![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
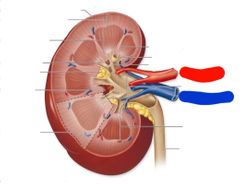
|
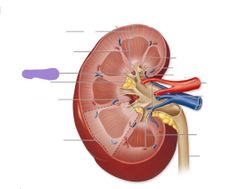
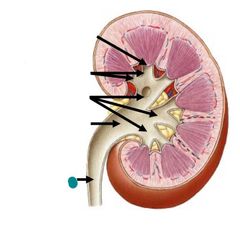
Red: renal artery Blue: renal vein |
|
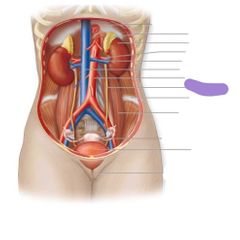
|
Ureter |
|
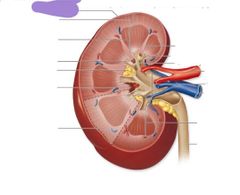
|
Fibrous capsule |
|
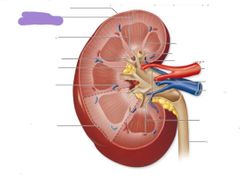
|
Renal cortex |
|
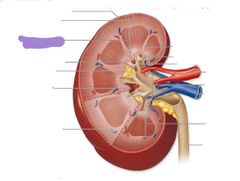
|
Renal medulla |
|
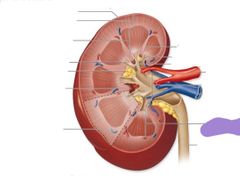
|
Renal pyramids |
|
|
Renal papilla |
|
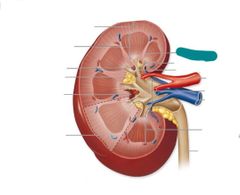
|
Renal columns |
|
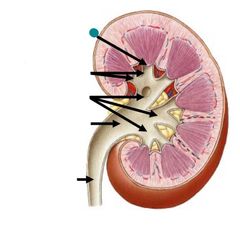
|
Renal papilla |
|
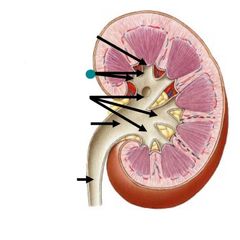
|
Minor calyces |
|
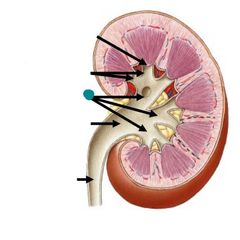
|
Major calyces |
|
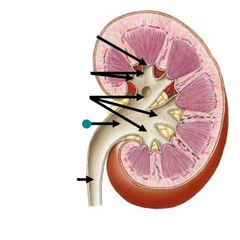
|
Renal pelvis |
|
|
Ureter |
|
|
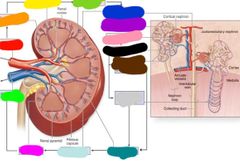
Blood flow through kidneys |
Renal artery Segmental arteries Interlobar arteries Arcuate arteries Interlobular arteries Afferent arteriole Glomerulus Efferent arteriole Peritubular capillaries of vasa recta Interlobular veins Arcuate veins Interlobar veins Renal vein |
|
|
Red: renal artery Orange: segmental arteries Yellow: interlobat arteries Green: arcuate arteries Blue: interlobular arteries Purple: afferent arteriole Pink: glomerulus Black: efferent arteriole Brown: peritubular capillaries Gray: vasa recta Teal: interlobular veins Light blue: arcuate veins Hot pink: interlobar veins Lime green: renal vein |
|
|
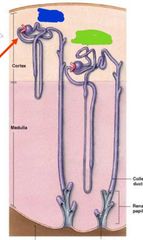
Blue: cortical nephron Green: juxtamedullary nephron |
|
|
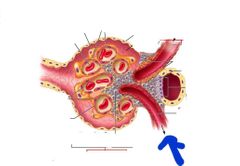
Efferent arteriole |
|
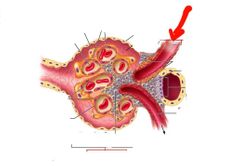
|
Afferent arteriole |
|
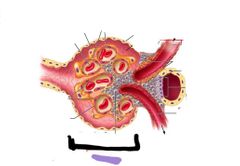
|
Renal corpuscle |
|
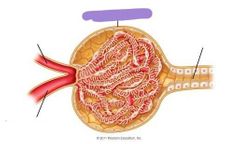
|
Bowmans capsule |
|
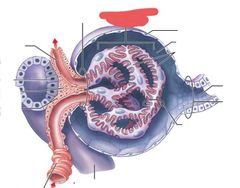
|
Glomerulus |
|
|
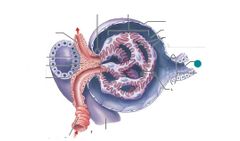
What makes up the renal corpuscle |
Bowmans capsule Glomerulus |
|
|
Proximal convoluted tubule |
|
|
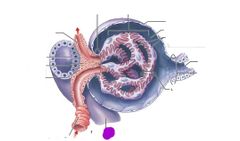
Yellow: loops of henle Red: thick loop of henle Orange: thin loop of henle |
|
|
Distal convoluted tubule |
|
|
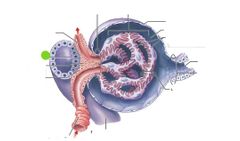
Macula densa |
|
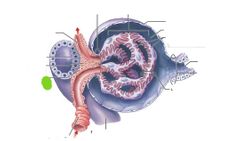
|
Juxtaglomerular cells |
|
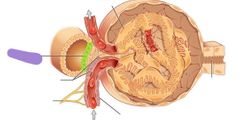
|
Macula densa |
|
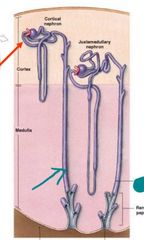
|
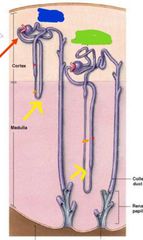
