![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
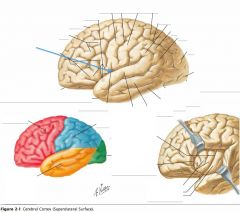
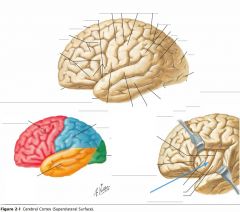
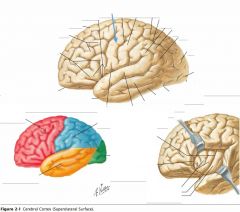
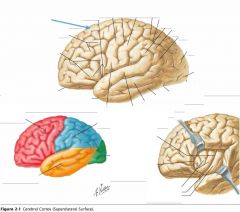
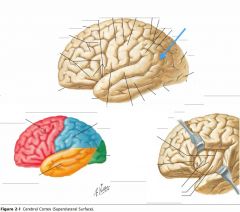
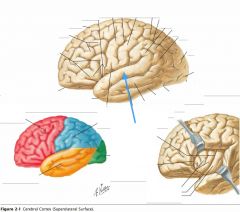
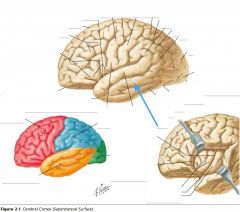
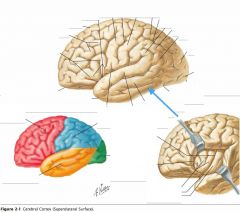
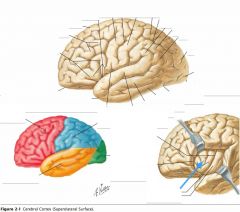
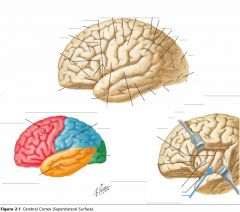
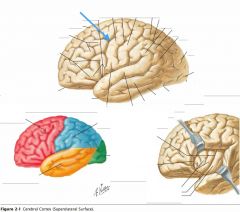
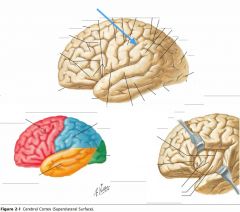
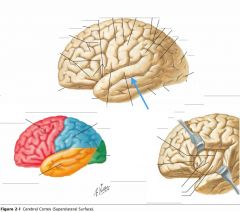
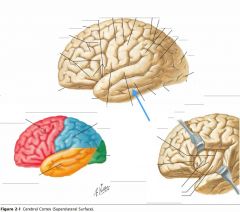
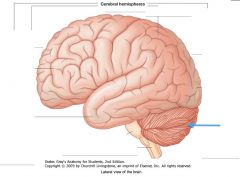
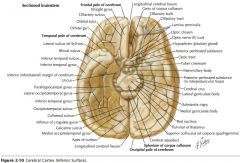
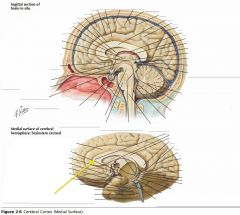
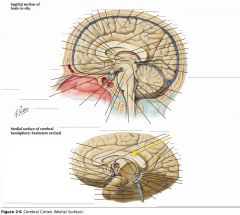
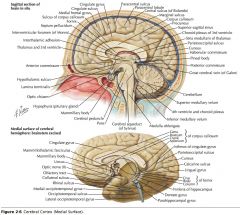
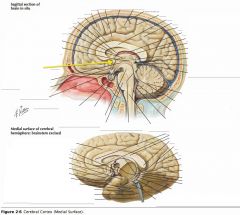
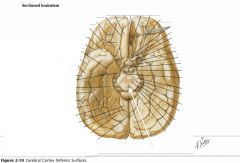
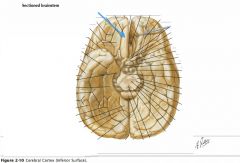
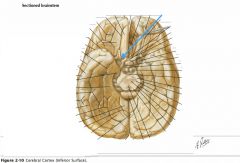
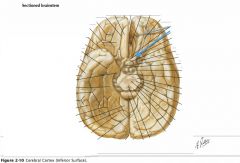
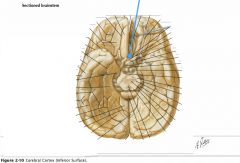
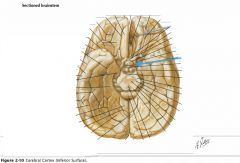
What sulcus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Lateral Sulcus (or Sylvian Fissure)
|
|
|
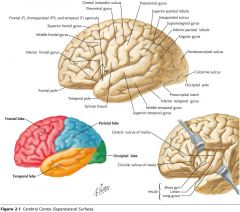
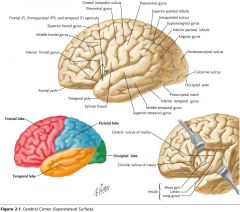
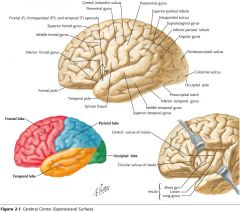
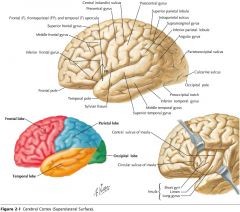
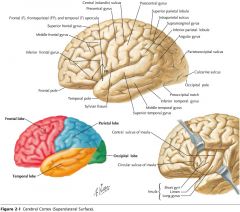
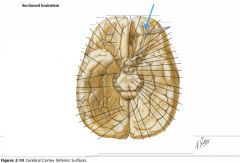
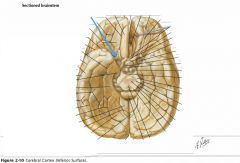
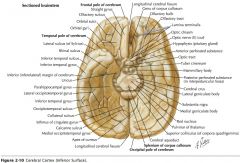
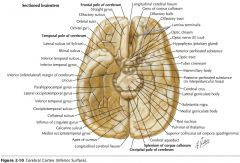
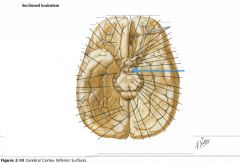
What feature is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Longitudinal Fissure.
