![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
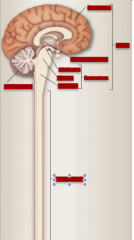
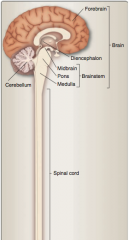
Brain, brainstem, forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain, pons, medulla, cerebellum, spinal cord |
|
|
|
Identify the primary germ layer:
Develops into internal organs Gives rise to somites (bone, skeletal muscle, and dermis of skin) Develops into neural structures and epidermis of the skin
Innervation to mesodermic structures is through what part of nervous system? To endodermic structures? |
Endoderm Mesoderm Ectoderm
Somatic Visceral |
|
|
The process of a longitudinal band of ectoderm thickening to form the neural plate around week 3 of gestations is initiated by what? |
Notochord => the primary induced in the early embryo |
|
|
When do neural folds begin to close, forming a neural tube?
What end of the tube develops into brain? What end into spinal cord? |
End of week 3
Rostral = brain Caudal = spinal cord
|
|
|
What cells (as the fusion of the neural tube occurs and they dissociate from the top crest of each neural fold) migrate away from the neural tube and differentiate into a variety of cell types including the sensory neurons in the ganglia of the spinal nerves and some cranial nerves (V, VII, VIII, IX, and X), postganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous system, the Schwann cells of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), and the adrenal medulla. |
Neural crest cells |
|
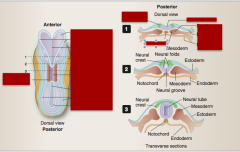
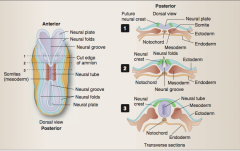
Somites Neural folds Neural plate Cut edge Neural tube Neural groove Neural plate Neural folds Ectoderm Endoderm Future neural crest |
|
|
|
At what week does development of the brain begin? |
4 |
|
|
What are the three primary vesicles and where do they appear on the neural tube (what end)? |
Prosencephalon Mesencephalon Rhombencephalon |
|
|
What are the five secondary vesicles and at what week do they appear?
|
Telencephalon Diencephalon Mesencephalon Metencephalon Myencephalon
|
|
|
What are the three components of the brain? |
Forebrain Midbrain Hindbrain |
|
|
What does the forebrain consist of |
Cerebral hemispheres and deep structures |
|
|
What are the midbrain and hindbrain collectively referred to as? |
Brainstem and cerebellum |
|
|
What are the three major vesicles from the neural tube? Then identify the five secondary vesicles. |
Prosencephalon => telencephalon and diencephalon Mesencephalon => mesencephalon Rhombencephalon => metencephalon and myelencephalon |
|
|
What do the telencephalon and diencephalon develop into? |
Telencephalon => cerebral hemispheres
Diencephalon => thalamus, hypothalamus, and subthalamus |
|
|
What does the mesencephalon develop into? |
Midbrain |
|
|
What do the metencephalon and myencephalon develop into? |
Metencephalon => pons and cerebellum Myencephalon => medulla |
|

Identify: Myencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, diencephalon, telencephalon, prosencephalon, rhombencephalon, neural crest, neural tube |
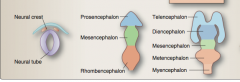
|
|
|
Forebrain: Ventral surface is also what surface? Dorsal suface is what surface? |
Ventral = inferior Dorsal = superior |
|
|
Brainstem and spinal cord: Ventral surface is what surface? Dorsal surface is what surface? |
Ventral = anterior Dorsal = posterior |
|
|
What is the term for a collection of neuronal cell bodies?
Collection of nerve cell bodies within the CNS?
Collection of nerve cell bodies in PNS?
Sum of all fiber tracts?
Bundle of axons in PNS?
Bundle of axons traveling from one area to another? |
Gray matter
Nucleus
Ganglion
White matter
Tract (myelination => "white appearance")
Nerve |
|
|
What are ridges in the cortex called? What are grooves in the cortex called? What separates the two hemispheres? What separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobe? What separates the occipital lobe from the parietal lobe? |
Gyri Sulci Longitudinal fissure Lateral (Sylvian) fissure Parietooccipital fissure |
|
|
What is the frontal lobe separated from the temporal lobe by?