Collecting duct |
|

|
Red: medulla Orange: cortex Blue: renal corpuscle |
|
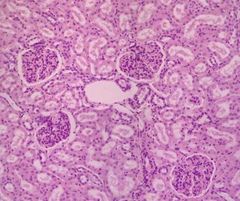
|
Cortex |
|
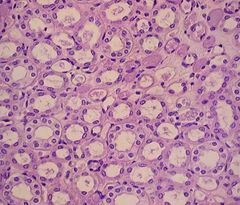
|
Medulla |
|
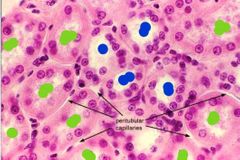
|
Blue: distal convoluted tubule Green: proximal convoluted tubule |
|
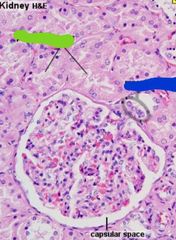
|
Blue: macula densa Green: proximal convoluted tubule |
|
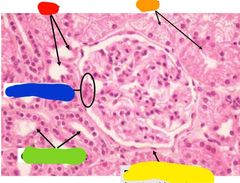
|
Red: distal convoluted tubule Orange: proximal convoluted tubule Yellow: bowmans caspule Green: collecting ducts Blue: macula densa |
|
|
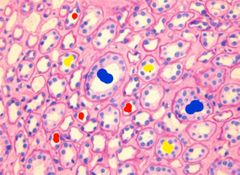
Blue: collecting ducts Red: thin loops of henle Yellow: thick loops of henle |
|
|
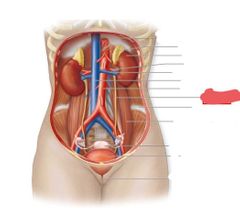
Ureters |
|
|
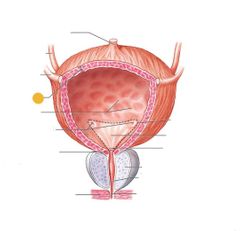
Detrusor muscle |
|
|
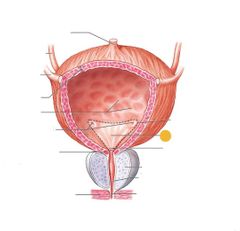
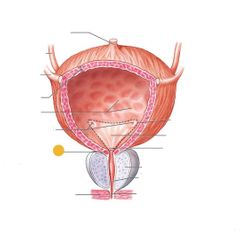
Trigone |
|
|
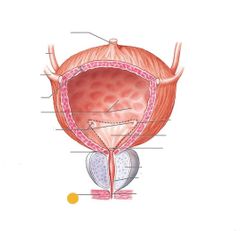
Internal urethral sphincter |
|
|
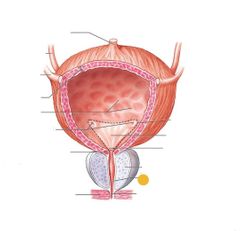
External urethral sphincter |
|
|
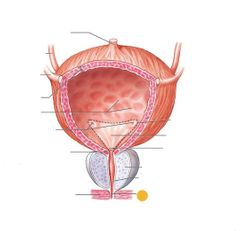
Prostatic urethra |
|
|
Membranous urethra |
|
|
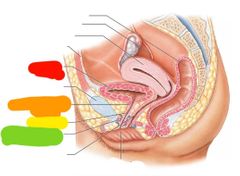
Red: urinary bladder Orange: internal urethral sphincter Yellow: urethra Green: external urethral sphincter |
|
|
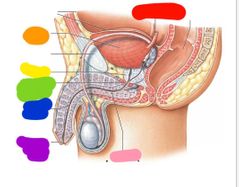
Red: ureter Orange: urinary bladder Yellow: prostate Green: external urethral sphincter Blue: spongy urethra Purple: dont need to know Pink: urethra |
|
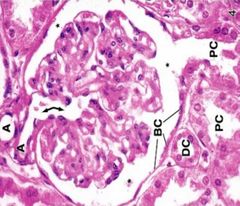
What am I |
Renal corpuscle |
|
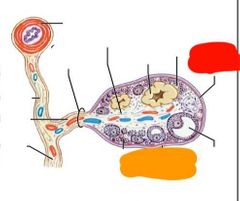
|
Red: tunica albuginea Orange: germinal epithelium |
|
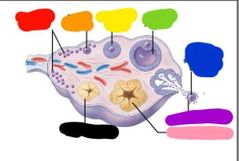
|
Red: primordial follicles Orange: primary follicle Yellow: secondary follicle Green: tertiary follicle Blue: released secondary oocyte Purple: corona radiata Pink: corpus luteum Black: corpus albicans |
|
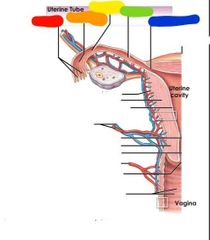
|
Red: fimbriae Orange: infundibulum Yellow: ampulla Green: isthmus Blue: uterine part |
|
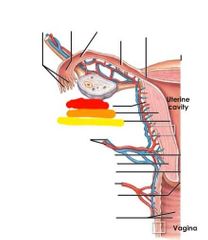
|
Red: perimetrium Orange: myometrium Yellow: endometrium |
|
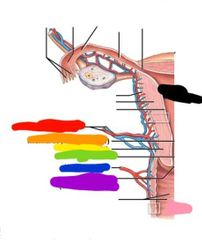
|
Red: uterine artery and vein Orange: internal os Yellow: isthmus Green: cervical canal Blue: vaginal artery Purple: external os Pink: vagina Black: uterine cavity |
|
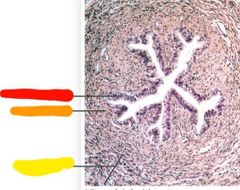
|
Red: columnar epithelium Orange: lamina propria Yellow: smooth muscle |