|
|
|
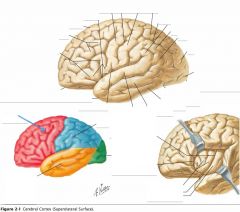
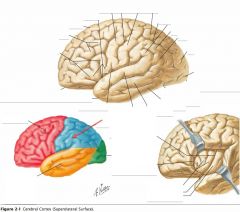
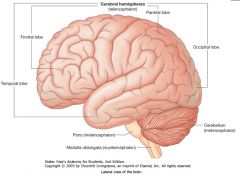
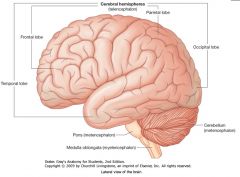
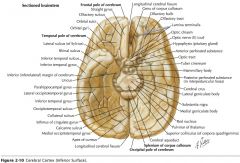
What lobe is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Frontal Lobe
|
|
|
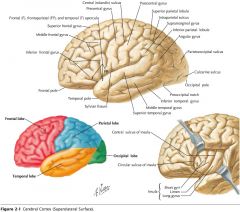
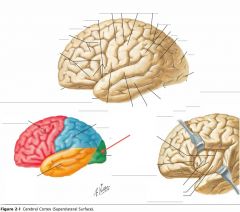
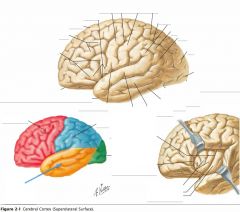
Which lobe is indicated by the red arrow?
|
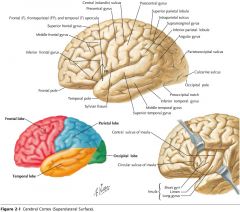
The Parietal Lobe
|
|
|
Which lobe is indicated by the red arrow?
|
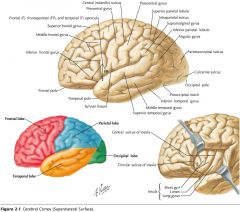
The Occipital Lobe
|
|
|
Which lobe is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
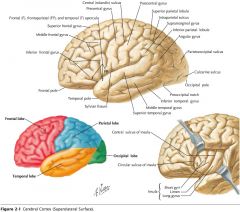
The Temporal Lobe
|
|
|
Which lobe is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
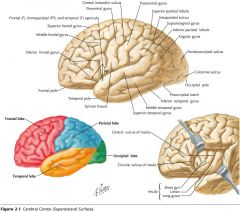
The Insula
|
|
|
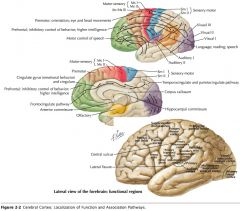
What is the functional role of the Frontal Lobe?
|
The cortex found in this region is associated with motor control, and, in the pre-frontal area, with judgment, the ability to formulate a plan of action in response to circumstances.
(Side 3) |
Also some aspects of memory and smaller functions.
|
|
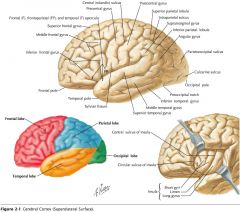
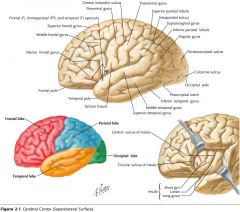
What is the functional role of the Parietal Lobe?
|
The cortex in this region is associated with somatosensation, and with the integration of sensory information.
|
|
|
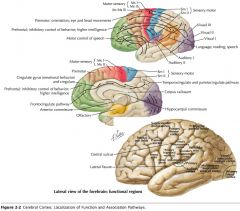
What is the functional role of the Occipital Lobe?
