![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Medical Evacuation Priorities |
Priority I - URGENT/Priority IA - Urgent Surgical - 1 Hour Priority II - Priority - 4 hours Priority III - Routine - 24 Hours Priority IV - Convenience - Not required |
|
|
Medical Treatment Priorities (Triage Categories (I-D-M-E)) |
IMMEDIATE - Patients require immediate care to save life or limb DELAYED - Patients who, after emergency treatment, incur little additional risk by delay or further treatment MINIMAL - Require limited treatment and can be returned to duty. EXPECTANT - Patients so critically injured that complicated and prolonged treatment will improve life expectancy |
|
|
Classes of Supply |
1. Rations 2. Clothing and Equipment 3. POL 4. Construction 5. Ammunition 6. Personal demand items 7. Major end items 8. Medical Material 9. Repair Parts 10. Material to support non-military programs |
|
|
Area of Operation |
Oreint (N/S/E/W, General Location) Box (BN AO, Grid lines or linear terrain) Trace (CO AO, Rivers, roads, LOA, phase lines) Familiarize (Small Features, ABF, SBF, ATK) |
|
|
Area of Interest |
1. CAS - Type, Location, Trigger, Time 2. Artillery - Type, Location, Trigger, Time 3. Reserves - Type, Location, Trigger, Time 4. Other |
|
|
Mission Analysis |
Restated Mission Tentative Decisive Point Initial Commander's Intent Initial Risk Assessment |
|
|
Engagement Area Development |
1.) Enemy Avenue of Approach 2.) Enemy Scheme of Maneuver 3.) Where to kill enemy 4.) Emplace Weapon Systems 5.) Emplace Obstacles 6.) Indirect Fires 7.) Rehearse Execution of Operations in EA |
|
|
COA DEV |
1.) Analyze Relative Combat Power 2.) Generate Options 3.) Array Forces 4.) Develop a Concept of Operations 5.) Assign Responsibilities 6.) Prepare a COA Statement and Sketch |
|
|
War Fighting Functions |
Mission Command - Related tasks and systems commanders use to balance art of command and science of control. Intelligence - Related tasks and systems to understand enemy, terrain, and civil considerations Fires - Systems for coordinated use of IDF, CAS, Joint Fires Movement and Maneuver - Move and employ forces to achieve position of advantage over enemy Sustainment - Support and services to ensure freedom of action Protection - Preserve the force to accomplish the mission |
|
|
Use of Operational Graphics |
What the commander uses to command and control his forces during the execution of the operation. (i.e. All Battalion OPS, PL, CPs, Directions of Attack, Breach Lanes, TRPs, IDF) Black ink, won't change or move. |
|
|
Use of Intent Graphics |
Used to display action through phases or COAs. Blue ink, (i.e. Tactical Tasks, Unit Symbols) |
|
|
Task Organization of IBCT Infantry Company |

|
|
|
Task Organization of IBCT Weapons Company |
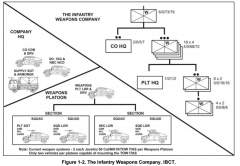
|
|
|
DSCA |
Defense Support of Civil Authorities - Support provided by U.S. in response to requestsfor assistance from civil authorities for domestic emergencies, law enforcement support, and other domesticactivities, or from qualifying entities for special events. The fourth decisive action, (Offense, Defense, Stability, DSCA) |
|
|
Priority Fires vs. Priority Target |
Priority Fires - The commander’s guidanceto organize and employ fire support in accordance with the relative importance of theunit’s mission. Priority Target - A target, based on either time or importance, on which the delivery of fires takes precedenceover all the fires for the designated firing unit or element. |
|

|
Medical Treatment Facility - A facility established for the purpose of furnishing medical and/or dentalcare to eligible individuals. |
|
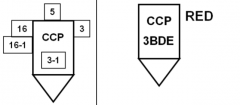
|
Casualty Collection Point - Predesignated along the axis of advance or evacuation routes |
|
|
Three Methods of Resupply |
Tailgate - They come to you Service Station - You go to them Emergency |
|
|
Surface Danger Zone |
Delineates that portion of the earth and the air above in which personnel and/or equipment may be endangered by ground weapons firing or demolition activities. |
|
|
Movement Box |
A movement box is designed to accommodate movement to an objective. Shooters move within the designated "box" and may engage multiple targets or moving targets downrange. |
|
|
Two Types of SDZs |
Cone - Static/Known Distance Batwing - For greater containment of all ricochets, better for maneuver |
|
|
Impact Area |
The Primary danger area for the impact of all rounds. |
|
|
Dispersion Area |
Distribution of a series of rounds from one weapon aimed at one point of impact. |
|
|
Angle P |
Dispersion area in Degrees (5 Degrees) |
|
|
Ricochet Area |
The area provided to contain ricochet projectiles. |
|
|
Angle Q |
Ricochet Area expressed in degrees (5 degrees) |
|
|
Area A |
The area parallels the impact area to contain fragments. |
|
|
Area B |
The area on the downrange side of the impact area. |
|
|
Area F |
Backblast Area |
|
|
Gun Target Line |
Line - Firing position to target position |
|
|
Distance W |
The maximum lateral edge of the ricochet area. W(Meters) = Range(KM) * Mils (Degrees x 18) |
|
|
REDs |
Risk Estimate Distances - The minimum distance friendly troops can approach the effects of friendly fires without 0.1 percent or more probability of incapacitation. |
|
|
Line of Sight |
An imaginary line, from the firers eye, through the sights, to the point of aim on the target |
|
|
Burst of Fire |
A number of successive rounds fired with the same elevation and point of aim when the trigger is held to the rear. |
|
|
Trajectory |
The curved path a round takes during it's flight. Affected by air resistance and gravity |
|
|
Maximum Ordinate |
The highest point above the line of sight to which a project rises during it's flight. Approx: 2/3 along the trajectory. |
|
|
Cone of Fire |
Group of trajectories resulting from a burst of fire |
|
|
Beaten Zone |
The pattern formed when the cone of fire strikes the ground. |
|
|
Dangerous Space |
Between the muzzle of the machine gun and the point where the lowest round in the beaten zone strikes the ground. |
|
|
Dangerous Zone |

Dangerous space and beaten zone. |
|
|
Dead Space |
Any fold or depression in the ground that prevents a target from being engaged from a fixed position. |
|
|
Grazing Fire |
Level terrain, center of the cone of fire does not rise more than 1 meter above the ground. Dangerous zone is from muzzle to end of beaten zone. |
|
|
Plunging Fire |
Long ranges, ground changes high to low, low to high. Danger zone is only beaten zone. |
|
|
Four Classes of Fire (Target) |
Frontal Fire Flanking Fire Oblique Fire Enfilade Fire |
|
|
Five Classes of Fire (Weapon) |
Fixed Fire Traversing Fire - Width Searching Fire - Depth Traversing and Searching Fire Free-Gun Fire |
|

|
Avenue of Approach - An air or ground route of an attacking force of a given size leading to its objectiveor to key terrain in its path. Avenues of approach are classified by type (mounted, dismounted, air, or subterranean),formation, and speed of the largest unit that can travel on it |

