![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ROM Test:
•None Muscle Test: 19A •Supine, flex hip 75º, with 110º of knee flexion. (toward butt) •Abduct femur 10º •Internally rotate femur to abduct tibia (try to get back to midline) •Dorsiflex and fully externally rotate the foot •Long head has more posterior superior attachment, sits a little further from the joint in the knee flexed position. Tester: •Stand at the base of the patient •Stabilize the front of the knee •Action hand cups the heel •Pull out and up (extension at the knee) Palpation: Ischial Tuberosity (Lower/posterior aspect) •Patient lying prone •Palpation on lower posterior aspect of ischial tuberosity. •Long head ties into the Sacrotuberous ligament which makes it play a role in SI joint stability. •Same thing as before, basically cover the whole ischial tuberosity as they all mash together. Head of the Fibula •Patient lying prone •Common attachment site with the Short Head •Find the fibular head, DO NOT wrap around it the same way we did for semimembranosus (want to avoid the peroneal nerve which is on the inside of the head of the fibula). •Have them flex knee, feel tendon, follow the tendon around to the head of the fibula. •Come right on the most posterior and lateral aspect of the head of the fibula, avoid the inside (Peroneal nerve). •Don’t compress into the tissue, come into it, and hit the head of the fibula, and come lateral on it. |
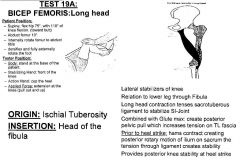
Biceps Femoris: Long Head
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Muscle Test: 19B •Supine, flex hip 75º, with 70º of knee flexion. (further away) •Abduct femur 10º •Internally rotate femur to abduct tibia •Dorsiflex and fully externally rotate the foot Tester: •Stand at the base of the patient •Stabilize the front of the knee •Action hand cups the heel •Pull out and up (extension at the knee) Palpation: •You can treat both heads of Biceps Femoris at the same time if they both tested weak. Posterior Femoral Shaft (lower 1/3) •Patient lying prone •Have them flex knee to create slack, feel lateral tendon, come lateral to that and slide right into the lower lateral 1/3 of the posterior shaft of the femur and palpate deep into lower femoral shaft •Lower 1/3, lateral aspect, try to stay outside of the tendon •On the lower lateral supracondylar ridge (ridge above the lateral condyle) Head of the Fibula •Patient lying prone •Have client flex knee and follow tendon into fibular head •Stay lateral to avoid the peroneal nerve •Common attachment with the long Head |
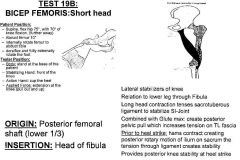
Biceps Femoris: Short Head
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 18: Hip External rotation with hip and knee flexion •Test 25: Hip External Rotation Muscle Test: 9 •Supine, flex hip 110º with full external rotation of the femur at the hip. Tibia parallel to the table. Tester: •Stand on side of leg being tested. •Stabilize the lateral side of knee. •Action hand cups the heel. •Pull toward you (apply force into internal rotation). Palpation: Ischial Spine (Outer Surface) •If you come up and over from the superior ischial tuberosity at a 45º angle you will find the ischial spine and continue to palpate on the ischial spine. •Palpate up and in from the top of the ischial tuberosity move 45º up and in to feel the bump of the spine of the ischium. Greater Trochanter Fossa •Superior, medial, deep aspect of trochanter into the fossa •Feel for tip of greater trochanter, curl deep to the top corner of greater trochanter (superior, medial, posterior, deep, in the fossa) around the tip. |
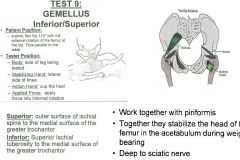
Gemellus Superior/Inferior
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 21: Active Hip Extension •Test 23: Hip Extension with External Rotation Muscle Test: 1A •Try to keep head in neutral, lie head in face rest, arms at sides •Lie prone, externally rotate femur 45º, abduct leg 10º, fully extend hip Tester: •Stand on side being tested •Stabilizing hand on opposite PSIS •Action hand on lower 1/3 of involved thigh •Push down and slightly out Palpation: •All fibers have same insertion •If one tests weak, treat as a whole •Find the tip of the coccyx & lateral posterior PSIS, palpate line in between those two. Lateral to PSIS down to top of Sacrum •Attaches to lateral