|
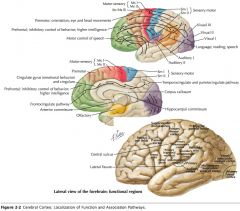
The cortex in this region is involved with vision and the processing of visual information.
|
|
|
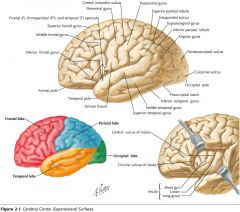
What is the functional role of the Temporal Lobe?
|
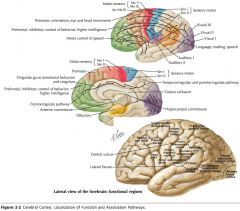
The cortex in this region is involved with receiving and processing auditory information, speech and olfaction. Also some involvement with the limbic system.
|
|
|
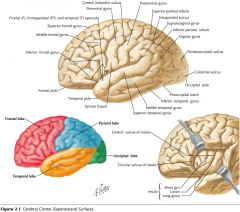
What is the functional role of the Insula?
|
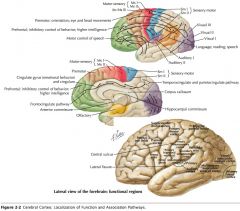
Possibly nociception and visceral function, but not certain.
|
|
|
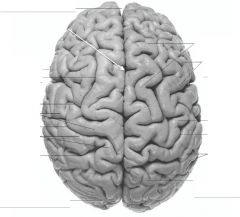
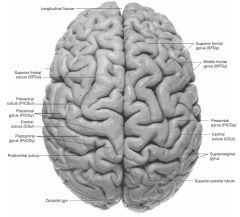
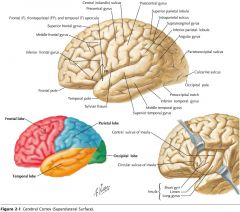
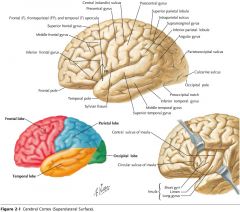
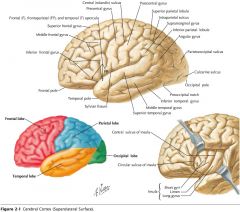
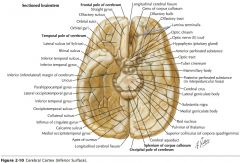
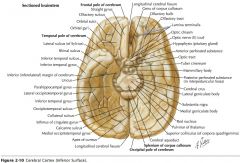
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
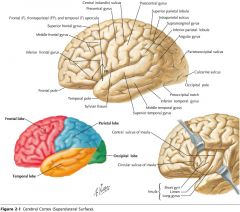
The Precentral Gyrus.
|
|
|
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
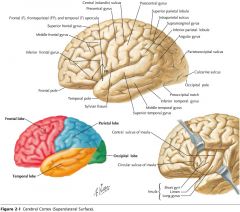
The Superior Frontal Gyrus
|
|
|
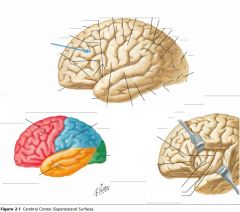
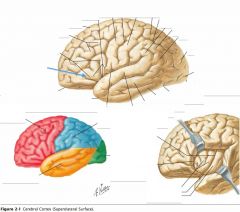
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Middle Frontal Gyrus
|
|
|
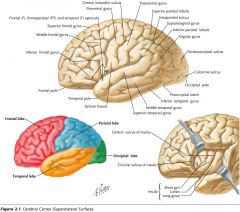
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
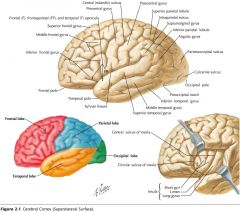
The Inferior Frontal Gyrus
|
|
|
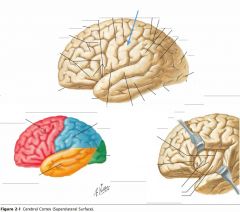
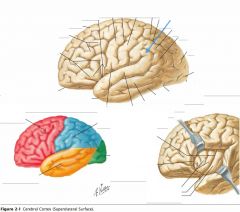
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Postcentral Gyrus
|
|
|
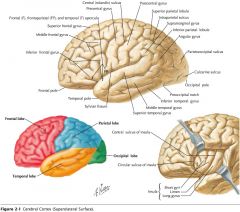
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
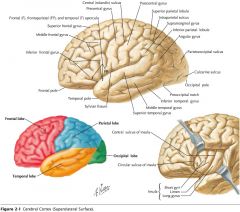
The Supramarginal Gyrus
|
|
|
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
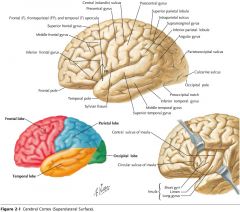
The Angular Gyrus.