What contains the primary motor areas in the frontal lobe? |
Central sulcus Pre-central gyrus |
|
|
That is the area of the frontal lobe associate with emotion, motivation, personality, initiative, judgement, ability to concentrate, and social inhibitions?
What area on the medial surface is also important for modulating emotional aspects of behavior? |
Prefrontal association areas
Cingulate gyrus |
|
|
Located in the parietal lobe, what is the primary somatosensory area of the cortex? |
Postcentral gyrus |
|
|
Receptive or sensory aspects of language are also processed int he parietal lobe primarily in the dominant (typically left) hemisphere in what area? |
Wernicke area |
|
|
Which lobe involves aspects of spatial orientation and perception, including self-perception and interaction with the world around us? |
Parietal lobe |
|
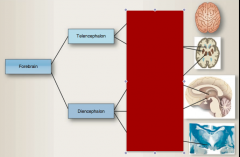
Complete |
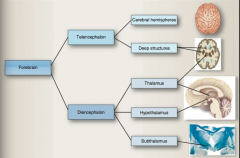
|
|
|
Which lobe is involved primarily in processing visual information? How is it separated from the parieto-occipital sulcus? The primary visual area is located on the medial side of what sulcus? |
Occipital Parieto-occipital sulcus Calcarine sulcus |
|
|
What lobe is important for processing auditory information? What is the area where our ability to hear and interpret what we hear is processed? |
Temporal lobe
Superior temporal gyrus |
|
|
What are the two components of limbic lobe? |
Cingulate and parahippocampal gyri |
|
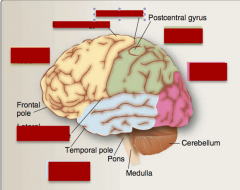
Identify frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe, precentral gyrus, central sulcus, lateral (Sylvian fissure). |
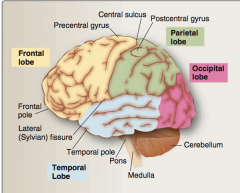
|
|
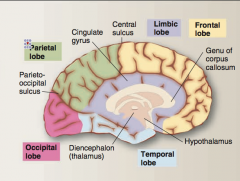
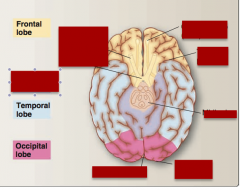
Idenfity occipical lobe, temporal lobe, parietal lobe, frontal lobe, limbic lobe, central sulcus, parieto-occipital sulcus, hpothalamus, thalamus |
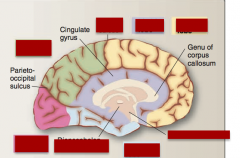
|
|
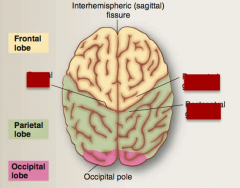
Identify precentral gyrus, postcentral gyrus, central sulcus. |
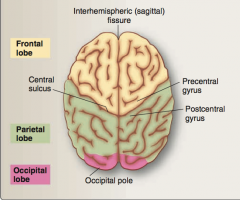
|
|
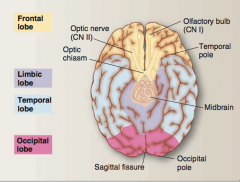
Identify olfactory bulb (CN I), optic nerve (CN II), optic chiasm, temporal pole, midbrain, limbic lobe, occipital pole, sagittal fissure. |
|
|
|
What is a group of interconnected, interacting nuclei within the forebrain, diencephalon, and midbrain? |
Basal ganglia |
|
|
What are the forebrain components of the basal ganglia?
