![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
126 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many Kingdoms are there? |
Five |
|
|
Living organisms are classified according to...? |
Shared characteristics |
|
|
Features of Protista |
Single-celled, have a nucleus, some have chloroplasts, no cell wall,organelles present. |
|
|
Feeding method of protista |
Photosynthesis or ingestion of other organisms or both. |
|
|
Movement of protista |
Move using flagella or cilia |
|
|
Features of Monera |
Single-celled, no nucleus, no chloroplasts, have a cell wall. |
|
|
Feeding method of Monera |
Absorb nutrients through the cell wall, or make their own. |
|
|
Movement of Monera |
May or may not move |
|
|
Features of Fungi |
Multicellular,have a nucleus, no chloroplasts, have a cell wall |
|
|
Feeding method of Fungi |
Acquire nutrients from material that decays. |
|
|
Movement of fungi |
No mechanism for movement |
|
|
Features of plants |
Multicellular, have a nucleus, chloroplasts and cell walls. |
|
|
Feeding Method for plants |
Need sunlight to make food by photosynthesis |
|
|
Movement of plants |
Most don't move |
|
|
Features of animal |
Multicellular, have a nucleus, no chloroplasts, no cell walls |
|
|
Feeding methods for animals |
Need nutrients by ingestion |
|
|
Movement of animals |
Using cilia, flagella or muscles |
|
|
Problems with classifying organisms |
Some can reproduce to hybrids, so they are not new species. Evolution. Asexual reproducing organisms. |
|
|
What do evolutionary trees display? |
Relationships between organisms in the kingdom |
|
|
What does Monera represent? |
Earliest group of organisms |
|
|
5 kingdoms are divided into..? |
Phyla |
|
|
Each phylum is divided into..? |
Classes |
|
|
Each class is divided into..? |
Orders |
|
|
Order divided into...? |
Families |
|
|
Each family into...? |
Genera/ genus |
|
|
Each genus into...? |
Species |
|
|
Example of a binomial name. |
Home sapiens |
|
|
Species who vary in habit may have... |
Evolved |
|
|
What is it called when a species gains a characteristic from an ancestor? |
Inherited |
|
|
Organisms with similar characteristics can be evolved from..? |
Adapting to environment |
|
|
What is artificial classification? |
Observed characteristics designed for a purpose |
|
|
What is natural classification? |
Use of natural relationships between organisms. E.g internal and external features. |
|
|
Organisms that are closely related have what...? |
A high degree of DNA sequencing |
|
|
List 4 invertebrates in the group arthropods? |
Crustacean Insect Arachnids Myriapod |
|
|
What do arthropods all have In common |
Limbs with joints and exoskeleton |
|
|
Features of crustacean |
10 or more legs, antennae |
|
|
Examples of crustacean |
Crabs, lobsters |
|
|
Features of insects |
6 legs, antennae |
|
|
Example of insects |
Dragonflies |
|
|
Features of Arachnids |
8 legs. No antennae |
|
|
Examples of Arachnids |
Spiders, mites, scorpions |
|
|
Features of Myriapods |
8-750 legs. Antennae |
|
|
Examples of Myriapods |
Centipedes, millipedes |
|
|
What do food chains show? |
Transfer of energy from one organism to another |
|
|
Green plants absorb sunlight to make..? |
Glucose |
|
|
Why are green plants producers? |
Because they produce biomass during photosynthesis |
|
|
What are consumers? |
Organisms which feed of other organisms |
|
|
What is the trophic level? |
Position or stage that organism occupies in food chain, what it eats and what eats it |
|
|
What is lost at every trophic level? |
Biomass and energy |
|
|
What is lost from organisms faeces? |
Material and energy during egestion |
|
|
Energy is lost through...? |
Movement and respiration |
|
|
The length of foodchain depends on..? |
Efficiency of energy transfer |
|
|
If you know how much energy is stored in the living organism then use the calculation for efficieny... |
Energy efficiency= energy converted to biomass/ total energy taken in X 100 |
|
|
Another form of food chain |
Food Web |
|
|
What is a pyramid of numbers for? |
To show the quantity of organisms at each stage in food chain |
|
|
What are th problems with pyramids of numbers? |
Some organisms may belong to more than one trophic level. Measuring biomass is tricky to dry out and weigh of large organisms. |
|
|
What do pyramid of biomass do? |
Show dry mass of living material at each stage in chain. |
|
|
Where does a lot of biomass remain? |
In the ground as the root system |
|
|
Name 2 recycled elements |
Carbon and nitrogen |
|
|
Why does it take longer to recycle nutrients in a waterlogged or acidic soils? |
They lack oxygen for decomposes and acidic soil is not the best pH for decomposes. |
|
|
A constant recycle of carbon is called? |
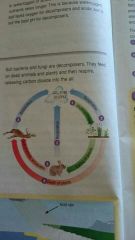
Carbon cycle |
|
|
Where else is carbon recycled except in animals? |
The sea |
|
|
How much nitrogen is the air made up of? |
78% |
|
|
What is nitrogen used in the production of? |
Proteins |
|
|
Why can't animals and plants use nitrogen? |
It's unreactive |
|
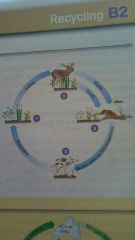
List the process of nitrogen cycle |
Plants absorb nitrates from soil to make protein for growth. Animals eat plants, using the nitrogen to make animal protein,feeding passes this on. Dead animals and plants broken down by decomposes releasing nitrates back into soil. |
|
|
What is the job of nitrogen-fixing bacteria? |
Converts atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates in the soil |
|
|
The job of nitrification bacteria |
Converts ammonium compounds into nitrates in the soil. |
|
|
Denitrifying bacteria does? |