|
|
|
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
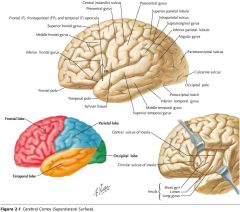
The Superior Temporal Gyrus.
|
|
|
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
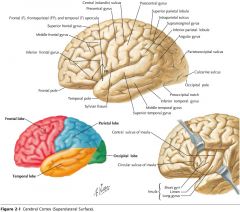
The Middle Temporal Gyrus
|
|
|
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
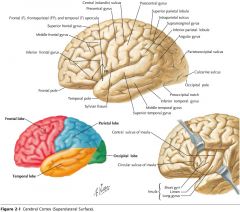
The Inferior Temporal Gyrus.
|
|
|
What gyri are indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Short Gyri of the Insula.
|
|
|
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Long Gyrus of the Insula
|
|
|
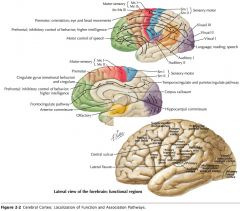
What sulcus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Precentral Sulcus.
|
|
|
What sulcus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Postcentral Sulcus
|
|
|
What sulcus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Superior Temporal Sulcus
|
|
|
What sulcus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Inferior Temporal Sulcus
|
|
|
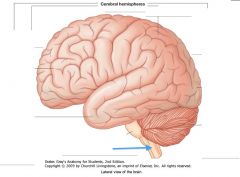
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Medulla Oblongata
|
|
|
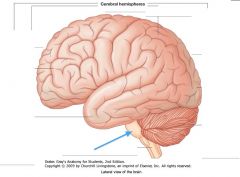
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Pons
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
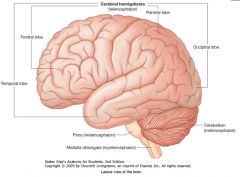
The Cerebellum
|
|
|
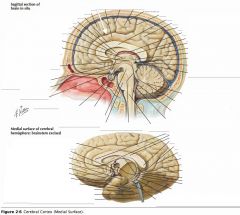
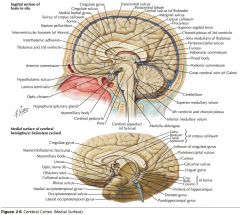
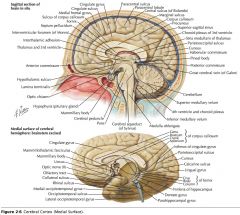
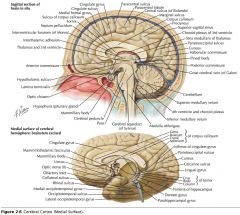
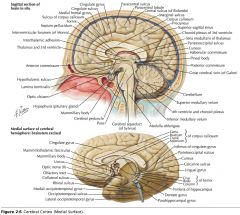
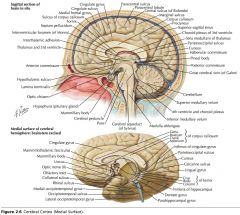
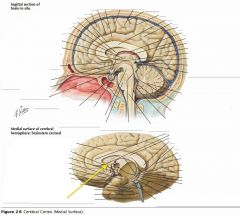
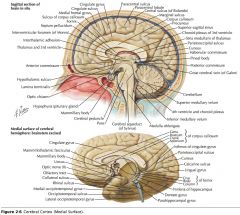
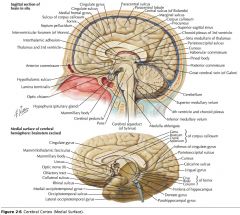
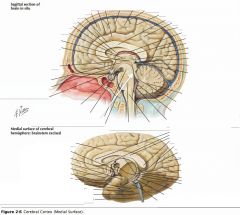
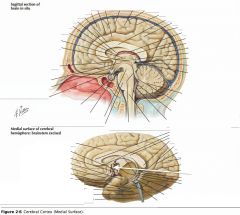
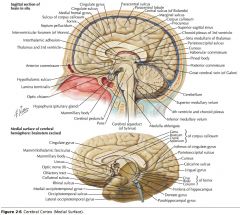
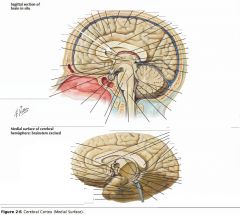
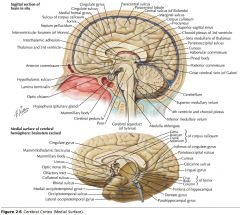
What sulcus is indicated by the white arrow?
|
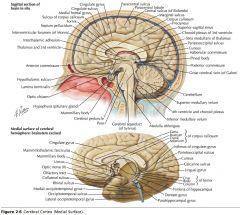
The Cingulate Sulcus.
|
|
|
What sulcus is indicated by the white arrow?