aspect of PSIS down to the top of the sacrum •Find top of ilium, come around, find two big bumps (PSIS) •Sink right down into the posterior lateral aspect of PSIS Gluteal Tuberosity of femur: approx 2 inches •Come into side below crest of ilium, work way down until you find the top of the greater trochanter, work way around to the posterior aspect, have them gently lift their leg, and if you’re in the right spot it will lift you directly off the bone. •Work way around to the back, feel for bump, and work your way down the bump (gluteal tuberosity= big bump off the lower portion of greater trochanter) Treat attachment into the IT-band •Gluteal tuberosity is going to attach into the IT band, which is about 2 inches down from the gluteal tuberosity. We are going to treat a span of about two inches from gluteal tuberosity to IT band. Follow IT-band to lateral condyle and to tibial tubercle (between patella & head of fibula) •Follow IT band into the lateral condyle of femur and tibial tubercle, treat those insertions of IT band •Come down squeeze into sides of femur, feel lateral aspect of lateral condyle, feel IT band, feels plucky, come into where that meets the bone, work down that line just below that, it will be a fascial attachment into the IT band, about 2 inches. •Flex the knee, feel for tibial tuberosity and head of fibula, the tibial tubercle will be the bump in between. |

Gluteus Maximus: Iliac Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 21: Active Hip Extension Muscle Test: •Prone fully extend hip, slight abduction 10º •Push straight down for resistance Tester: •Stand on side being tested •Stabilizing hand on opposite PSIS •Action hand on lower 1/3 of involved thigh •Push down (hip flexion) Palpation: •All fibers have same insertion • If any one tests weak, treat as a whole. •Find the tip of the coccyx & lateral posterior PSIS, palpate line in between those two. •Attaches to posterior lateral portion of the sacrum Lateral Border of Sacrum •Attaches to posterior lateral portion of the sacrum. Gluteal Tuberosity of femur: approx 2 inches •Come into side below crest of ilium, work way down until you find the top of the greater trochanter, work way around to the posterior aspect, have them gently lift their leg, and if you’re in the right spot it will lift you directly off the bone. •Work way around to the back, feel for bump, and work your way down the bump (gluteal tuberosity= big bump off the lower portion of greater trochanter) Treat attachment into the IT-band •Gluteal tuberosity is going to attach into the IT band, which is about 2 inches down from the gluteal tuberosity. We are going to treat a span of about two inches from gluteal tuberosity to IT band. Follow IT-band to lateral condyle and to tibial tubercle (between patella & head of fibula) •Follow IT band into the lateral condyle of femur and tibial tubercle, treat those insertions of IT band •Come down squeeze into sides of femur, feel lateral aspect of lateral condyle, feel IT band, feels plucky, come into where that meets the bone, work down that line just below that, it will be a fascial attachment into the IT band, about 2 inches. •Flex the knee, feel for tibial tuberosity and head of fibula, the tibial tubercle will be the bump in between. |
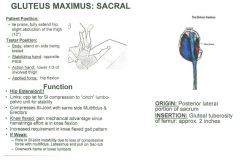
Gluteus Maximus: Sacral Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 21: Active Hip Extension •Test 22: Hip Extension with Internal Rotation Muscle Test: •Full internal rotation of femur, fully extend hip Tester: •Stand on side being tested •Stabilizing hand on opposite PSIS •Action hand on lower 1/3 of involved thigh •Push down Palpation: •All fibers have same insertion •If any one tests weak, treat as a whole. •Attaches to posterior lateral portion of the coccyx. Lateral Border of Coccyx •Attaches to posterior lateral portion of the coccyx. Gluteal Tuberosity of femur: approx 2 inches •Come into side below crest of ilium, work way down until you find the top of the greater trochanter, work way around to the posterior aspect, have them gently lift their leg, and if you’re in the right spot it will lift you directly off the bone. •Work way around to the back, feel for bump, and work your way down the bump (gluteal tuberosity= big bump off the lower portion of greater trochanter) Treat attachment