![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dorothea Orem’s Compensatory categories
Wholly compensatory |
Those unable to engage in self-directed actions i.e. patients in a coma, patients who cannot ambulate, and patients who cannot make judgments/decisions for themselves
|
|
|
Dorothea Orem’s Compensatory categories
Partially compensatory |
Those with limitations in mobility, knowledge and skills required to meet medical conditions.Are not completely dependent on others. Lack of psychological readiness to perform or learn the specific activities.
|
|
|
Dorothea Orem’s Compensatory categories
Supportive-educative |
Clients whose only requirement for help are confined to decision making, behavior control and acquiring knowledge and skills.
|
|
|
Dorothea Orem's Self-Care Deficit Theory is a general theory that consists of what three subtheories
|
(1) Every person’s ability to care for themselves is based on self action
(2) Inability of individuals to perform the necessary action is termed a “deficit” (3) Through the actions of nurses or nursing agency, patient self care deficits are relieved |
|
|
State Erikson’s 8 developmental conflict stages
(conflict and age group) |
Stage 1 Infancy: Trust Vs. Mistrust
Stage 2 Early Childhood: Autonomy Vs. Shame & Doubt Stage 3 Preschool: Initiative Vs. Guilt Stage 4 Childhood: Industry Vs. Inferiority Stage 5 Early adolescence: Identity Vs. Role Confusion Stage 6 Young Adulthood: Intimacy Vs. Isolation Stage 7 Middle Adulthood: Generativity Vs. Stagnation Stage 8 Maturity: Ego Integrity Vs. Despair |
|
|
What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs theory?
|
Maslow's theory states that certain internal, external, physical and psychological needs are common to all people.
|
|
|
(def)
Nonverbal communication |
Sending or receiving information by facial expressions
or body language. |
|
|
Discuss levels of Maslow Hierarchy of needs pyramid.
|
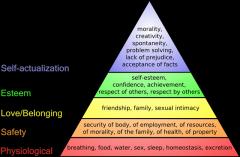
|
|
|
(def)
Verbal communication |
Sending or receiving communication through the spoken or written word.
|
|
|
(def)
Affective communication |
Sending or receiving information through feeling tone.
|
|
|
(def)
Active listening |
Hearing sounds and searching for information relevant to those sounds so the sounds may be understood.
|
|
|
The most commonly used active listening behaviors include - (8)
|
1. restating,
2. clarifying, 3. reflecting, 4. paraphrasing, 5 minimal encouraging, 6. remaining silent, 7. summarizing, 8. validating. |
|
|
Common blocks to communication involve (6)
|
1. False reassuring
2. probing, 3. chiding, 4. belittling, 5. giving advice, 6. pat answers. |
|
|
(def)
Communication blocks |
Stops meaningful conversation.
|
|
|
(def)
Assertiveness |
A way of accepting responsibility for oneself by expressing thoughts and feelings directly and honestly, without blaming oneself or others.
|
|
|
(def)
Aggressiveness |
An attacking type of behavior that occurs in response to frustration and hostile feelings.
|
|
|
(def)
nursing process |
Systematic problem-solving method by which nurses individualize care for each patient.
|
|
|
The five steps of the nursing process are
|
(1) assessment
(2) diagnosis (3) planning (4) implementation (5) evaluation |
|
|
(def)
assessment |
First step of the nursing process-The purpose is to gather information for health problem identification.
Activities required in the first step are 1 .data collection, 2. data validation, 3. data sorting 4. data documentation. |
|
|
(def)
nursing diagnosis |
The second step of the nursing process, during which the patient's actual and potential unhealthy responses to an illness or condition are identified.
Formal statement of an actual or potential health problem that nurses can legally and independently treat. |
|
|
(def)
planning |
The third step of the nursing process, "Patient centered" Process of designing interventions to achieve the goals and outcomes of health care delivery
|
|
|
(def)
implementation |
The fourth step of the nursing process,
Implementation ='s doing Initiation and completion of the nursing actions necessary to help the patient achieve health care goals. |
|
|
(def)
evaluation |
The fifth step of the nursing process,
Determination of the extent to which established patient goals have been achieved. |
|
|
Traditional adult learner
|
Comes from an educational program directly from high school or from another program of study
|
|
|
Returning adult learner
|
Has been out of school for several years
|
|
|
What type of learners are important part of the LPN/LVN team?
|
Adult learners with prior education beyond high school
|
|
|
Recycled adult learners
|
Adult learner might have tech school or college experience or an undergraduate or graduate degree in a discipline other than nursing
|
|
|
Formal education
|
Vocational technical school or junior college
Planned, organized learning, such as the nursing course of study. |
|
|
Informal education
|
Obtained through school of life.
|
|
|
Positive mental attitude (PMA)
|
"I want to", "I can", "I will", "I'm going to"
|
|
|
Dangers for the traditional adult learner
|
Grade inflation, social activities, and employment
|
|
|
Dangers for the returning adult learner
|
Physical, social and family responsibilities
|
|
|
Dangers for the recycled adult learner
|
Attitude
|
|
|
(def)
Active learning |
Must open yourself up, reach out, and stretch to gain knowledge and skills
|
|
|
(def)
Self-evaluation |
Should be able to look at their nursing actions and be aware of their strong behaviors and behaviors that need improvement
|
|
|
(def)
Objective awareness |
One's own behaviors is an important skill to have as an employee
|
|
|
(def)
Open ended question- |
Open-ended- allows patient to respond in a way they choose
e.g. Where did you fall? What happened? |
|
|
(def)
Closed-ended- question |
Closed –ended questions- requires a specific answer (yes or no)
Did you fall? Did you hurt your arm? |
|
|
(def)
Focused questions |
more definitive answer (provides more focused information) Ex: how did you feel when you fell?
When you fell, were you dizzy first? |
|
|
What are the responsibilities of the LPN regarding the nursing process?
|
provides input into the assessment, planning, and evaluation of nursing care; and implements the plan of care under the RN’s direction
|
|
|
Blocks to Communication (6)
|
(1) False reassurances
(2) Probing (3) Chiding (scolding) (4) Belittling (5) Giving advice (6) Pat answers False reassurances- “Everything will be okay” The chemotherapy will work. Probing- According to your medical record you are single-How long have you been divorced? Chiding- I cannot believe you are still eating chocolate- when you know how bad that is for your diabetes. Belittling- You had a fractured arm, not open heart surgery! From their perspective only…… Giving advice- I know I have cancer, should I have chemotherapy? Instead… what are your thoughts? Pat answers- Its no big deal- we do this surgery every day instead “ I will be here when you get back” |
|
|
(def)
Subjective statements |
usually feelings, “what the patient says” to you, this includes your pain assessment!
|
|
|
(def)
Objective: measurements |
(what the nurse observes) according to an accepted standard,
Ex: temp of 39 degrees C Seeing, hearing, smelling, measuring |

