![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Autotroph
|
An organism that uses an inorganic carbon source and light energy to synthesis complex organic molecules
|
|
|
Define Heterotroph
|
An organism that requires organic nutrients to supply it with a source of carbon. They digest complex organic molecules to release the chemical potential energy stored within them.
|
|
|
Write the equation for photosynthesis
|
6CO2 + 6H2O ------> C6H12O6 + 6O2
(light energy) |
|
|
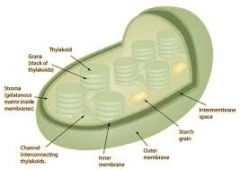
Draw and annotate the structure of a chloroplast
|
|
|
|
Explain the structure of
a) lamellae b) grana c) thylakoids d) starch grain e) stroma |
a) sheets; in a chloroplast, the lamellae are membranes within it
b) stacks of thylakoids c) membrane-enclosed spaces in a chloroplast where the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis takes place d) energy store e) the background material; where the light independent reaction takes place. |
|
|
Explain how the chloroplast is adapted to its function
|
1) grana are surrounded by the stroma so the products of the light-dependent reaction can readily pass to the stroma
2) proteins embedded in the grana hold the photosystems in place 3) photosynthetic pigments are arranged in photosystems to allow maximum absorption of light energy 4) using genetic information in the chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts can make proteins needed in photosynthesis - the chloroplast ribosomes assemble the proteins 5) inner membrane controls the entry and exit of molecules 6) grana provide a large surface area for photosynthetic pigments, ATP synthase enzymes and electron carriers 7) Stroma contain enzymes needed to catalyse light independent reactions |
|
|
Define photosynthetic pigment
|
A molecule that absorbs some wavelengths of light but not others and transfers the light energy to chemical energy
|
|
|
What happens to the wavelengths of light that are not absorbed?
|
They are reflected
|
|
|
What are the majority of pigments in a chloroplast?
|
Chlorophyll a +b
|
|
|
What is a photosystem?
|
A cluster of pigment and protein molecules that harvest light energy and channel it to chlorophyll molecules
|
|
|
What is an absorption spectrum?
|
A graph that shows the wavelengths of a light absorbed by a pigment
|
|
|
What is an accessory pigment?
|
A pigment that is different from the main light absorbing pigment - such as carotenoids, they help absorb more wavelengths of light than would be absorbed by chlorophyll alone and may also help protect chlorophyll from damage by intense light
|
|
|
What happens in the light dependent stage?
|
Photophosphorylation - cyclic and non-cyclic
|
|
|
Define photophosphorylation
|
The production of ATP using energy from light; it takes place on the thylakoid membranes of a chloroplast
|
|
|
Outline what occurs in photophosphorylation |
* Light energy that hits a chlorophyll molecule transfers its energy to two electrons which become excited * These electrons are passed along a series of electron carriers which releases energy * This energy is used to pump hydrogen ions across the thylakoid membrane into the thylakoid space, creating a proton gradient * The proton gradient results in the flow of H+ ions down their gradient through channels associated with ATP synthase enzymes= chemiosmosis * Chemisomosis provides a force that allows the generation of ATP: ADP + Pi -> ATP |
|
|
What photosystem does cyclic photophosphorylation use?
|
PSI
|
|
|
Outline what happens in cyclic photophosphorylation
|
Light energy is absorbed by PSI and energy is transferred to electrons in chlorophyll a which become so excited that they leave the chlorophyll molecule and are passed down a series of electron carriers. This releases energy which is used to make ATP by chemiosmosis. Electrons then are returned to PSI.
|
|
|
What photosystem(s) does non-cyclic photophosphorylation involve?
|
PSI and PSII
|
|
|
Outline what happens in non-cyclic photophosphorylation
|
1) Light hits PSII, exciting two electrons that leave chlorophyll from the primary pigment reaction centre and pass along a chain of electron carriers
2) ATP is generated by photophosphorylation (see other flashcards) 3) Light energy is also absorbed by PSI, exciting two electrons which are emitted and join with protons to combine with NADP to make reduced NADP 4) Electrons from photolysis replace electrons lost in PSII and electrons from PSII replace the electrons lost in PSI. |
|
|
What is photolysis?