into the IT-band •Gluteal tuberosity is going to attach into the IT band, which is about 2 inches down from the gluteal tuberosity. We are going to treat a span of about two inches from gluteal tuberosity to IT band. Follow IT-band to lateral condyle and to tibial tubercle (between patella & head of fibula) •Follow IT band into the lateral condyle of femur and tibial tubercle, treat those insertions of IT band •Come down squeeze into sides of femur, feel lateral aspect of lateral condyle, feel IT band, feels plucky, come into where that meets the bone, work down that line just below that, it will be a fascial attachment into the IT band, about 2 inches. •Flex the knee, feel for tibial tuberosity and head of fibula, the tibial tubercle will be the bump in between. |
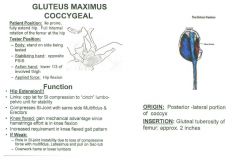
Gluteus Maximus: Coccygeal Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 2: Straight leg, abduction & internal rotation •Test 24: Hip Internal Rotation Muscle Test: 10A •Supine, abduct the hip 30º, fully internally rotate the femur Tester: •Stand at the base of the patient •Stabilize the opposite ankle •Action hand on lateral side of the distal tibia. •Apply force into adduction toward the midline. Palpation: Outer Surface of Ilium below Iliac Crest (Anterior 1/2) •Have them lie on their side •Come/cup around iliac crest thumb to finger •Palpate upward into anterior ½ of iliac crest, palpate up and in •Try to get under the lip of the ilium more than the TFL, getting the anterior ½ •Once you get off the lip, come down about 1 finger widths space, and then down a little bit, and you are palpating towards the lip Greater Trochanter (Lateral/Superior & Posterior Border) •Landmark the trochanter, get on the superior lateral aspect, a little bit more posterior •Palpate downward onto posterior lateral surface of greater trochanter. |
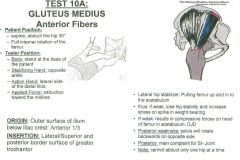
Gluteus Medius: Anterior Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Muscle Test: 10B •Supine, abduct the hip 30º, with no rotation Tester: •Stand at the base of the patient •Stabilize the opposite ankle •Action hand on lateral side of distal tibia. •Apply force into adduction toward the midline. Palpation: •Gluteus Medius middle fibers bring leg back to neutral from internal or external position (like rectus abdominis). Outer Surface of Ilium below Iliac Crest (Middle 1/3) •Have them lie on their side •Come/cup around iliac crest thumb to finger •Palpate upward into middle 1/3 of iliac crest, palpate up and in •Try to get under the lip of the ilium more than the TFL, getting the middle 1/3 •Once you get off the lip, come down about 1 finger widths space, and then down a little bit, and you are palpating towards the lip Greater Trochanter (Lateral/Superior & Posterior Border) •Landmark the trochanter, get on the superior lateral aspect, a little bit more posterior •Palpate downward onto posterior lateral surface of greater trochanter. |
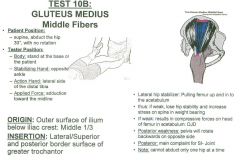
Gluteus Medius: Middle Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 6: Straight leg, external rotation of the femur •Test 7: Straight leg, abduction and external rotation Muscle Test: 10C •Supine, abduct the hip 30º, Fully externally rotate the femur Tester: •Stand at the base of the patient •Stabilize the opposite ankle •Action hand on the lateral side of the distal tibia •Apply force into adduction toward the midline. Palpation: Outer Surface of Ilium below Iliac Crest (Posterior 1/3) •Have them lie on their side •Come/cup around iliac crest thumb to finger •Palpate upward into posterior 1/3 of iliac crest, palpate up and in •Try to get under the lip of the ilium more than the TFL, getting the posterior 1/3 •Once you get off the lip, come down about 1 finger widths space, and then down a little bit, and you are palpating towards the lip Greater Trochanter (Lateral/Superior & Posterior Border) •Patient Lying on side •Landmark the trochanter, get on the superior lateral aspect, a little bit more posterior •Palpate downward onto posterior lateral surface of greater trochanter. |
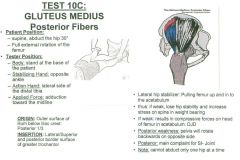