|
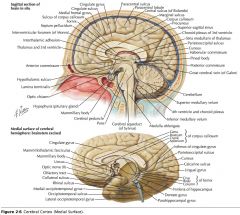
The Sulcus of the Corpus Callosum (Callosal Sulcus)
|
|
|
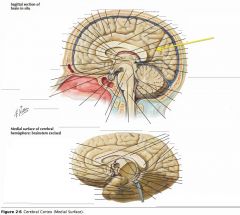
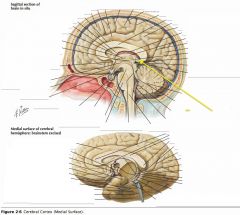
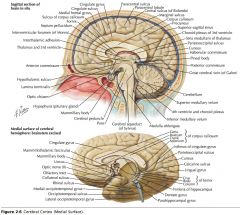
What sulcus is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
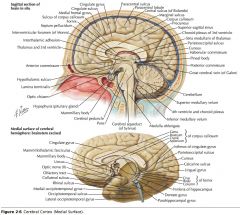
The Parieto-occipital Sulcus
|
|
|
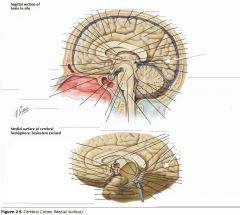
What sulcus is indicated by the white arrow(s)?
|
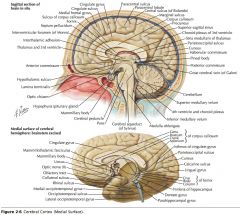
The Calcarine Sulcus.
|
|
|
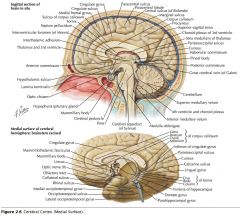
What is the importance of the Calcarine Sulcus as a landmark?
|
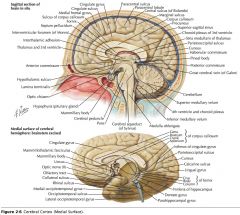
The primary visual cortex is located on either side of this sulcus.
|
|
|
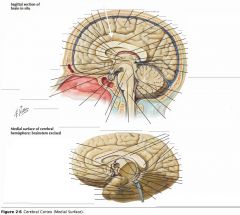
What gyrus is indicated by the white arrow?
|
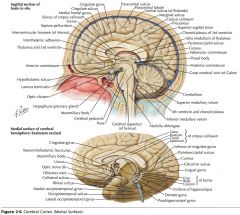
The Cingulate Gyrus.
|
|
|
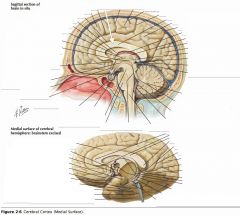
What structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
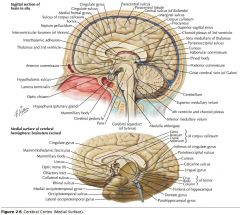
The Corpus Callosum
|
|
|
What gyrus is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Parahippocampal Gyrus
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Uncus
|
|
|
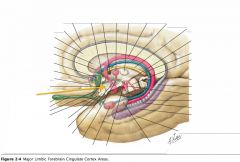
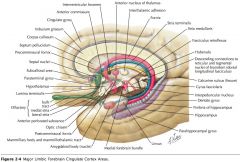
What are the Cingulate Gyrus, the Parahippocampal Gyrus and the Uncus collectively called?
|
The "Limbic Lobe." (along with some associated structures)
|
|
|
What does the Limbic System do?
|
It is involved with emotion and certain kinds of memory.
|
|
|
What information does the Uncus receive?
|
It receives olfactory input
|
|
|
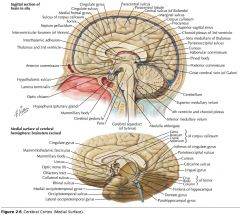
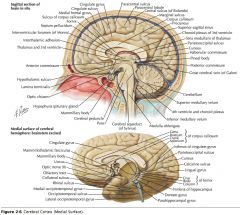
What region of the Corpus Callosum is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
The Rostrum.
|
|
|
What region of the Corpus Callosum is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
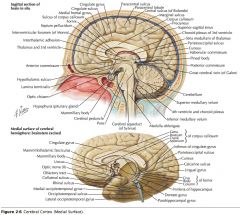
The Genu
|
|
|
What region of the Corpus Callosum is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
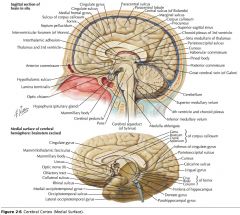
The Body
|
|
|
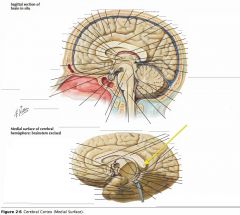
What region of the Corpus Callosum is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
The Splenium
|
|
|
What is the role of the Corpus Callosum?
|
It connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres, ensuring communication through commissural fibres.
|
|
|
What collection of fibres is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
The Anterior Commissure
|
|
|
What collection of fibres is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
The Posterior Commissure.
