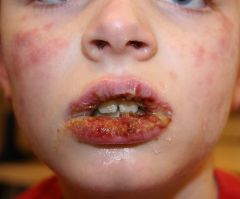
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
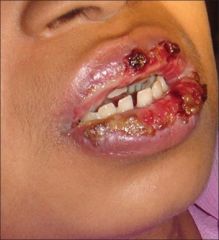
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
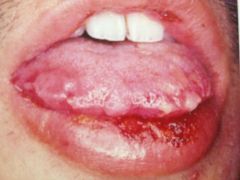
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
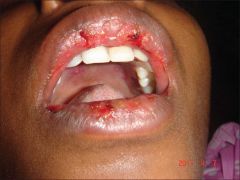
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
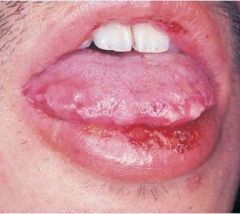
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
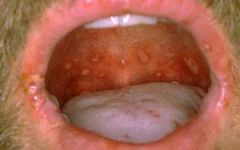
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MIGRANS
|
|
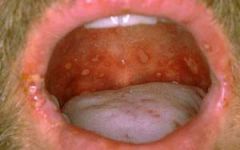
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MIGRANS
|
|
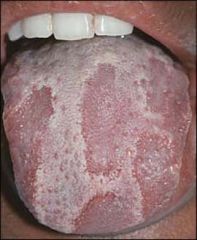
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MIGRANS
|
|
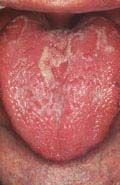
Identify the lesion:
|
ERYTHEMA MIGRANS
|
|
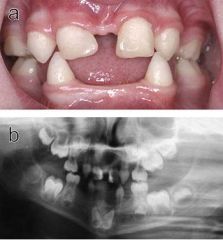
Identify the lesion:
|
ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA
|
|
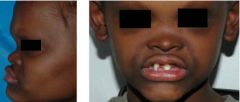
Identify the lesion:
|
ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA
|
|
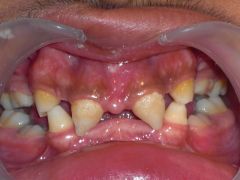
Identify the lesion:
|
ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA
|
|
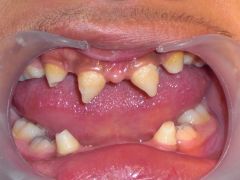
Identify the lesion:
|
ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA
|
|
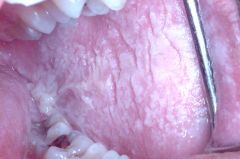
Identify the lesion:
|
WHITE SPONGE NEVUS
|
|
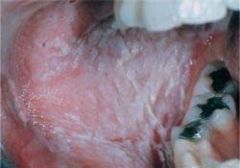
Identify the lesion:
|
WHITE SPONGE NEVUS
|
|
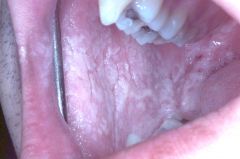
Identify the lesion:
|
WHITE SPONGE NEVUS
|
|
|
Which condition has "target" lesions on the skin?
|
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
|
Define SYMBLEPHARON:
|
- scarring of the conjunctiva of the eye produces adhesions
|
|
|
CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID shows what kind of histologic finding?
|
SUBEPITHELIAL cleft
|
|
|
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS shows what kind of histologic finding?
|
INTRAEPITHELIAL cleft
|
|
|
Biopsy sample for lesions suspected to be PEMPHIGOID should be submitted in which solution?
|
Michel's
|
|
|
What is the TREATMENT of CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID?
|
- topical steroids for oral lesions
- better oral hygeine measures - should be referred to an OPHTHALMOLOGIST |
|
|
What is the difference in management of BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID and CICATRICIAL?
|
- Bullous pemphigoid resolves spontaneously in 1-2 years
|
|
|
What is hte most common of the significant auto-immune mediated systemic disease?
|
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
|
|
|
What is the most significant component of LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS?
|
Renal involvement may lead to kidney failure
|
|
|
What are some clinical features of LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS?
|
- fever
- weight loss - arthritis - MALAR BUTTERFLY RASH - skin lesions flare with sun exposure - oral lesions |
|
|
What is treatment of CUTANEOUS LUPUS?
|
- avoid excess UV exposure
- topical corticosteroids - better prognosis that SLE |
|
|
Define EHLER'S DANLOS SYNDROME:
|
- group of inherited connective tissue disorders characterized by abnormal COLLAGEN synthesis
|
|
|
Which condition has PAPYRACEOUS SCARRING?
|
- Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
|
|
|
Defects in which type of Collagen is associated with Ehler's Danlos?
|
TYPE III (3)
|
|
|
What are the oral findings of EHLERS DANLOS?
