![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of vitD precursor is found in animal tissue (food)? |
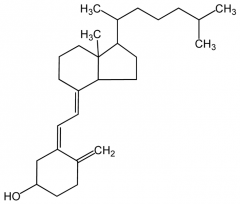
Vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol |
|
|
What type of vitD precursor is found in plants? |
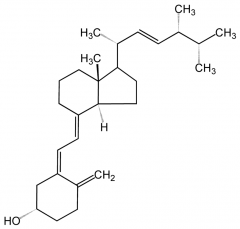
Vitamin D2 or ergocalciferol |
|
|
How is cholecalciferol synthesised in the body? |
It is made by isomerisation of 7-dehydrocholesterol in the epidermis (bottom two layers) in the presence of UVB radiation. |
|
|
What wavelength range of UVB is suitable for cholecalciferol synthesis in the skin? |
290-315 nm |
|
|
What is the active form of vitamin D? |
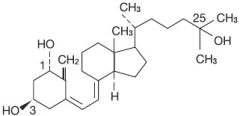
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D or 1.25-dihydroxycholecalciferol |
|
|
What is the first stage in active vitamin D synthesis? |
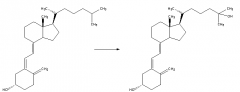
Hydroxylation of cholecalciferol by 25-hydroxylase to produce 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. Occurs in the liver. |
|
|
What is the second stage in active vitamin D synthesis? |
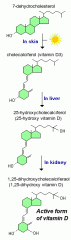
Hydroxylation of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol by 1(alpha)-hydroxylase to produce 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Occurs in the kidney. |
|
|
What is the principle action of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D? |
Maintenance of adequate plasma calcium levels |
|
|
How does 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D regulate calcium levels? (3 points) |
1) Increases Ca absorption in the gut by acting as a transcription factor that promotes gene expression of calcium transport protein (calbindin). 2) It promotes Ca reabsorption by the kidneys together with PTH. 3) It stimulates bone resorption when blood Ca is low. |
|
|
What is the suggested RDA of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D? |
RDA = 200 - 800 IU, where 1 IU = 25 ng for vit D. |
|
|
What disorders are caused by vitamin D deficiency? |
1) Rickets - in younger people with still present epiphyseal plates. 2) Osteomalacia - in adults with ossified epiphyseal lines. |
|
|
What are the features of osteomalacia? |
Impaired mineralisation of bone, leading to accumulation of unmineralised bone matrix - osteoid. Primary cause - vitamin D deficiency. |
|
|
What are the clinical features of osteomalacia? (5 points) |
1) Can be asymptomatic 2) Bone pain - local or general 3) Bone tenderness 4) Proximal muscle weakness without atrophy 5) Difficulty rising/walking |
|
|
How do you diagnose osteomalacia? |
1) Imaging: reduced BMD, osteopenia 2) Isotope bone scan 3) Serum biochemistry 4) Bone biopsy |
|
|
What is the difference between osteomalacia and rickets? |
Rickets occurs in individuals with open epiphyseal plates, whereas osteomalacia occurs in individuals with closed epiphyseal plates. |
|
|
How many different types of rickets are there and what is the difference between them? |
1A - no hydroxylation at 1 alpha 1B - 25-hydroxylase deficiency 2A - defect in vitamin D receptor gene 2B - Abnormally expressed hormone interferes with a functioning receptor |