|
|
|
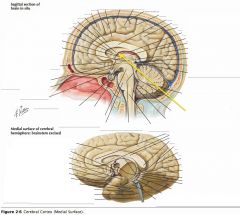
What collection of fibres is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
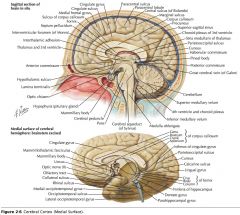
The Fornix.
|
|
|
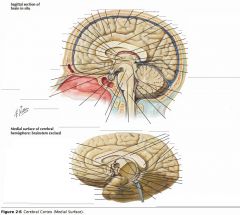
What two lobes are connected by the Anterior Commissure?
|
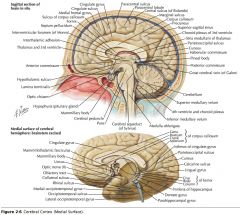
The right and left Temporal Lobes.
|
|
|
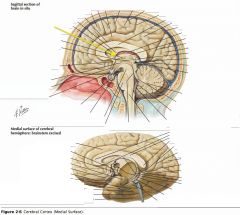
What foramen is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
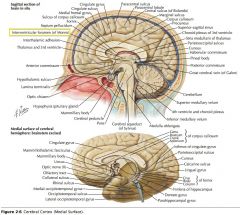
The Interventricular Foramen.
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Corpora Quadrigemina (well, a part of it)
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Cerebral Aqueduct.
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Cerebral Aqueduct.
|
|
|
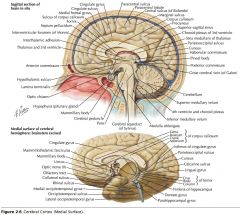
What is the function of the Posterior Commissure?
|
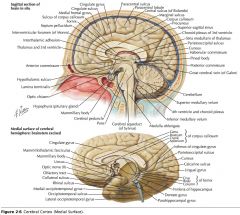
It consists of axons which mediate reflexes associated with pupillary constriction.
|
|
|
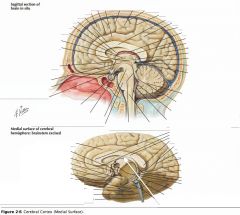
What portion of the Fornix is indicated by the white arrow?
|
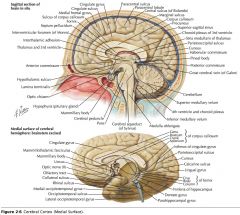
The Body.
|
|
|
What portion of the Fornix is indicated by the white arrow?
|
One of the Columns.
|
|
|
What septum is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Septum Pellucidum.
|
|
|
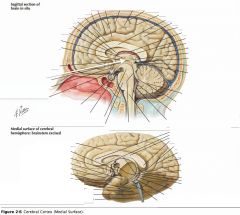
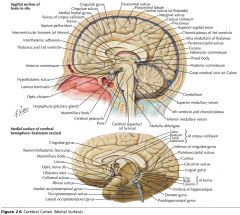
What structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Thalamus.
|
|
|
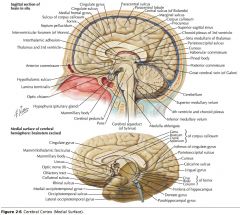
What structure is indicated by the orange arrow?
|
The Hypothalamus.
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the orange arrow?
|
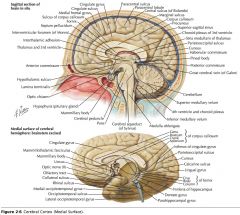
The Pineal Body.
|
|
|
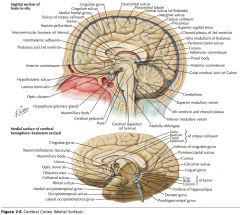
What is the function of the Thalamus?
|
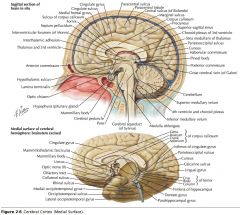
Its nuclei process sensory, motor, and limbic information, along with a variety of other kinds of information which are then sent to the cerebral cortex.
|
|
|
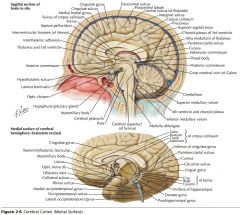
What is the function of the Hypothalamus?
|
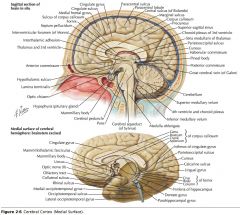
It's intimately involved in the control of visceral activity and in the maintenance of homeostasis.
