![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Stroke is:
|
sudden neurological dysfunction due to a vascular cause.
|
|
|
Types of Ischemic Stroke:
|
1) Cardioembolic stroke (about 25%)
*Strokes of cardiac origin *Includes atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease 2) Small vessel disease (about 25%) *Strokes due to occlusion of vessels 0.05-0.5 mm *Often due to HTN, diabetes 3) Large vessel disease (about 25%) *Strokes due to occlusion of vessels 1-4 mm (carotid [3-4 mm], middle cerebral artery [1-2 mm]) *Often due to high cholesterol 4) Rare and unknown cause (about 25%) *Includes stroke due to arterial dissection (tear), blood coagulation abnormality |
|
|
Superior branch of MCA?
Inferior? |
M2
M1 |
|
|
Small vessel disease is most often attributed to:
|
Hypertension
|
|
|
Left middle cerebral artery (MCA) stroke:5
|
-Aphasia
-Right hemiparesis (weakness); face and arm more than leg -Right hemianesthesia (sensory loss) -Right hemianopia (visual loss on the right out of each eye) -Deviation of eyes to left |
|
|
Right middle cerebral artery (MCA) stroke
|
-Neglect to left side.
-Left hemiparesis (weakness); face and arm more than leg. -Left hemianesthesia (sensory loss) -Left hemianopia (visual loss on the left out of each eye) -Deviation of eyes to right |
|
|
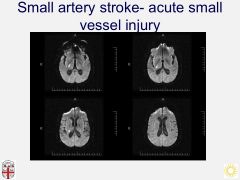
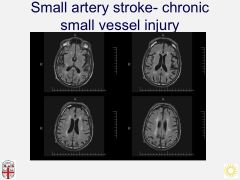
Lacunar stroke:
*3 syndromes |
-Typically one side weakness W/O aphasia or neglect.
-Brainstem lacunes may have crossed findings e.g. *Weber syndrome= 3 + contraletaral hemiparesis (midbrain) *Benedikt syndrome= 3 + contraletaral dysmetria (midbrain) *Millard-Gubler syndrome= 6 + 7 + contraleral hemiparesis (pons) -IIIrd palsy -INO (MLF compromise) |
|
|
Right MLF stroke=
|
Right INO.
|
|
|
Spinal cord infarction:
|
-Affects anterior portion of spinal cord (ASA)
-Occurs typically in setting of AAA rupture or repair with hypoperfusion -There may be associated renal failure -Impaired motor and pinpoint/temp -Preserved position/vibration |
|
|
A left middle cerebral artery (MCA) stroke is typically associated with all of the following except:
A. Aphasia B. Gaze deviation to the right C. Right side weakness D. Right hemianopia |
B. Gaze deviation to the right
|
|
|
A left lacunar stroke is typically associated with all of the following except:
A. Aphasia B. Right hemiparesis C. Right hemianesthesia D. Right hemiataxia |
A. Aphasia
|
|
|
Acute stroke treatment: proven treatments
|
-tPA within 4.5 hours
the sooner the better! (NNT 3 within 90 minutes, 8 within 180 minutes, 23 within 270 minutes) -Aspirin within 48 hours *NNT 100 *Use if pt not eligible for tPA -Stroke units *NNT 20-30 |
|
|
tPA basic facts:
|
-B/t 0-4.5 hours
-Time last known well (25% of patients wake up with stroke. Timed to when they went to sleep). -CT: must have no hemorrhage -BP must be < 185/110 -Glucose must be b/t 50-400 -Platelets must be > 100 -INR should be < 1.7 (if not on warfarin, no need to wait) -No “recent” procedures or events (1-3 months for surgery, MI, stroke) |
|
|
Acute stroke treatment: unproven
|
-Heparin and heparinoids
*Not even in atrial fibrillation or large vessel atherosclerosis (such as carotid stenosis) Oxygen Intravenous fluids Laying head of bed flat Modifying blood pressure Intra-arterial therapy |
|
|
ABCDE of stroke treatments:
|
-Antiplatelets/anticoagulants
-BP control -Carotid repair/Cholesterol lowering/cessation of smoking -Diet -Exercise |
|
|
antiplatelet meds:
|
[aspirin, aspirin/dipyridamole (Aggrenox), cilostazol (Pletal)*, clopidogrel(Plavix)])
-Best choice for non-atrial fibrillation stroke -Avoid combination of aspirin and clopidogrel for more than 12 months |
|
|
anticoagulant meds:
|
[apixaban (Eliquis, dabigatran (Pradaxa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), warfarin (Coumadin)]
Best choice for atrial fibrillation stroke |
|
|
BP control to prevent stroke:
|
-Ideal target to be determined
-In general, less than 140/90 recommended -Less than 130/80 may be helpful for lacunar strokes -Use pharmacological (ACE inhibtors, ARBs, diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ß-blockers, alpha blockers) AND non-pharmacological (reduced salt diet, DASH diet) measures |
|
|
Carotid a repair to reduce stroke risk and recurrence:
|
Stroke patients with more than 70% narrowing of the internal carotid artery on the same side of stroke have a significant reduction in stroke risk compared to medical therapy alone-- 9% risk versus 26% over 2 years
50-69% narrowing with symptoms 16% versus 22% over 5 years >60% narrowing and no symptoms 5% versus 11% over 5 years |
|
|
Cholesterol lowering to prevent stroke:
|
-LDL target is < 100
-HDL > 40 recommended for men ; > 50 for women -Triglyceride target < 150 -Reduction can be achieved with diet, exercise and medications (including statins) -Some statin effects appear to be independent of lipid lowering No proven clinical benefit of niacin, gemfibrozil |
|
|
Cessation of smoking to prevent stroke:
|
-Average number of quit attempts is 7
-Additional measures that can increase success include nicotine patch, buproprion (Zyban, Wellbutrin), and varenicline (Chantix*) -*Depression and suicidal ideation are common after stroke and may be exacerbated by varenicline (Chantix) |
|
|
Diet to prevent stroke:
|
-In general, low fat diet recommended
-Increased consumption of fruits, vegetables -Examples include DASH diet, Mediterranean diet DASH diet is associated with lower blood pressure and weight loss -Mediterranean diet is associated with reduced recurrent MI and death |
|
|
Exercise to prevent stroke:
|
-30 minutes on most days of the week recommended
-Poor exercise capacity is associated with an increased risk of stroke (as powerful a risk factor as hypertension) -Tendency after stroke to reduce physical activity -Patients should be encouraged to increase mobility and activity |
|
|
In a patient with atrial fibrillation and stroke, the treatment of choice for secondary stroke prevention is:
A. Aspirin B. Clopidogrel (Plavix®) C. Aspirin/Dipyridamole combination (Aggrenox®) D. Warfarin (Coumadin®) |
D. Warfarin (Coumadin®)
|
|
|
A patient with a left MCA stroke had 75% stenosis of the left internal carotid artery. Of the following, the best treatment to prevent a stroke over the next 2 years is:
A. Aspirin B. Clopidogrel (Plavix®) C. Carotid endarterectomy D. Smoking cessation |
C. Carotid endarterectomy
|
|
|
Which of the following is not recommended long-term after stroke?
A. Aspirin B. Blood pressure lowering C. Exercise D. None of the above |
D. None of the above
|
|
|
Lacunar artery:
|
A single deep penetrating artery that arises directly from the constituents of the Circle of Willis, cerebellar arteries, and basilar artery.
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|

