![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cancer of the lymphatic system and the lymph nodes. These are malignant cells that forms into mass. |
Lymphoma |
|
|
2 types of lymphoma |
⚪Hodgkin ⚪Non-hodgkin –- most common |
|
|
Etiology of lymphoma |
✅In hodgkin lymphoma – the cancer usually affect one lymph node after another in order. ✅In non-hodgkin lymphoma – tumors may arise in different lymph nodes, skipping some node |
|
|
Risk factors for hodgkin lymphoma |
✔Ages between 15 and 34 years and over 55 years ✔Common in men ✔Common in U.S, Canada, Northern Europe ✔Siblings, twins ✔Affluence ✔HIV |
|
|
Risk factors for non-hodgkin lymphoma |
✔Age 60 and older ✔White american ✔Gender ✔Radiation and chemicals ✔Immunodeficiency ✔Infection ✔Breast implants ✔Body weight and diet |
|
|
Curable form of lymphoma |
Hodgkin's lymphoma |
|
|
Signs & symptoms of hodgkin's lymphoma |
✅swollen lymph nodes ✅Cough and shortness of breath ✅Fever ✅Tiredness ✅Weight loss ✅Itchy skin |
|
|
Diagnosis for hodgkin's lymphoma |
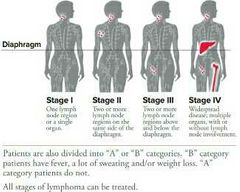
lymph node biopsy – surgeon remove all or part of an enlarged lymph nodeStaging |
|
|
Subtypes of hodgkin lymphoma |
✔Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma – 95% of patient have this type - Nodular sclerosis - Mixed cellularity - Lymphocyte depleted - Lymphocyte- rich classical ✔Nodular Lymphocyte- predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma |
|
|
Tx of hodgkin lymphoma |
Chemotherapy |
|
|
Absence of this type of cell is a characteristic of non-hodgkin lymphoma |
reed- sternberg cell |
|
|
A condition which is a result of genetic mutation, and divide uncontrollably being neoplastic cells. |
Non-hodgkin lymphoma |
|
|
Types of non-hodgkin lymphoma |
According to site: ✅Nodal lymphomas – found in the lymph nodes ✅Extranodal lymphoma – found in other tissue or organs
B-cell Lymphoma: Diffuse large B cell Lymphoma – most common and is aggressive Follicular lymphoma – indolent lymphoma, caused by translocation of Chromosome 14 and chromosome 18. causing blocked cell death. Burkitt lymphoma – highly aggressive lymphoma, from chromosal translocation. Increased cell division. Mantle cell Lymphoma- aggressive lymphoma, chromosomal translocation between 14 and 11. cell growth Marginal zone lymphoma – indolent lymphoma. ---Common type is Mucosa Associated Lymphoid tissue – lining of the stomach
T-cell lymphoma: Adult t-cell lymphoma – caused by t- lymphoytopic virusMycosis fungoides – t-cell lymphoma of skin. Has ‘’cerebriform” nucleus. |
|
|
This virus infects lymphocytes , incorporates DNA into the host DNA. |
Epstein Barr virus |
|
|
Indolent type of lymphoma that produce M proteins causing blood gets thick and viscious |
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma |
|
|
Condition in which M proteins cause blood to get thick and viscious |
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. |
|
|
Types of T-cell lymphoma Types of T-cell lymphoma |
✔Adult t-cell lymphoma – caused by t- lymphoytopic virus ✔Mycosis fungoides – t-cell lymphoma of skin. Has ‘’cerebriform” nucleus. |
|
|
Types of B-cell lymphoma |
✔Diffuse large B cell Lymphoma – most common and is aggressive ✔Follicular lymphoma – indolent lymphoma, caused by translocation of Chromosome 14 and chromosome 18. causing blocked cell death. ✔Burkitt lymphoma – highly aggressive lymphoma, from chromosal translocation. Increased cell division. ✔Mantle cell Lymphoma- aggressive lymphoma, chromosomal translocation between 14 and 11. cell growth ✔Marginal zone lymphoma – indolent lymphoma.---Common type is Mucosa Associated Lymphoid tissue – lining of the stomach |
|
|
Symptoms of non-hodgkin lymphoma |
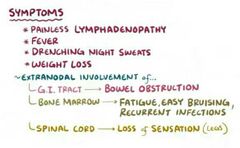
|
|
|
Diagnosis & Tx of non-hodgkin lymphoma |

|