Gluteus Medius: Posterior Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 2: Straight leg, abduction & internal rotation •Test 4: Straight leg, hip flexion, abduction and internal rotation •Test 17: Hip internal rotation with hip and knee flexion Muscle Test: 11A •Supine, flex and abduct the femur 30º •Full internal rotation of the femur Tester: •Stand at the base of the patient •Stabilize the opposite ankle •Action hand on lateral side of the distal tibia. •Apply force directly across into adduction toward the midline. Palpation: Ilium (Anterior ¼ of Outer Middle Portion) •Patient lying on side •Landmark Iliac Crest, landmark Superior border of Greater Trochanter, its halfway in between. •Getting 2-3 finger widths, come through tissue, sink down and slide up and in superiorly to the ilium •Apply direct pressure into anterior quarter of ilium. •Going to feel a hardness, or resistance (not bone), do not go through the resistance. Greater Trochanter (Anterior Border) •Patient lying on side •Attaches more anteriorly on the trochanter, which gives it a component of hip flexion. •Landmark the trochanter, come more anterior •Palpate down and in to anterior, superior portion of greater trochanter |
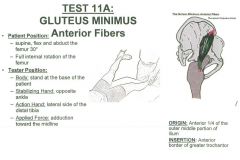
Gluteus Minimus: Anterior Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 7: Straight leg, abduction and external rotation •Test 9: Straight leg, hip flexion, abduction and external rotation •Test 20: Hip flexion, abduction, and external rotation Muscle Test: •Supine, flex and abduct the femur 30º •Full external rotation of the femur Tester: •Stand at the base of the patient •Stabilize the opposite ankle •Action hand on lateral side of the distal tibia. •Apply force into adduction toward the midline. Palpation: Ilium (Anterior 2nd ¼ of Outer Middle Portion) •Patient lying on side •Landmark Iliac Crest, landmark Superior border of Greater Trochanter, its halfway in between. •Getting 2-3 finger widths, come through tissue, sink down and slide up and in superiorly to the ilium •Apply direct pressure into anterior 2nd quarter of ilium. •Going to feel a hardness, or resistance (not bone), do not go through the resistance. Greater Trochanter (Anterior Border) •Patient lying on side •Attaches more anteriorly on the trochanter, which gives it a component of hip flexion. •Landmark the trochanter, come more anterior •Palpate down and in to anterior, superior portion of greater trochanter |

Gluteus Minimus: Lateral Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 17: Hip internal rotation with hip and knee flexion •Test 25: Hip External Rotation Muscle Test: 7A •Prone, flex knee 90º, abduct thigh 10º with full external rotation of femur. •Monitor pelvis/sacrum to make sure they don’t compensate. Tester: •Stand on same side as leg being tested •Stabilize the opposite pelvis •Action hand on the medial ankle •Pull out (internal rotation of the hip) •Make sure your arm is perpendicular to the leg (lever) which determines your direction of pull. Muscle Test: 7B •Supine, flex hip and knee to 110º, with maximum internal rotation of the femur •110º at knee and hip Tester: •Better to stand on opposite side and pull leg toward you as they resist. •Stabilize the medial knee •Action hand needs to cup hand around ankle •Apply force into external rotation. Palpation: •IF EITHER OR BOTH TESTS ARE WEAK, SAME PALPATION. •At neutral the Piriformis is an external rotator•Past 90º it’s an internal rotator•At 90º Piriformis is an abductor. Sacrum •Lie them prone, & palpate on sacrum ½ way between PSIS and Coccyx •Find where you were for Gluteus Maximus, instead of palpating on the sacrum, slip off the sacrum and come along and get as much of the tissue as it comes out underneath the sacrum, (slide past the sacrum & get as deep as possible) •Not going to be a bony palpation, its going to be a tissue after it exits out from underneath the bone •Feel the Sacrum and drop off the edge of it, and get as deep as you can along the edge of the sacrum •You’ll be getting into more of the tendinous junction •Just below gapping of SI joint •Done want to palpate sacrum, palpate the tissue underneath the sacrum. Greater Trochanter (Superior-Posterior Border) •Palpate on posterior/superior aspect of the greater trochanter •Find posterior aspect of trochanter •Look for the posterior-superior corner •Move the leg, wiggle it back and forth to try to weasel your way into that posterior superior corner, trying to “hook in” on the tip |

Piriformis