Converts nitrates and ammonium compounds into atmospheric nitrogen |
|
|
The size or distribution of a population can be affected by? |
How well organisms compete for limited resources |
|
|
What do animals and plants compete for? |
Animals- food, water,shelter, mates. Plants- light,water and minerals |
|
|
Which competitor will get the most resources? |
Better adapted |
|
|
What determines the distribution and Abundance? |
Interdependence |
|
|
List the 2 types of competition |
Interspecific- individuals of different species compete for same resources in ecosystem. Intraspecific - individuals from same species are competing for same resources. |
|
|
What do similar organisms compete to occupy? |
Ecological niche |
|
|
What is it called when population of a species decreases? |
Endangered |
|
|
What are predators? |
Animals that kill and eat other animals |
|
|
What is a prey? |
Animals that are eaten |
|
|
Cyclical fluctuations are? |
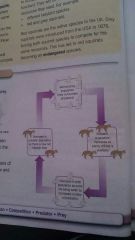
The varying numbers of each species |
|
|
What are organisms that live off other organisms? |
Parasites |
|
|
A host is? |
The organism parasites live off |
|
|
What is a mutualistic relationship? |

When two organisms form a relationship from which both organisms benefit. |
|
|
What are adaptations? |
Special features or behaviours that make organism particularly suited to environment. |
|
|
List adaptations to cold environments |
Being well insulated to reduce heat loss. Having a small surface area to volume ratio to prevent heat loss. Behavioural adaptations to help animals to survive cold temperatures |
|
|
Describe counter-current heat exchange systems using penguins |
Penguins have heat exchange blood flow to colder regions. Warm blood enter feet and flippers flows past cold blood leaving feet and flippers and warms it up. The walmed up blood Re-enter the rest of the body and doesn't affect core temperature of body. |
|
|
Hot and dry environment adaptations |
Behavioural methods- finding shade, going out at night, shedding fur, panting, taking a swim. |
|
|
How do cacti cope In hot conditions? |
Long roots to reach water. Thick waxy cuticle to reduce water loss. Spines to reduce water loss and protect water stored in spongy layer from predators. |
|
|
How do camels adapt to dry environments? |
Body fat stored In hump, little insulation under skin. Drinks many litres of water in one go and stores in blood. Tolerates body temperature changes. Hair-lined nostrils traps moisture in its breath before exhaled and moisture returned. |
|
|
What are extremophiles? |
Organisms Biochemically adapted to extreme conditions |
|
|
What is a specialist? |
Organism suited to certain habitats. |
|
|
What is a generalist? |
Can live in a range of habitats but can be out competed by other organisms. |
|
|
List Predator adaptations |
Built for speed Camouflaged to avoid being spotted Sharp teeth Binocular vision Hunting strategy Fewer offspring |
|
|
List prey adaptations |
Built for speed Camouflaged Live In groups Monocular vision Breeding strategies Mimicry |
|
|
Charles Darwins theory |
Animals and plants that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive. This theory is called natural selection |
|
|
What is evolution? |
Slow continual change of organisms to become better adapted to their environment. These arise through mutations |
|
|
Adaptations are controlled by? |
Genes and can be passed on to future generations. |
|
|
Peppered moths example |
