![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
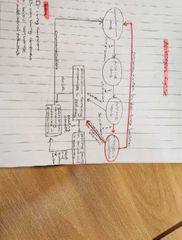
What are the 4 key stages of the nitrogen cycle |
Nitrogen fixation Ammonification Nitrification Denitrification |
|
|
Describe nitrogen fixation |
- atmospheric nitrogen gas is converted into nitrogen containig compounds -this is carried out by nitrogen fixing bacteria - the bacteria is found inside the root nodules of leguminous plants such as peas, beans and clover - the bacteria have a symbolic relationship with these plants - the bacteria provides plants with nitrogen containing compounds and the plants provide the bacteria with organic compounds such as carbohydrates |
|
|
Describe Ammonification |
Nitrogen compounds in waste products and dead organisms are converted into ammonia by saprobionts This forms ammonium ions in the soil |
|
|
Describe Nitrification |
-the ammonium ions in the soil are converted by nitrifying bacteria into nitrogen compounds known as nitrates -initially, nitrifying bacteria such as nitrsomonas convert ammonium ions into nitrites -different nitrifying bacteria then convert these nitrites into nitrates |
|
|
Describe denitrification |
-denitrifying bacteria using nitrates in the soil during respiration - this process produces nitrogen gas which returns to the atmodphere - this process occurs in anaerobic conditions |
|
|
Summary of the nitrogen cycle |
|
|
|
What is the phosphorus cycle |
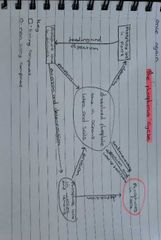
Shows how phosphorus is recycled in ecosystems |
|
|
Describe the first process in the phosphorus cycle |
Phosphorus in rocks is slowly released into the soil and into water sources in the form of phosphate ions by the process of weathering |
|
|
Describe the seconfd stage |
Phosphate ions are taken up from the soil by plants through their roots or absorbed from water by algae |
|
|
Describe the third stage |
-Phosphate ions are transferred to consuoduring feeding -phosphate ions in waste products and dead organisms arw released into the soil or water during decomposition by saprobionts |
|
|
Describe the finalstage of the phosphorus cycle |
Thw phosphate ions can noe be taken up and used again by producers ir may be trapped in sediments that over very long geographical time periods may turn into phosphorus containing rock once again |
|
|
Summary of the phosphorus cycle |
|
|
|
Describe fertilisers |
-when organisms in natural ecosystems die or produce waste the waste and dead matter decompose. This is carried out by saprobionts -this ensures that nutrients in dead matter and waste are continually recycled back into these natural ecosystems |
|
|
What do fertilisers do |
Used to add mineral ions such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium back into the soil |
|
|
Describe natural fertilisers |
Consist of the dead and decaying remains of plants and animals as well as waste such as slurry manure and bone meat |
|
|
Describe artificial fertilisers |
Mined from rocks and deposits and then converted into different forms and blended together to give the appropriate balance of minerals for a particular crop. Compounds containing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are always present |
|
|
Describe mycorrhizae |
-fungus root - mutualistic threads grow in and around the roots -this increases surface area and may be more efficient at absorbing minerals -fungus gets sugars from the plant,plant benefits from enhanced absorption of water and mineral ions |

