![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The diencephalon is composed of four components. What are they? |
1. The epithalamus (which includes the pineal body) 2. The dorsal thalamus (commonly considered to be the thalamus proper) 3. The ventral thalamus (reticular nucleus and subthalamic nucleus) 4. The hypothalamus |
|
|
The three main functions of the thalamus are? |
1. Relay input from subcortical structures to the cortex 2. Control (gate) which sensory information reaches the cortex 3. Synchronize cortical activity that relates to consciousness |
|
|
Medial to the thalamus lies what? Laterally? |
Medially - third ventricle; laterally - internal capsule |
|
|
Which structure interconnects the two thalami? |
Massa intermedia |
|
|
The blood supply to the thalamus is predominantly from? |
The posterior circulation |
|
|
How is the thalamus divided? |
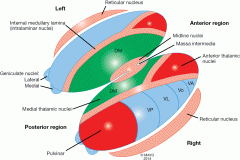
Functionally into the dorsal and ventral thaalmus |
|
|
The dorsal thalamus or thalamus proper can be divided into three groups of nuclei based on what? |
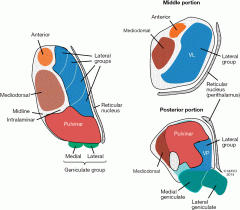
Function and afferent input: 1. First order relay 2. High order relay or associative 3. Nonspecific nuclei |
|
|
What is the isothalamus? |
A term that is sometimes used to describe the first order relay and high order relay nuclei together |
|
|
What is the allothalamus? |
A term that is sometimes used to describe the nonspecific nuclei of the thalamus |
|
|
What are first order relay neurons? |
Those neurons that receive primary input from subcortical sensory or motor areas and project to primary sensory or motor areas |
|
|
Which thalamic nuclei are considered first order? (7) |
1. Anterior nucleus 2. Ventral anterior 3. Ventrolateral 4. Ventral posteriolateral 5. Ventral posteriomedial 6. Medial geniculate body 7. Lateral geniculate body |
|
|
Which thalamic nuclei are considered high order relay nuclei? (3) |
1. Pulvinar 2. Dorsomedial 3. Anterior nuclei |
|
|
What is the role of the high order relay nuclei? |
Integrate cortical and subcortical information and project to high order multimodal cortex |
|
|
What is the thalamic reticular nucleus composed of? |
A thin layer of interconnected GABAergic neurons between the posterior limb of the internal capsule and the external medullary lamina |
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus has a function in memory? |
Dorsomedial nucleus |
|
|
What is the function of the reticular nucleus? |
To modulate, or gate, the responses of the thalamic neurons to incoming cerebral cortical input |
|
|
Thalamocortical neurons respond to input from sensory pathways of the cortex how? |
By discharging in 1 of 2 modes: tonic or rhythmic bursts |
|
|
Patients with absence seizures may display what on the electroencephalogram (EEG)? |
A 3-Hz spike-and-wave discharge; fast bursting cortical neurons may initiate these seizures via corticothalamic projections. Excitatory cortical input to the reticular nucleus of the thalamus overrides the intrinsic GABA-receptor-mediated local inhibitory mechanisms. |
|
|
Cortical (EEG) activity seen in wakefulness and REM sleep? |
High frequency (30-50 Hz, gamma band) |
|
|
Which thalamic nuclei are targets of deep brain stimulation? |
1. Ventrolateral or ventral intermedius 2. Ventral anterior 3. Centromedian/parafasciular 4. Ventral posteriore |
|
|
Clinical applications of the different thalamic nuclei that are targets for deep brain stimulation? |
1. Ventrolateral - Tremor 2. Ventral anterior - dystonia (possibly) 3. Centromedian - seizures and Tourettes 4. Ventral posterior - possibly central pain |