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 18: Hip External rotation with hip and knee flexion •Test 25: Hip External Rotation Muscle Test: 8 •Supine, flex hip 75º with full external rotation of the femur at the hip. Tibia parallel to the table. •Keep knee and hip in the sagittal plane as you externally rotate. Tester: •Stand on side of leg being tested •Stabilize the lateral side of knee •Action hand cups heel •(Pull out at the heel while stabilizing the knee, applying a force into internal rotation. Palpation: Ischial Tuberosity (Superior Lateral) •Go to gluteal fold, and find ischial tuberosity. •Put hand on back of thigh, come towards midline, not the crease, and push down and into the inferior ischial tuberosity •Palpate up and in to the bottom of the ischial tuberosity for a landmark. •Bring other hand around and move in perpendicular to the bottom of the ischium. •Walk your way up the bone to the superior-posterior aspect •Find that most posterior-superior aspect, drop off the side, into the lateral aspect, palpate 2 finger widths. Intertrochanteric crest •Easier to find greater trochanter if you internally rotate the femur. •Intertrochanteric Crest = between the two trochanters. •Is deep to the gluteal tuberosity •Get as deep as the Piriformis, but more inferior and medial •If you internally rotate the femur it will bring the ledge of the trochanter straight up towards you, feel for the tension, go to the posterior superior corner and palpate just posterior and inferior. |

Quadratus Femoris
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 3: Straight Leg, Hip flexion & Internal Rotation Muscle Test: •Lie supine, flex hip 30º, keep the leg in neutral position: test •Repeat test with the femur fully internally rotated for reflected head. •Keep leg neutral in sagittal plane and push straight down (test 1) •Test 2 Reflected head is the same thing but internally rotate, pushing straight down Tester: •Stand at base of patients feet •Stabilize the opposite ankle •Action hand on top of the distal tibia •Push straight down (extension) Palpation: •The Rectus femoris works as a cable •The moment arm lengthens during hip flexion, giving it the MAd, as it gets further away from the hip socket. •During knee flexion the rectus femoris lengthens at the hip and shortens at the knee. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine (AIIS): •Find that ASIS, come down and in, work along that crease of the hip, feel for that bump, palpate •You can have them extend their leg a little bit & try and follow that tendon into that AIIS, palpate the inferior aspect of the AIIS. Groove of Upper Brim of Acetabulum above Femoral Head: •Come onto the AIIS, go 2 finger widths down and in, make sure you feel for pulse, find a flat spot, the brim of the Acetabulum will feel relatively flat just inferior and medial to where you were on the AIIS. Go inferior and medial to brim of Acetabulum and palpate the anterior aspect of brim of Acetabulum Base of Patella: •Block kneecap (stabilize it) and palpate the most superior aspect of it, the direction the muscle is coming into the patella. •Go to very superior aspect and palpate while holding the kneecap Tendon attachment to Tibial Tuberosity: •Then follow that patella tendon down and get onto the top, superior aspect of the tibial tuberosity, the direction of force of palpation should be down onto that tibial tuberosity. (want to palpate where the tendon comes into the bump which will be superior and there will be more tissue there) •Palpate directly downward on top of the tibial tuberosity at the tissue bone junction. |

Rectus Femoris
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 18: Hip External rotation with hip and knee flexion •Test 20: Hip flexion, abduction, and external rotation Muscle Test: 6 •Lie supine, flex, abduct, and externally rotate femur at hip (lateral malleolus under opposite knee) •Place ankle just below opposite knee. •Watch rotation of pelvis upon abducting. •People will try to bring the knee down via spinal rotation if they cant get that abduction of the hip. Tester: •Stand at base of patient •Stabilize the ipsilateral knee •Action hand on posterior aspect of distal tibia •Pull their ankle toward you (knee extension while maintaining the abducted position) Palpation: •When the foot is fixed: anterior pelvic tilt/hip flexion ASIS: •Easier to get into the ASIS if they flex the hip •Let leg abduct and fall out onto your leg and relax in the abducted position. •Position foot on opposite knee to abduct thigh. •Find ASIS, come up underneath (inferior to ASIS) and palpate inferior ASIS. Pes-Anserine: •Palpate most anterior/lateral on tibia relative to pes-anserine, at the Supero-medial tibial shaft. •Below medial condyle of tibia, come to flat part medial to tibial tuberosity (palpate coming across toward you) •Sartorius is the most lateral anterior of the attachments at pes anserine |