Pale peppered moths are easily Camouflaged amongst the lichens on silver birch tree bark. But dark moths are in areas of high pollution so the silver birch tree is discoloured by soot. |
|
|
Describe Lamarks theory |
Evolution happened by inheritance of acquired characteristics. This was rejected due to not supporting evidence. |
|
|
Explain the term 'survival of the fitest' |
When an organism is better adapted to environment that are more likely to survive and produce offspring. |
|
|
Why Is human population increasing? |
Because birth rate is exceeding death rate |
|
|
Give an example of a finite resource |
Fossil fuels |
|
|
List 2 areas of pollution that are I greater amount |
Household waste and sewage Sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide |
|
|
Consequences of a high demand for resources: |
Raw materials like oil are used up and minerals faster than they are made Pollution and waste build up at alarming rates Resources become in short supply, more expensive. |
|
|
Define the term ' carbon footprint ' |
Amount of greenhouse gases a person or event is responsible for emitting in a given timescale. This depends on a lifestyle. |
|
|
What is and ozone? |
Natural gas found high in the earths atmosphere. |
|
|
What does the gas ozone do? |
Prevents many harmful Uv rays reaching earth. |
|
|
What are CFC'S? |
Chlorofluorocarbons |
|
|
Acid rain is caused by and what can it do? |
Burning fossil fuels. This can corrode metals, dissolving of limestone statues, destruction of forests, and lakes becoming acidic,killing fish, other wildlife |
|
|
What is the greenhouse effect? |
The atmosphere keeping the earth warm. |
|
|
The green house effect process |

|
|
|
What are the organisms called that can evolve to resist effects of pollution? |
Indicator species |
|
|
Advantages of indicator species |
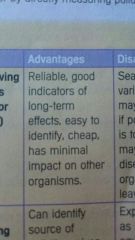
|
|
|
Disadvantages |

|
|
|
Advantages of using non-living methods |

|
|
|
Disadvantages of using non-living methods |

|
|
|
Describe sustainable resource |
One that came be used and replaced |
|
|
What is sustainable development? |
Ensuring of resources being used and maintained without comprising the needs of future generations. |
|
|
Resources can be sustained by... |
Replenishment Restocking |
|
|
What are endangered species? |
Species that are in danger of becoming extinct unless something is done to prevent it. |
|
|
Survival of a plant of animal can be threatened by: |
Climate change Destruction of habitats Hunting Increased competition Pollutants |
|
|
How to protect endangered species? |
Educating people Breeding in captivity Protecting habitats Artificial ecosystems Legally protecting Prohibiting hunting Making seedbanks. |
|
|
What is a conservation programme? |
A protection scheme to benefit both humans and maintain a foodchain. |
|
|
What do conservation programmes play a role in? |
Protecting food supply for humans Stabilising ecosystems Studying and identifying plants Protecting culture |
|
|
Causes of whale deaths? |
Becoming entangled on fishing nets and drowning. Affected by Pollutants Colliding with ships during migration Effects of climate change Culling and hunting. |
|
|
How can money be made from whales? |
Big tourist attraction Dead whales can be food,oil and to make cosmetics. |
|
|
Aspects of whale biology that need to be known still. |
How they communicate over large distances How they migrate How they dive and survive at extreme depths. |

