![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what does the strength of the bases ammonia and amines depend on? |
the strength depends on the availability of the lone of of electrons from the nitrogen to bond with H+ |
|
|
explain why the strength of bases is in such a order ethylamine> ammonia > phenylamine |
ethylamine has an alkyl group which is electron donating so the lone pair of electrons in N atom is more available to bond with H+, phenylamine has the lone pair of electrons from N atom delocalised into the benzene ring due to voerlap p orbital, less available to form coordinate dative bond with H+ |
|
|
3 ways to make an amines? |
1) nucleophilic substitution of a halogenoalkane and ammonia(use excess hot ethanolic ammonia) 2)KCN in ethanol refluxed with halogenoalkane, then nitrile is reduced by hydrogen gas, with nickel catalyst or LiAlH4 in dry ether 3)use LiAlh4 to reduce amides to amines |
|
|
how do you prepare phenylamine? |
reduce nitrobenzene by heating with Sn & conc HCl, releasing h20 as byproduct |
|
|
name the diazonium ion in it's chemical formula |
C6H5N2 + |
|
|
what is the name of the precipitate formed from reaction of phenylamines and bromine(aq) , what is the colour? |
2,4,6- tribromophenylamine, white ppt |
|
|
what is the temp condition for reaction of phenylamine and aq bromine and how is the condition kept and why is it needed? |
temp must be at below 10 degrees using ice because diazonium salt is unstable n can decompose to give N2 gas |
|
|
for diazotisation, give the chemical equation for producing nitrous acid in the same test tube as phenylamine. |
NaNO2 + HCl --> HNO2 + NaCl |
|
|
what is the first step in synthesis of dyes? |
production of benzenediazonium chloride is first, phenylamine + nitrous acid + HCl---> benzenediazonium chloride + 2 H2O |
|
|
what is the second step for formation of dyes? |
reaction of diazonium salt with alkaline solution of phenol in coupling reaction. the diazonium ion substitutes into position 4 of the phenol |
|
|
why are dyes stable? |
the delocalised pi bonding system extends between the two benzene rings through the NN group |
|
|
how do you make an amide? |
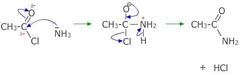
reacting the acyl chloride with conc NH3 solution or ethylamine to give a substituted amide |
|
|
what is produced in acid and alkali hydrolysis of amides? |
RCOOH + RNH2 or RNH3+Cl- in excess HCL
RCOO-Na+ + RNH2 in alkali |
|
|
what is electrophoresis used for? |
to separate , identify and purify proteins |
|
|
why can't the lone pair of electrons from the nitrogen in the amide donate to an electron deficient species such as H+? |
there is an electron withdrawing oxygen and the lone pair of electrons are drawn towards it making it unavailable |
|
|
what is electrophoresis? |
it is a separation technique based on mobility of ions in an electric field positive ions move to negative electrode and vice versa ions have different migration rate depending on charge |
|
|
amine groups react with excess acid to produce what? |
ammonium salts |
|
|
what happens when you react CH3NH2 + HCl? |
CH3NH2 + HCl--> CH3NH3+Cl- |
|
|
difference in condition of reacting a benzene group with NO2+ and phenol with NO2+? |
di HNO3 in room temp for phenol and NO2+ but for benzene, you need conc HNO3 and 55 degrees |

