![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
General Characteristics of Microorganisms
1.Cellular organization |
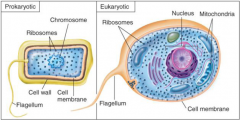
|
|
|
Viruses are living organisms
|
False
|
|
|
Free living species refers to
|
non-disease causing agent
|
|
|
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
|
First one invented microscope
|
|
|
Louis Pasteur
|
Invented pasteurization
Finally disproved abiogenesis |
|
|
Robert Koch
|
Koch’s postulates are the cornerstone of the germ theory of disease
|
|
|
Biogenesis theory
|
Living organism come from living organism
|
|
|
Abiogenesis theory
|
Living organism com from non living
|
|
|
Spontaneous generation
|
Living organism come from nonliving
|
|
|
Hypothesis?
|
A general approach to explain a natural phenomenon
|
|
|
Steps of proving hypothesis
|
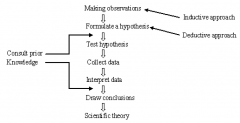
|
|
|
Steps of proving a hypothesis in inductive approach begin with
|
making observations
|
|
|
Taxonomic system has three primary functions
|
Classification
Nomenclature Identification of species |
|
|
Species, Genus, Family, Order, Class, Phylum, Kingdom
|
spaghetti, green, for, over, came, Philip, King
|
|
|
Naming Micoorganisms
|
Binomial (scientific) nomenclature, Gives each microbe 2 names Genus - noun, always capitalized, species adjective, lowercase. Both italicized or underlined, Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis), Escherichia coli (E. coli), Homo sapiens (H. sapiens)
|
|
|
Five Kingdom Classification System
|
Monera: Prokaryotes
Protista: Simple or primarily unicellular eukaryotes Fungi: Eukaryotic decomposer, having cell wall, not photosynthetic Animalia: multicellular eukaryotes, muscular and nervous system Plantae: Multicellular eukaryotes, photosynthesis |
|
|
Six Kingdom
|
Eubacteria, Archaea, Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia
|
|
|
Five Kingdom
|
Monera (eubacteria & archaea), Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia
|
|
|
3 Domains Classification System
|
Bacteria: true bacteria, peptidoglycan (1 kingdom) Archaea: lack peptidoglycan, live in extreme environments (1 kingdom)
Eukarya: have a nucleus and organelles (4 kingdoms) |

