![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Quant instrument maintenance schedule
|
-Monthly:
1. Background Calibration 2. ROI Inspector 3. Check PC & Defragment -Quarterly: 4. Hardware Test 5. Lamp -Semi-annualy: 6. ROI Calibration 7. Pure Spectral Assay |
|
|
What are the phases of amp process in Quant?
|
1. Exponential/Geometric amp
2. Linear amp 3. Plateau region |
|
|
What does IPC stand for?
|
internal PCR control
|
|
|
Describe the plateau phase of quant
|
-signifies depletion of critical reagents and is know as the plateau
-amp process ceases |
|
|
Describe the exponential phase of quant |
-theoretical doubling of amplicons with each cycle -baseline determined by measuring background fluorescence signal (noise) -baseline establishes threshold |
|
|
Explain cycle threshold |
-the point in which the level of fluorescence exceeds the threshold -Ct is lower for a sample with higher initial concentration (higher Ct for a sample with lower concentration DNA) |
|
|
What is the size of the human telemorase reverse transcriptase target gene? |
62 bases |
|
|
How is baseline determined? What does it establish? |
-baseline determined by measuring background fluorescence signal (noise) - baseline establishes threshold |
|
|
What is the purpose of DNA quantitation? |
-To estimate the amount of HUMAN DNA present in the sample -helps determine the target amount of DNA needed to get a good profile -PCR assays work best in a fairly narrow range of DNA -target is 1.0 ng of DNA -too little= may fail to amp/dropout -too much= off scale peaks/blowout |
|
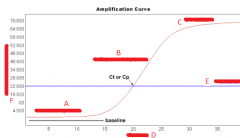
|
A. Exponential product growth B. Linear product growth C. Plateau phase D. Cycle number E. Threshold F. Normalized fluorescence |
|
|
Describe the linear phase of quant |
-the consumption of 1 or more PCR reagents during amp will impede the efficiency causing the onset of linear phase -product amp slows down, yielding an inconsistent ratio of input DNA to product -not commonly used in data analysis |
|
|
Purpose of minor groove binder? |
-linked to 3' end of probe -forms extremely stable duplexes with ssDNA targets, allowing shorter probes to be used -increase melting temperature without increasing probe length -increase sensitivity because it's more specific for single base mismatches and fluorescence quenching more efficiently |
|
|
What is Rn? What is ΔRn? |
Rn: normalized reporter is the the ratio of the fluorescence emission intensity of the reporter dye to the fluorescence emission intensity of the passive reference dye Δ Rn: normalization of Rn obtained by subtracting the baseline: Δ Rn= Rn - baseline |
|
|
What is the y-intercept in quant data? |
-theoretical value for nucleic acid concentration -indicates the expected Ct value for a sample with quantity= 1 ng/uL |
|
|
A. How many pg of DNA are in 1 haploid cell? 1 diploid cell? B. How many cells are in 1 ng of DNA in a haploid/diploid cell? C. How many copies in a diploid single-copy locus with concentration of 23 pg? haploid single copy locus? |
A. 3 pg (haploid), 6 pg (diploid) B. 333 cells/333 copies (haploid) 167 cells/333 copies (diploid) C. 3-4 copies (haploid), 7-8 copies (diploid) |
|
|
What is the amplification plot for quant? |
-plot of the fluorescence signal v. cycle number -reactions are characterized by the point in time during cycling when amplification of PCR product is first detected -the higher the starting copy number of the nucleic acid target, the sooner a significant increase fluorescence is observed |
|
|
A. true negative B. invalid result C. disregard IPC result D. partial PCR inhibition |
A. quant: no amp & IPC: amp B. quant: no amp & IPC: no amp C. quant: amp (low Ct, high ΔRn) & IPC: no amp D. quant: amp (high Ct, low ΔRn) & IPC: no amp |
|
|
Purpose of the IPC |
-troubleshoot -detects inhibitors, contamination, true negative samples, or failure of run -should give amp product even if no sample DNA is present |
|
|
5' Nuclease Assay Process: How does probe work? How is fluorescence detected? |
-FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer) -multicopy sequence specific probe (TaqMan): binds to targeted template -probe has 2 dyes: reporter (5' end) and quencher (3' end) -close proximity of 2 dyes allows energy transfer to occur between the two; quencher suppresses fluorescence of reporter -probe hybridizes to complementary target: is then cleaved by 5' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase -cleavage separates reporter dye from NFQ: increases reporter dye fluorescence at each PCR cycle: amount of fluorescence measured at each cycle |
|
|
It is recommended that samples exhibiting a RT-PCR quant greater than --A-- should be diluted and requanted as the RT-PCR data may have exceeded the --B-- of the standard curve. |
A. 100 ng/uL B. linear range |
|
|
Describe denaturation, annealing, and extension for quant reaction. How many cycles? |
1. denaturation: 94-95 C, dsDNA becomes ssDNA 2. annealing: temp is decreased, primers and probes anneal to template DNA, no fluorescence detected, NFQ is absorbing reporter dye energy according to FRET 3. extension: temp is increased, Taq extends forward primer by adding complementary dNTPs, Taq cleaves probe, reporter dye fluoresces |
|
|
Full name of quant probe |
Taqman Minor Groove Binding Probe |
|
|
Components of IPC assay |
-IPC template DNA (synthetic sequence, not found in nature) - One Taqman MGB probe labeled with VIC dye for detecting amped IPC DNA: linked to 5' end of probe -NFQ on 3' end of probe -MGB on 3' end of probe |
|
|
What is Ct? What is the equation for Ct? |
-cycle threshold: intercept at which the amp signal exceeds the background signal and crosses the threshold Ct= m [log(Qty)] + b (where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept) |
|
|
What is the correlation coefficient? |
-R^2 -relationship between the standard concentrations and concentrations calculated based on the standard curve -closeness of fit between the standard curve regression line and individual Ct data points of the standards * should NOT be lower than 0.98 |
|
|
Is the probe used for quant single copy or multicopy sequence? |
multicopy sequence specific |
|
|
What are the 3 human specific target loci in quant trio? |
1. Small Autosomal: primary quant target: 75 to 80 bases in length: helps determine sample concentration 2. Large Autosomal: greater than 200 bases in length: aids in determining sample degradation 3. Y-chromosome: 75 to 80 bases in length: helps determine male sample concentration |
|
|
Does quant trio use multi-copy or single-copy target loci? |
-multi-copy -each target loci consist of multicopies dispersed on various chromosomes |
|
|
What are the four QT 5' nuclease assays? |
-two separate target-specific human assays 1. one with a short PCR amplicon 2. one with a long PCR amplicon -target specific human male DNA assay -internal PCR control (IPC) assay |
|
|
Explain small autosomal human target in QT |
-amplicon length= 80 bases -ploidy= diploid -copy number= multicopy -dye= VIC dye -quencher= MGB quencher |
|
|
Explain large autosomal human target in QT |
-amplicon length= 214 bases -ploidy= diploid -copy number= multicopy -dye= ABY dye -quencher= QSY quencher |
|
|
Explain the male human target in QT |
-amplicon length=75 bases -ploidy= haploid -copy number= multicopy -dye= FAM dye -quencher= MGB quencher |
|
|
Explain the internal PCR control in QT |
-amplicon length= 130 bases -ploidy= n/a -copy number= synthetic IPC template is included in the primer mix -dye= JUN dye -quencher= QSY quencher |
|
|
With QT how do you indicate DNA degradation? |
-by comparing the ratio of the large autosomal target with the ratio of small autosomal target quantification |
|
|
What are the IPC components in QT? |
1. IPC template DNA (sequence no found in nature) 2. Primers for amplifying the 130 base IPC template DNA 3. TaqMan probe dye-quencher (JUN dye with QSY quencher) |
|
|
Explain 5' Nuclease Assay process in QT. |
-takes place in every cycle of PCR amplification and doesn't interfer with exponential accumulation of product -4 steps: 1. polymerization 2. strand displacement 3. cleavage 4. completion of polymerization |
|
|
What happens to the 5' Nuclease Assay in polymerization? |
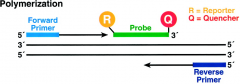
-Taqman probe anneals specifically to a complementary sequence between the forward and reverse primer sites -because the reporter dye and quencher are close in proximity, there is suppression of reporter fluorescence (due to energy transfer) |