|
- Gorlin sign: touch tip of nose with tip of tongue
- easy bruising and bleeding during minor manipulation - recurrent subluxation of TMJ - increased periodontal disease at early age - dental abnormalities |
|
|
GORLIN SIGN is present in which condition?
|
EHLERS DANLOS
|
|
|
Define GORLIN SIGN:
|
touch the tip of the nose with the tip of the tongue
|
|
|
How can a diagnosis of HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIECTASIA be diagnosed?
|
THREE OF FOUR:
1) recurrent spontaneous epistaxis 2) telangiectasias of skin and mucosa 3) arteriovenous malformation involving lungs, liver or CNS 4) family history |
|
|
What is a common systemic blood related finding with HHT?
|
Chronic iron-deficiency anemia
|
|
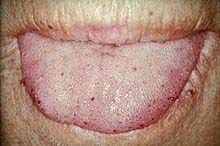
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIECTASIA
|
|
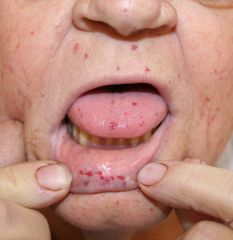
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIECTASIA
|
|
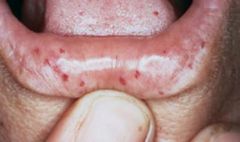
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIECTASIA
|
|
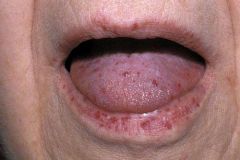
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIECTASIA
|
|
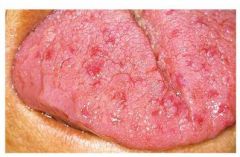
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIECTASIA
|
|
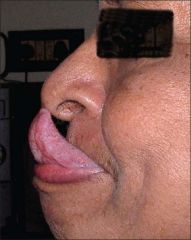
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
GORLIN SIGN
|
|
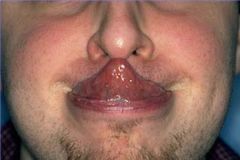
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
GORLIN SIGN
|
|
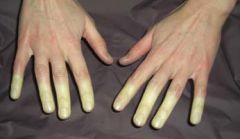
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
RAYNAUDS PHENOMENON
|
|
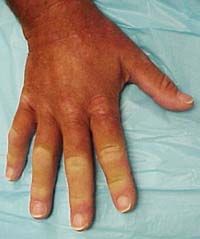
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
RAYNAUDS PHENOMENON
|
|
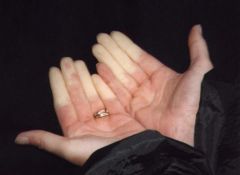
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
RAYNAUDS PHENOMENON
|
|
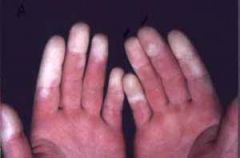
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
RAYNAUDS PHENOMENON
|
|
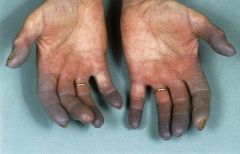
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
RAYNAUDS PHENOMENON
|
|
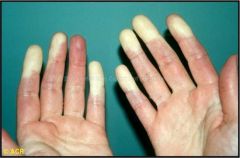
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
RAYNAUDS PHENOMENON
|
|
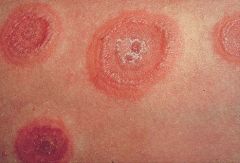
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
TARGET LESIONS of ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
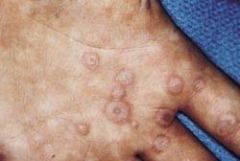
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
TARGET LESIONS of ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
|
|
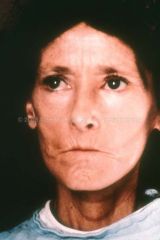
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
"Mouse Faces" of SCLERODERMA
|
|
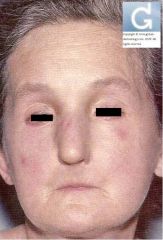
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
"Mouse Faces" of SCLERODERMA
|
|
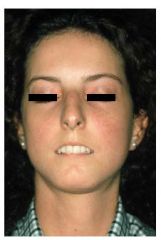
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
"Mouse Faces" of SCLERODERMA
|
|
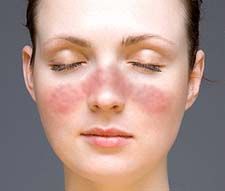
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
MALAR RASH of LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
|
|
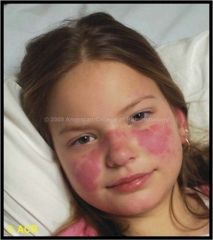
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
MALAR RASH of LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
|
|
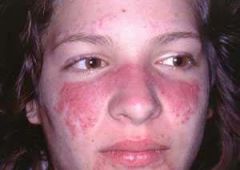
Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
MALAR RASH of LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
|
|

Identify the dermatologic condition:
|
MALAR RASH of LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
|