What do the basal ganglia play a critical role in? |
Caudate and lenticular (putamen and globus palidus) nuclei
Initiation and control of voluntary movements. |
|
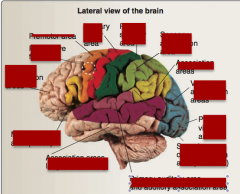
Identify: frontal association areas, frontal eye fields, primary motor area, premotor area, association areas, sensory association, primary sensory, visual association areas, primary visual area, primary auditory area, speech comprehension (Wernicke), primary auditory area, motor speech (Broca). |
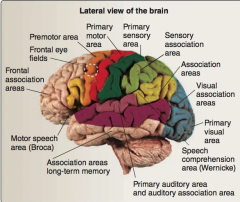
|
|
Identify: primary visual cortex, visual association areas, primary sensory areas, sensory association areas, premotor area, primary motor area, frontal association areas, limbic areas, association areas long-term memory. |
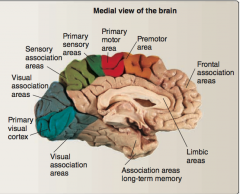
|
|
|
The _____ system consists of interconnected and interacting structures that provide a neuroanatomical substrate for drive-related and emotional behaviors and play a role in learning and memory. The deep forebrain components of the limbic system include the _____ and _____, both of which are located in the temporal lobe. |
The limbic system consists of intercon- nected and interacting structures that provide a neuroanatomi- cal substrate for drive-related and emotional behaviors and play a role in learning and memory. The deep forebrain components of the limbic system include the amygdala and hippocampus, both of which are located in the temporal lobe (see Figure 2.10). |
|
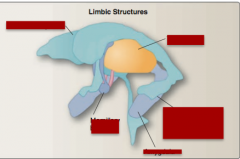
Identify: ventricular system, maxillary bodies, amygdala, hippocampus in the floor of the lateral ventricle, thalamus. |
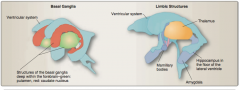
|
|
|
What fibers connect cortical regions in the same hemisphere? What fibers reciprocally connect areas of cortex in one hemisphere with corresponding areas of opposite hemisphere? What fibers carry information to and from cerebral cortex?
What is the largest set of commissural fibers? Largest set of projection fibers? |
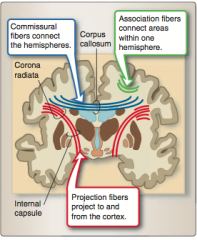
Corpus callosum Corona radiata (bundled into the internal capsule and contains all the fibers traveling among the cortex, spinal cord, and deep forebrain structures). |
|
|
What is the critical processing station for all sensory information (except olfactory) and plays key roles in processing motor information, integrating higher order cognitive and emotional information, and in regulating cortical activity (the "gatekeeper" to the cortex)?
|
Thalamus |
|
|
What structure is structurally part of the diencephalon but functionally part of the limbic system. It plays key roles in coordinating and integrating endocrine, auto- nomic, and homeostatic functions? |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
What structure is part of the basal ganglia and plays an important role in modulating and inte- grating voluntary movement and muscle tone? |
Subthalamus |
|
|
Through the activity of what structures does the brainstem achieve integrative function? |
Reticular formation nuclei |
|
|
What tract that mediates voluntary motor activity travels through the cerebral peduncles? |
Corticospinal tract |
|
|
What structure connecting the third and fourth ventricles is found in the dorsal area of the midbrain? |
Cerebral aqueduct |
|
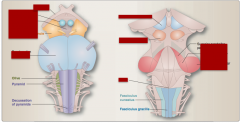
Identify basal portion of pons, interpeduncular fossa, basis peduculi or cerebral peduncle, mamillary body, optic tract.
Also superior colliculus, inferior colliculus, superior/middle/inferior cerebellar peduncle, and obex. |
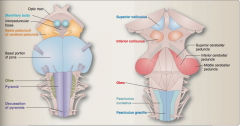
|
|
|
What does the basal pons consist of? |
Corticospinal fibers Transverse pontocerebellar fibers (carry information from pontine nuclei to opposite cerebellum through middle cerebellar peduncles) |
|
|
What does the posterior surface of the pons consist of? |
Fourth ventricle and rostral the superior cerebellar peduncles |
|
|
What is located on the anterior rostral portion of the medulla? What is contained in this?