|
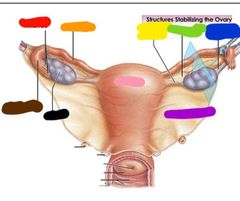
|
Red: fimbriae Orange: uterine tube Yellow: ovarian ligament Green: mesovarium Blue: suspensory ligament Purple: broad ligament Pink: uterus Black: ovary Brown: infundibulum |
|
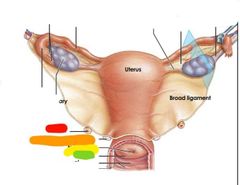
|
Red: ureter Orange: uterosacral ligament Yellow: external os Green: cervix |
|
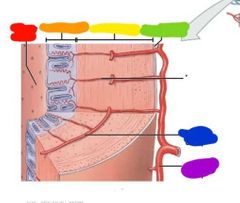
|
Red: uterine cavity Orange: endometrium Yellow: myometrium Green: perimetrium Blue: arcuate artery Purple: uterine artery |
|
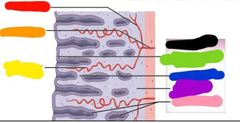
|
Red: straight artery Orange: radial artery Yellow: spiral artery Green: simple columnar epithelium Blue: functional layer Purple: basal layer Pink: uterine gland Black: endometrium |
|
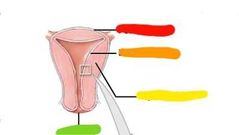
|
Red: perimetrium Orange: endometrium Yellow: myometrium Green: cervix |
|
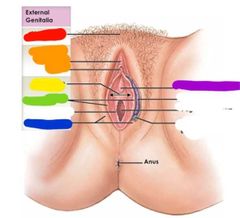
|
Red: mons pubis Orange: clitoris Yellow: vestibule Green: labia minora Blue: labia majora Purple: urethral opening |
|
|
Development is separated into what 2 periods |
Prenatal and postnatal |
|
|
What is embryology |
The study of developmental changes that occur during the prenatal period |
|
|
When is prenatal development |
Conception (fertilization) to childbirth |
|
|
When is postnatal development? |
From birth to maturity |
|
|
Subdivision of prenatal development |
Pre-embryonic development Embryonic development Fetal development |
|
|
When is the pre-embryonic development |
-Fertilization to implantation -2 weeks |
|
|
When does embryonic development occur? |
Implantation to the end of the eighth week of pregnancy |
|
|
When does fetal development occur |
9th week of pregnancy to birth |
|
|
What is fertilization |
The joining of 2 haploid gametes to create a diploid zygote |
|
|
What are gametes |
Sperm and oocytes -each one contains 23 chromosomes |
|
|
Function of spermatozoon |
Delivers the paternal chromosomes to the ovum |
|
|
Function of the ovum |
-provides the maternal chromosomes -provides all organelles -provides nourishment for embryonic development |
|
|
What is an immature ovum |
Oocyte |
|
|
Where does fertilization occurs in... |
The ampulla of the uterine tube |
|
|
How many sperm enter the vaginal canal and how many make it to the uterine tubes |
-200 million sperm -10,000 make it |
|
|
How many sperm make it to the egg |
Less then 100 |
|
|
How long to the sperms journey to the egg take |
30 minutes to 2 hours |
|
|