Sartorius
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Muscle Test: 17 •Supine, flex hip 75º, with 80º of knee flexion. (further away) •Abduct femur 10º •Internally rotate femur to abduct tibia (internally rotate femur enough to get it back to midline) •Dorsiflex and fully internally rotate the foot. Tester: •Stand at the base of the patient •Stabilize the front of the knee •Action hand cups the heel •Pull out and up (extension at the knee) •Pull more up than out. Palpation: Ischial Tuberosity: •Patient lying prone •Palpation is deepest and most medial on the Ischial Tuberosity •Semitendinosus and Semimembranosus criss-cross, so think of it as filling in the whole ischial tuberosity. •Not coming as posterior as the Quadratus Femoris, or as Superior as the Inferior Gemellus. Medial Condyle of Tibia (Posterior Aspect): •Patient lying prone •Have client flex knee and follow tendon into posterior medial tibia. •Below the tibial plateau •Feel for medial condyle of the femur, feel the top of the tibial plateau, follow that back and around, and compress inward to the posterior aspect of medial condyle of the tibia. •Palpate down to the condyle. •Come in medially. •Feel kind of a groove you can get into. |
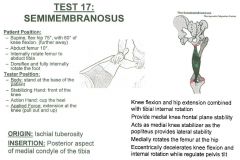
Semimembranosus
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Muscle Test: 18 •Supine, flex hip 75º, with 110º of knee flexion. (toward butt) •Abduct femur 10º •Internally rotate femur to abduct the tibia •Dorsiflex and fully internally rotate the foot. •REMEMBER AS SEMI-110DINOSUS! Tester: •Stand at the base of the patient •Stabilize the front of the knee •Action hand cups the heel •Pull out and up (extension at the knee) •Pull more out than up •The only action you want is at the knee Palpation: Ischial Tuberosity (Posterior): •Patient lying prone •Palpation on lower posterior aspect of ischial tuberosity •Deepest and most medial on the Ischial Tuberosity •Semitendinosus and Semimembranosus criss-cross, so think of it as filling in the whole ischial tuberosity. •Not coming as posterior as the Quadratus Femoris, or as Superior as the Inferior Gemellus. Pes Anserines Tendon (Proximal, Medial Shaft of Tibia): •Patient lying prone •Have client flex knee and follow most superficial tendon around to front of tibia. •Has a big tendon into the pes anserines |

Semitendinosus
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Test 3: Straight Leg, Hip flexion & Internal Rotation •Test 4: Straight leg, hip flexion, abduction and internal rotation •Test 17: Hip internal rotation with hip and knee flexion •Test 24: Hip Internal Rotation Muscle Test: 5 •Lie supine, flex hip 30º, fully internally rotate the femur, abduct the leg 20º Tester: •Stand at base of patients feet •Stabilize the opposite ankle •Action hand on top of the distal tibia •Push down and in (extension and adduction through the oblique plane) Palpation: •Similar to Gluteus Maximus •TFL kind of like the lateral Quad •Sits anterior/lateral in the oblique plane •During testing it has to be in the oblique plane. •TFL is Bi-articular as it crosses the hip & through IT-band it crosses the knee. •If weak, the pelvis can drop laterally and stress the ankle. ASIS: •Supine, up and into ASIS from posterior lateral position •Palpate up and under lip, posterior-lateral, not actually on ASIS, palpate on the thickening of inferior lip to ASIS Ilio-tibial tract (just below joint capsule): •Palpate into ilio-tibial tract just below joint capsule •Palpate at insertion into IT-Tract Lateral Femoral Condyle: •Palpate superior portion of lateral condyle of femur Tibial tubercle: •Palpate insertion into tibial tubercle (between patella and fibula, superior lateral) |

TFL
|