Posterior surface? |
Pyramids with descending corticospinal fibers
Caudal part of fourth ventricle Inferior cerebellar peduncles on posterolateral surface
|
|
|
What overlies the prominent olivary nuclear complex involved in modulating motor activity on the lateral surface of the rostral medulla? |
Olives |
|
|
What is an outgrowth of the pons that functions in processing of sensory information and coordination of voluntary motor activity? |
Cerebellum |
|
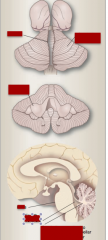
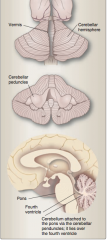
Identify vermis, cerebellar hemisphere, cerebellar peduncles, pons, fourth ventricle, cerebellum attachment to pons via peduncles. |
|
|
|
Where does the spinal cord end in newborns? Adults? |
Newborns = L3 level Adults = L1-L2 level |
|
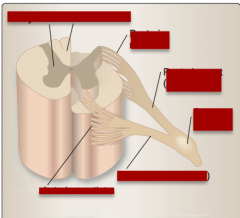
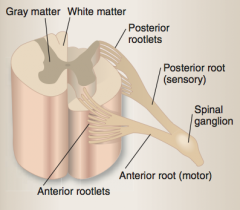
Identify gray matter, white matter, posterior rootlets, posterior root (sensory), spinal ganglion, anterior root (motor), anterior rootlets. |
|
|
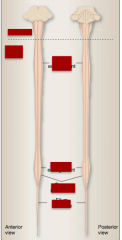
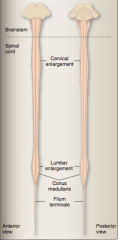
Identify brainstem, spinal cord, lumbar enlargement, cervical enlargement, conus medullaris, filum terminale |
|
|
|
CSF fills the ventricles and surrounds the brain in what space? |
Subarachnoid space |
|
|
Where is CSF produced? |
Choroid plexus (between two lateral ventricles and fourth ventricle) and some production through the brain parenchyma. |
|
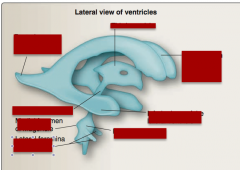
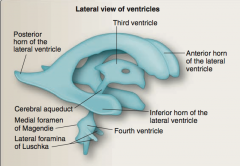
Identify posterior horn of lateral ventricle, anterior horn of the lateral ventricle, third ventricle, inferior horn of the lateral ventricle, fourth ventricle, lateral foramina of Luschka, medial foramen of Magendie, cerebral aqueduct. |
|
|
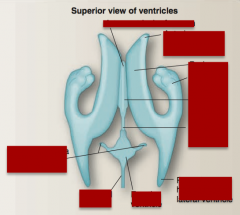
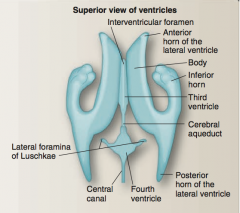
Identify interventricular foramen, body, inferior horn, anterior horn of the lateral ventricle, third ventricle, cerebral aqueduct, posterior horn of the lateral ventricle, fourth ventricle, lateral foramina of Luschkae, central canal. |
|
|
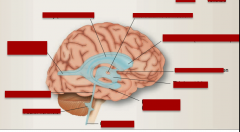
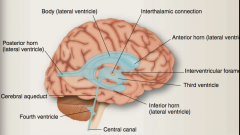
Identify body (lateral ventricle), anterior horn (lateral ventricle), inter thalamic connection, third ventricle, inter ventricular foramen, inferior horn (lateral ventricle), central canal, posterior horn (lateral ventricle), cerebral aqueduct, fourth ventricle |
|
|
|
How is CSF produced in the choroid plexus?
What is the major difference between CSF and plasma? |
Passage of substances through the fenestrated endothelium and active transport through the ependymal cells.
Passive transport and dissuasion of water to maintain osmolarity.
Major difference = protein content (much higher in serum). |
|
|
What is the main motor of CSF production?
What is the path of CSF circulation? |
Continuous production of new CSF.
Lateral => third => fourth ventricle => lateral foramina of Luschka and medial foramen of Magendie into subarachnoid space (central canal) of spinal cord. |
|
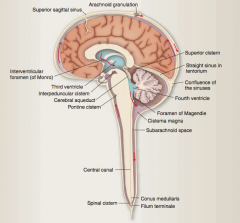
What are subarachoid cisterns? Where is the cisterna magna located? |
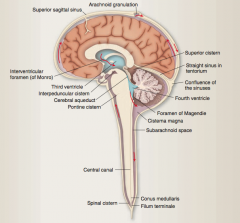
Regions with large amounts of CSF.