Certain regions are also involved with the limbic system. |
It acts both with neurologic control and with hormonal control (as an endocrine organ).
|
|
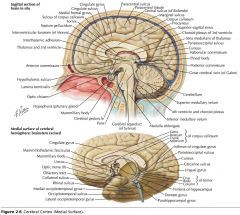
What is the function of the Pineal Body?
|
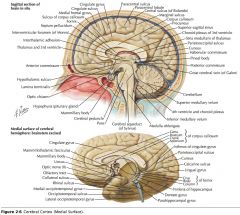
It secretes melatonin.
|
|
|
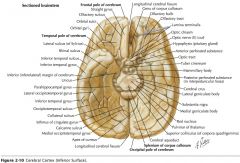
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
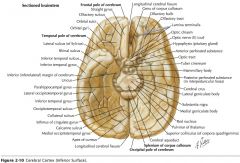
The Gyrus Rectus (or Straight Gyrus)
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
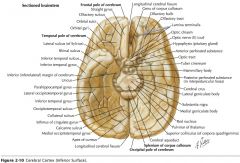
The Olfactory Bulb
|
|
|
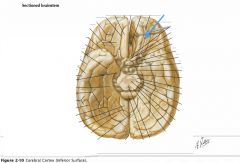
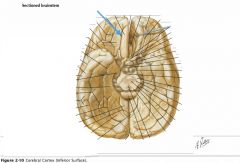
What tract is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Olfactory Tract.
|
|
|
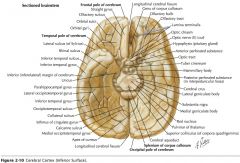
What sulcus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
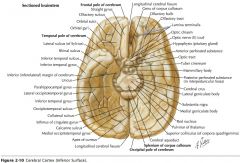
The Olfactory Sulcus
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
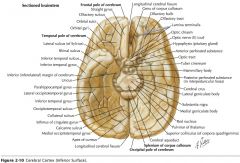
The Medial Olfactory Stria
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
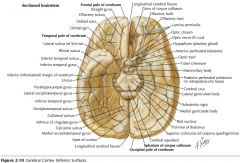
The Lateral Olfactory Stria.
|
|
|
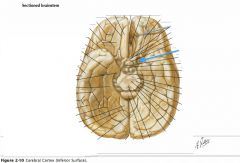
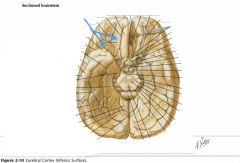
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Anterior Perforated Substance
|
|
|
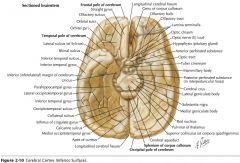
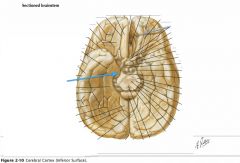
What gyri are indicated by the blue arrows?
|
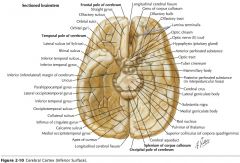
The Orbital Gyri
|
|
|
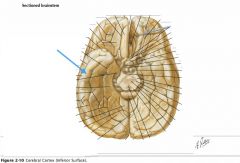
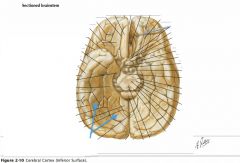
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Inferior Temporal Gyrus.
|
|
|
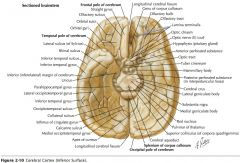
What gyri are indicated by the blue arrows?
|
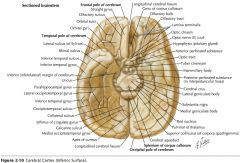
The Occipitotemporal Gyri (lateral and medial)
|
|
|
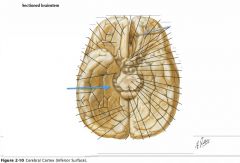
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
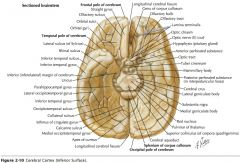
The Parahippocampal Gyrus.
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
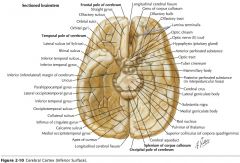
The Uncus
(a prominent bump on the Parahyppocampal Gyrus) |
|
|
What (dissected out) nerve is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Optic Nerve.
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Optic Chiasm (or chiasma)
|
|
|
What happens at the Optic Chiasma?
|
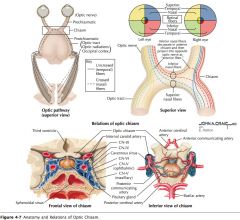
There is a partial crossing of the Optic Nerves.
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
An Optic Tract.
|
|
|
Where do the Optic Tracts terminate?
|
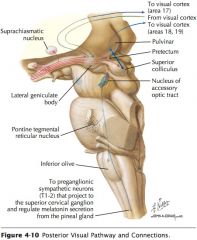
Mainly in the lateral geniculate bodies of the thalamus.