|
The splitting of a water molecule using energy from light
2H2O -> 4H+ + 4e- + O2 |
|
|
What provides the protons in non-cyclic photophosphorylation ? Explain the uses of the products of photolysis. |
PSII contains an enzyme that splits water when activated by light (photolysis) 2H2O -> 4H+ + 4e- + O2
PROTONS - are used in chemiosmosis and the reduction of NADP - it is accepted by coenzyme NADP to be used in the light dependent reaction
ELECTRONS - Are used to replace electrons lost in PSII
OXYGEN - Used for aerobic respiration or diffuses out of the stomata |
|
|
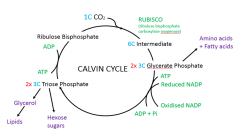
Draw the Calvin cycle
|
|
|
|
Explain the Calvin cycle
|
1) CO2 diffuses into the leaf through open stomata. In the stroma, it combines with 5C RuBP to from an intermediate 6C compound that immediately splits to form two molecules of 3C Glycerate phosphate. The carbon fixing is catalysed by Rubisco.
2) ATP and Reduced NADP from the light dependent reaction are now used to provide a phosphate and energy to change GP to 2x TP. 3) 5/6 of the TP go on to regenerate three molecules RuBP |
|
|
What can the products of the Calvin cycle be used for?
|
TRIOSE PHOSPHATE
*5/6 regenerates RuBP * Can be converted to glycerol and can then be combined with fatty acids made from GP to form lipids * Can be paired up to form hexose sugars such as glucose GLYCERATE PHOSPHATE * Used to make fatty acids and amino acids |
|
|
What are the limiting factors of photosynthesis?
|
- Light intensity
- CO2 conc - Temperature |
|
|
How does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
|
As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases up to a certain point
|
|
|
What does light do and how does this affect photosynthesis?
|
* Opens the stomata so CO2 diffuses in (CO2 is used in the Calvin cycle)
* Light is trapped by chlorophyll to excite electrons (these electrons are used in photophosphorylation) * Causes the splitting of water to produce protons (used in photophosphorylation) |
|
|
Draw and annotate a graph of show how light intensity is a limiting factor
|
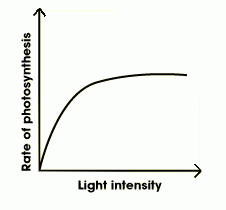
Light intensity is a limiting factor.
You reach a point where increasing the light intensity has no effect on the rate of photosynthesis as something else becomes the limiting factor (ex CO2 concentration) |
|
|
Describe how CO2 is used in photosynthesis
|
Plants absorb CO2 through diffusion into the stomata. During daylight, CO2 is being used in the Calvin cycle so the concentration of CO2 inside the leaf is lower than the concentration of CO2 outside the leaf so there is a gradient which keeps CO2 moving into the leaf.
|
|
|
How does temperature affect the kinetic energy of molecules?
|
A higher temperature increases the movement of molecules which mean there are more frequent collisions and that they collide with more energy. This increases the rate of the reaction.
|
|
|
What stage of photosynthesis does temperature affect?
|
Light independent - affects the enzyme catalysed reactions
|
|
|
How does temperature affect Rubisco?
|
At high temperatures it stops it binding CO2 and RuBP but instead O2 + RuBP = photorespiration
|
|
|
How does temperature affect the stomata?
|
Higher temperatures = more water loss from the stomata which induces a stress responses that closes the stomata, so CO2 availability is limited.
|
|
|
Explain, in terms of chemicals, how light affects the Calvin Cycle
|
Although the calvin cycle doesn't directly use light, it uses ATP and NADP from the light-dependent reaction to convert GP to TP. So if the light stops, the light dependednt stage stops and the supply of ATP and NADP to the Calvin cycle stops. GP can no longer be converted to TP and so builds up - the Calvin cycle stops when all TP is used up.
|
|
|
Explain, in terms of chemicals, how CO2 supply affects the calvin cycle
|
A short supply of CO2 means less GP is made and so less TP is made.
There is less CO2 to bind with RuBP so it builds up. RuBP must be replaced by TP, there is less TP avaliable to convert to RuBP and other amino acids/ lipids. The plant prioritises RuBP replacement/ |
|
|
What can you do to measure the rate of photosynthesis? |
- Measure volume of O2 produced per unit time -Measure uptake of CO2 - Measure rate of increase of dry mass of a plant |