Caudal to the cerebellum, just above the foramen magnum. |
|
|
How is CSF reabsorbed (what is the pathway)? |
Moves posteriorly around spinal cord and back up again anteriorly => reaches arachnoid granulations that protrude into superior sagittal venous sinus => absorption driven by pressure gradient between the subarachnoid space and the venous sinus. |
|
Identify bone, pia, cortex, arachnoid, two layers of the dura, middle meningeal artery, bridging vein, venous sinus, cerebral arteries and veins/CSF/arachnoid trabeculae |
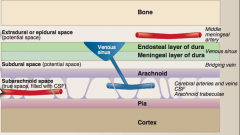
|
|
|
What type of hematoma after traumatic head injury with a skull fracture, which ruptures the middle meningeal artery. The pressure from the bleed separates the dura from the bone? |
Extradural/epidural |
|
|
What type of hematoma occurs when violent shaking of the head severs the veins connecting to the dural sinuses—“shaken baby syndrome?" |
Subdural |
|
|
What type of hematoma occur in hemorrhagic stroke or bleeding of an arterial aneurysm? |
Subarachnoid |
|
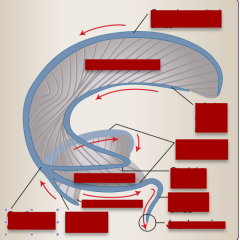
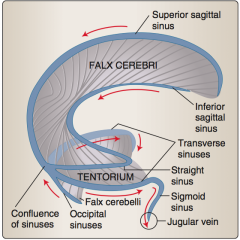
Identify superior sagittal sinus, tentorium, falx cerebri, occipital sinuses, confluence of sinuses, inferior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, transverse sinuses, sigmoid vein, jugular vein. |
|
|
|
What is a dural reflection that covers the pituitary fossa in the base of the skull?
What innervates dura mater in anterior and middle cranial fossae?
What about in the posterior cranial fossa? |
The dura mater is pain sensitive. Dura mater in the anterior and middle cranial fossae receives its innervation through meningeal branches from the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve [CN] V). Dura mater in the posterior cranial fossa is innervated by meningeal branches of the vagus nerve (CN X). |
|
|
What supplied the dura mater with blood? |
Middle meningeal artery (travel in the periosteal layer of the dura |
|
|
What small strands of collagenous material connect to the pia mater? |
Arachnoid trabeculae |
|
|
How can a subdural space be created? |
Bleed between the arachnoid and the dura. |
|
|
How do vessels enter the neuropil? |
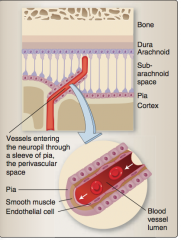
Through a sleeve of pia called the perivascular space. |
|
|
What type of hemorrhage occurs when an arterial aneurysm ruptures? |
Subarachnoid hemorrhage "worst headache of my life," sudden onset, spinal tap shows red cells in CSF |
|
|
What are the two sources of the blood supply to the brain? |
Internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries |
|
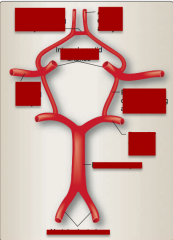
Label the parts of the circle of Willis: Vertebral arteries, posterior cerebral artery, basilar artery, middle cerebral artery, posterior communicating artery, internal carotid arteries, anterior communicating artery, anterior cerebral artery. |
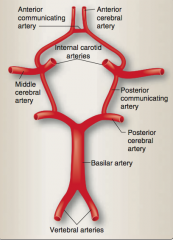
|
|
|
What is a direct extension of the internal carotid artery that supplies most of the lateral surface of the brain as well as deep structures, such as basal ganglia and the internal capsule? |
Middle cerebral artery |
|
|
What is the difference between communicating hydrocephalus and noncommunicating hydrocephalus? |
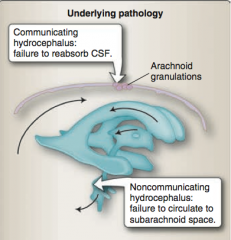
|