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
A Mamillary Body
|
|
|
What are the Mamillary Bodies?
|
Two hypothalamic nuclei that receive input from the limbic lobe via the fornix.
|
|
|
Which division of the brainstem is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Medulla Oblongata.
|
|
|
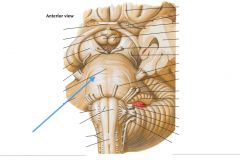
Which division of the brainstem is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The (Basilar) Pons
|
|
|
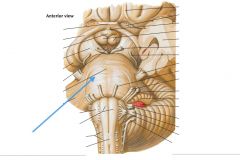
Which division of the brainstem is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
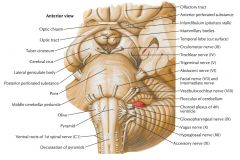
The (Basilar) Pons
|
|
|
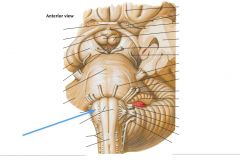
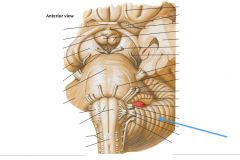
Which structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Olive of the Medulla Oblongata.
|
|
|
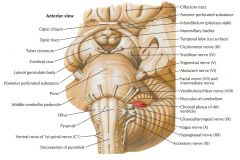
Which region of the brain is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
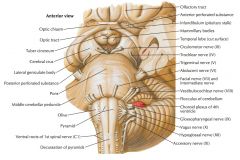
The Cerebellum
|
|
|
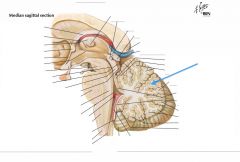
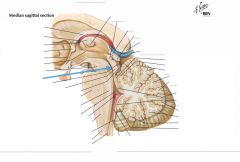
What is the branching white matter indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Arbor Vitae (the Tree of Life)
|
|
|
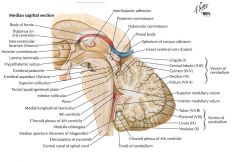
Which space is indicated by the blue arrow?
What does it do? |
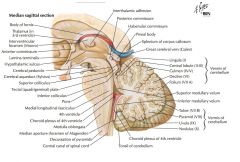
The Cerebral Aqueduct, connecting the Third and Fourth Ventricles.
|
|
|
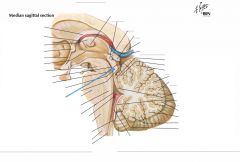
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Corpora Quadrigemina (Quadrigeminal Plate)
|
|
|
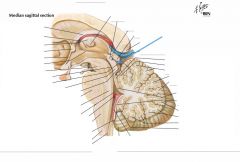
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
A Superior Colliculus of the Quadrigeminal Plate
(there are two superior colliculi) |
|
|
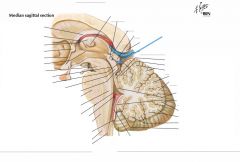
What is the function of the Superior Colliculi of the Corpora Quadrigemina?
|
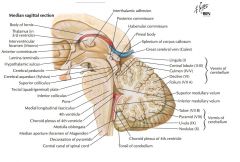
They are involved with visual functions.
|
|
|
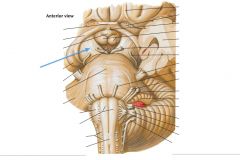
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
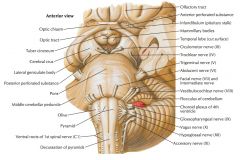
The Basis Pedunculi
(The Cerebral Crus is the anterior surface of the Cerebral Peduncle, another name for Basis Pedunculi) |
|
|
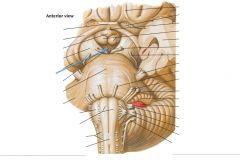
What surface is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
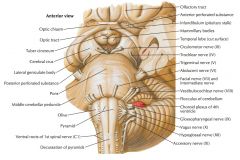
The Posterior Perforated Substance.
|
|
|
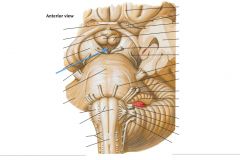
What is the space located anterior to the Posterior Perforated Surface?
|
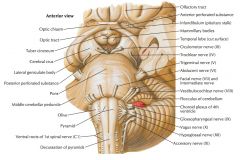
The Interpeduncular Fossa.
|
|
|
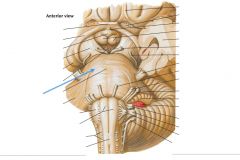
Describe the fibers of the Basilar Pons.
|
They are Transverse Fibers, and they cross over the anterior surface of the brainstem and continue into the Cerebellum.
|
|
|
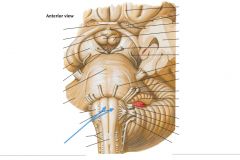
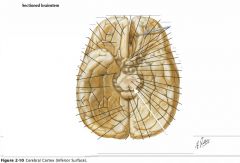
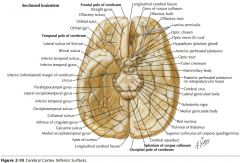
What tracts are indicated by the blue arrows?
|
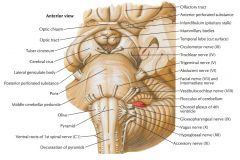
The Pyramidal Tracts of the medulla.
|
|

