![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Introduction |
Mammary glands are modified sweat glands which are used to produce milk for the nourishment of newborns. They are hemispherical in shape. They are functional in females and rudimentary in males. |
|
|
Situation |
Breasts lie in the superficial fascia of pectoral region in women. They are divided into 4 parts : UL, LL, UM and LM quadrants. |
|
|
Extent of base |
Vertically- from 2nd to 6th rib Horizontally- from lateral border of sternum to midaxillary line. |
|
|
Deep relations |
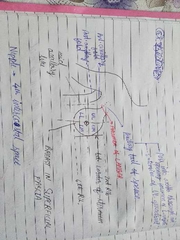
Lies on the deep fascia of pectoral region. Retromammary space- space between parenchyma of breast and the pectoral fascia. Helps in movement of breast over deep fascia. Directly above pectoralis major muscle. |
|
|
Structure |
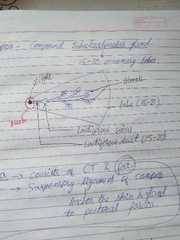
Skin, parenchyma and stroma. Skin- nipple (4th intercostal space, circular and longitudinal smooth muscle) and areola Parenchyma- compound tubuloalveolar gland. (15-20 lobes) Stroma- CT (suspensory ligaments of Cooper), fat (absent beneath areola and nipple) |
|
|
Arterial supply |

Axillary artery -3 branches Subclavian artery- 1 branch Posterior intercostal artery branches from behind. |
|
|
Nerve supply |
Anterior and lateral cutaneous branches of 4th to 6th intercostal nerve. Sensory fibre- to skin Autonomic fibre- to BVs and muscles. |
|
|
Lymphatic drainage |
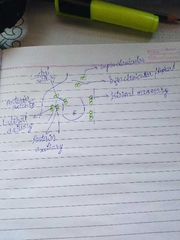
Lymph nodes- 1. Axillary lymph nodes: Anterior (pectoral), posterior (Subscapular), lateral (humeral), central, apical (infraclavicular) 2. Internal mammary / parasternal lymph nodes. 3. Others: supraclavicular, deltopectoral/cephalic, posterior intercostal, subdiaphragmatic and subperitoneal lymph plexus. |
|
|
Development of breast |
Ectodermal thickening- Mammary ridge, milk line or line of Schultz (from axilla to groin, 4th week of intrauterine life), gland is ectodermal, stroma is mesodermal. Mammary ridge converted into Mammary pit- gives rise to secondary buds which divide to form lobes. |
|
|
Clinical aspects |
1. Peau d'orange appearance- obstruction of superficial lymph vessels by cancer cells may produce oedema of the skin giving rise to an appearance like that of the skin of an orange. 2. Breast cancer may travel via lymphatics to abdomen. 3. Blood from nipple- can indicate intraductal carcinoma. |