What complicates the fertilization of the oocyte |
-corona radiata -oocyte metabolism suspended -oocyte is in metaphade of meiosis II |
|
|
What do sperm use to penetrate the corona radiata |
Hyaluronidase |
|
|
What releases hyaluronidase |
The acrosomal cap of the sperm |
|
|
What happens once the sperm gets past the corona radiata? |
-Sperm and oocyte membrane fuse and sperm enters ooplasm -and oocyte now completes meiosis II |
|
|
What keeps more then 1 sperm from fertilizing the oocyte? |
The membrane fusion when one sperm enters the egg and then becomes unresponsive to other sperm |
|
|
What is Amphimixis |
The fusion of the 2 pronuclei |
|
|
Pronucleus formation |
-haploid nuclear material in egg forms the female pronucleus -haploid nuclear material in sperm becomes the male pronucleus |
|
|
What needs to occur for diploid zygoto to form |
Pronucleus formation and amphimixis |
|
|
How long is the gestation period |
9 months |
|
|
What is prenatal development divided into |
3 trimesters |
|
|
What happens in the first trimester |
Rudiments of all organs appear |
|
|
What happens in the second trimester |
-Organs and organ systems develop further -fetus looks like a human |
|
|
What happens in the 3rd trimester |
-phase of rapid growth -most organ systems become functional |
|
|
What trimester do 80% of losses occur |
The first trimester |
|
|
What percent of pregnancies end in miscarriage |
26% |
|
|
What causes miscarriage most the time |
-spontaneous chromosomal non disjunction |
|
|
What causes trisomy |
Error in chromosomal attachment to spindle fibers from male or female |
|
|
How long is the first trimester |
1-12 weeks |
|
|
What 4 events occur with in the first trimester |
-cleavage (sequence of cell division) forms blastocytes -implantation in endometrial lining -placentation (formation of the placenta) -embryogensis (development of embryo |
|
|
Cleavage/repeated cell division of pre-embryo results in smaller cells called |
Blastomeres |
|
|
After 3 days of cell division the blastomeres form a solid ball called the |
Morula |
|
|
Cells migrate to the edge of the morula creating a hallow ball of cells called... |
The blastocyst |
|
|
Whats the blastocoele |
Fluid filled cavity of the blastocyst |
|
|
What cells make up the outer layer of the blastocyst |
Frophoblast |
|
|
What is the inner cell mass |
The cluster of cells that form at one edge of the blastocyst |
|
|
What provifes nutrients to developing embryo |
Trophoblast cells |