|
|
What happens to the 5' Nuclease Assay in strand displacement? |
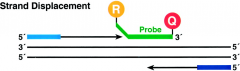
-TaqMan probe is displaced by DNA polymerase adding complementary sequence |
|
|
What happens to the 5' Nuclease Assay in cleavage? |
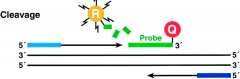
-Taq DNA polymerase enzyme cleaves probes that are hybridized to the target -cleavage separates reporter dye from quencher -results in increase in fluorescence by reporter -increase in fluorescence signal only occurs if the target sequence is complementary to probe and is amplified (so non-specific amplification isn't detected) |
|
|
What happens to the 5' Nuclease Assay in the completion of polymerization? |
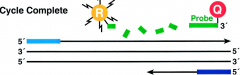
-polymerization of strand continues, but because the 3' end of the probe is blocked, there is no extension of the probe during PCR |
|
|
Explain steps which occur on the 7500 RT-PCR system for fluorescence detection |
1. a tungsten-halogen lamp directs light to each well on the reaction plate: the light excites the fluorescent dyes in each well on the plate 2. the CCD camera detects the fluorescence emission 3. the 7500 system obtains the fluorescence emission data from the CCD camera, and uses the data obtained form the pure-dye calibration to distinguish the individual contribution of each dye in the collective fluorescence as gathered by the instrument during a run, and applies data analysis algorithms |
|
|
How to make the 5 standards in QT? |
STD 1: 50.000 ng/uL: 10 uL (of 100 ng/uL stock) + 10 uL TE: dilution factor of 2X STD 2: 5.000 ng/uL: 10 uL STD 1 +90 uL TE: dilution factor of 10X STD 3: 0.500 ng/uL: 10 uL STD 2 + 90 uL TE: dilution factor of 10X STD 4: 0.050 ng/uL: 10 uL STD 3 + 90 uL TE: dilution factor of 10X STD 5: 0.005 ng/uL: 10 uL STD 4 + 90 uL TE: dilution factor of 10X **made with QuantTrio THP DNA Standard |
|
|
The STD curve for the QT kit is linear between what concentrations? |
5 pg/uL to 100 ng/uL *be cautious with anything less or greater |
|
|
Explain the R^2 value |
-measure of the closeness of fit between the STD curve regression line and the individual Ct data points of quant STD reactions -value of 1.00 is a perfect fit -R^2 value greater than or equal to 0.99 indicates a close fit between the regression line and Ct points |
|
|
What does the slope indicate in the regression line in quant? |
-indicates the PCR amplification efficiency for the assay -slope of -3.3 indicates 100% amplification efficiency |
|
|
The appropriate slope ranges for each target in QT? |
-small autosomal: -3.0 to -3.6 -large autosomal: -3.1 to -3.7 -Y target: -3.0 to -3.6 - if slopes fall outside range, interpret with caution |
|
|
What does the y-intercept indicate in quant regression line? |
-indicates the EXPECTED Ct value for a sample with a quantity of 1 ng/uL |
|
|
The IPC helps distinguish between a true negative and reaction affected by what? |
-presence of PCR inhibitors -assay setup -a chemistry or instrument failure |
|
|
For positive amp, what Ct value will it be? |
-Ct value for the target will be below 40 |
|
|
What can increase the IPC Ct value? |
-presence of PCR inhibitors -and/or concentrations of DNA |
|
|
What could cause complete amp failure? |
-incorrect thermal cycling -incorrect formulation of PCR reaction mix -severe PCR inhibition |
|
|
What indicates suppressed amplification? |
High Ct value and Low ΔRn value |
|
|
How sensitive is Quant Trio? |
-can reproducibly quantify 5 pg/uL of human genomic DNA -when 2 uL of a sample is loaded with 5 pg/uL of DNA, the well contains about 1.5 diploid human genome |
|
|
When do we start seeing stochastic effects? |
concentrations below 5 pg/uL |
|
|
What options do you have if quant indicates there is insufficient DNA? |
1. re-extract the sample and re-quant 2. concentrate the sample and re-quant |
|
|
How is the degradation index calculated? |
(small autosomal DNA concentration)/(Large autosomal DNA concentration) |
|
|
What affects the degradation index? |
-degree of degradation of the large autosomal target DNA -presence of PCR inhibitors (especially PCR inhibitors that negatively affect the LA target more so than the SA target) |

