![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
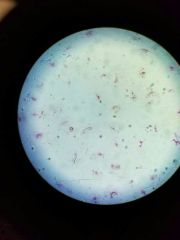
|
Noctiluca |
|
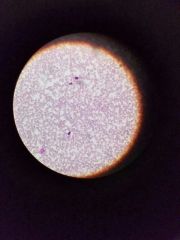
|
Trypanosoma cruzi (in blood smear) |
|

|
Opalina |
|
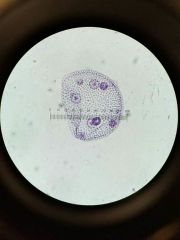
|
Volvox |
|
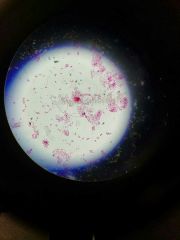
|
Astasia klebsi |
|
|
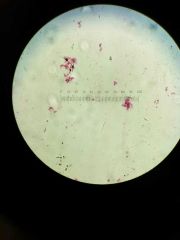
Ceratium |
|
|
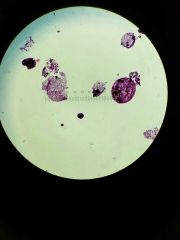
Volvox flagella |
|
|
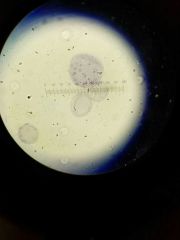
Volvox sexual stages |
|
|
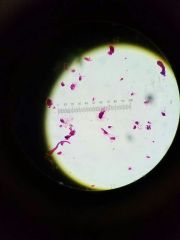
Trichobymphas (termite flagellates) |
|
|
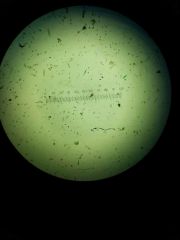
Mixed (marine) diatoms |
|
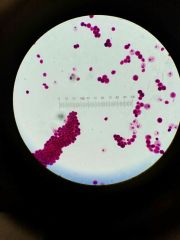
|
Chlamydomonas flagella |
|
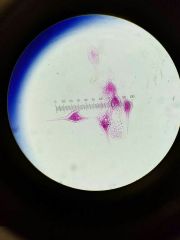
|
Dinoflagellates |
|
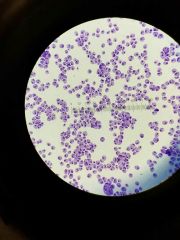
|
Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
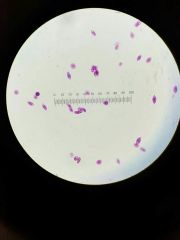
|
Euglena |
|
|
Phytoflagellates (5) |
-plantlike -mostly autotrophic -(chloroplasts, photosynthesis) -unicellular, may make chains -marine and freshwater -free-living and symbiotic relations |
|
|
Phylum Haptophyta (4) |
-Marine
-Have two unequalflagella -Have specialized organelle called haptonema -Some have calcareous exoskeleton -(coccolithophores) |
|
|
Phylum Cryptophyta (3) |
-freshwater and marine -"pocket" with two unequal flagella -most autotrophic, some mixotrophic |
|
|
Phylum Chlorophyta Order Volvocida (5) |
-unicellular, mostly colonial -2-4 apical flagella per cell -autotrophic, single chloroplast -have stigma (eyespot) -freshwater |
|
|
Phylum Heterokonta (3) |
-extremely diverse -all have heterokont life stages -motile, asexual stage -two different shaped flagella -most are algae -some animal- or fungus-like |
|
|
Class Bacillariophyceae (5 + common name) |
Diatoms or "Golden Plants" -unicellular, many chain -autotrophs, high carotenoid concentrations -2 unequal flagella (sexual stages only) -silica shell (conspicuous spines or ridges) -asexual via binary fision |
|
|
Class Opalina (5) |
-cillia-like organelles -multi-nucleated -unicellular -commensalistic -(in lower GI tract/colon) -sexual reproduction -Syngamy (anisogamy) |
|
|
Phylum Dinoflagellata (6 + common name) |
Dinoflagellates or "Fire Plants" -bioluminescent -most autotrophic, some hetero -marine and freshwater -mostly armored (some freshwater not) -asexual repro (binary fission and cysts) -2 flagella -Annulus and Sulcus |
|
|
PhylumEuglenozoa
Class Euglenoidea (7 + meaning of name) |
"eu" true "glene" eye -unicellular -flagellated (2, only 1 visible) -have stigma -Asexual repro -no rigid cell wall -autotrophic -freshwater |
|
|
Phylum Euglenozoa Class Kinetoplastida (3) |
-1-2 flagella emerge from kinetoplast -single large mitochondrial disc of DNA -mostly parasitic -vertebrate host, arthropod vector -asexual reproduction -all binary fission |
|
|
Zooflagellates (4) |
-unicellular -heterotrophic -no chloroplast or stigma -flagellated -symbiotic -commensalistic, mutualistic, parasitic |
|
|
Phylum Axostylata Order Trichomonadida (4) |
-commensal or parisitic -parisitic are obligate with direct life cycle -multiple anterior and single posterior flagella -in digestive or reproductive tract of host -asexual repro (binary fission of trophozoites) |
|
|
Phylum Axostylata Order Hypermastigida (4) |
-multiflagellated (a lot of flagella) -asexual repro -mutualistic -digestive tract of host, help digest cellulose -shed with host exoskeleton |
|
|
Phylum Retortamonada Order Diplomonadida (4) |
-bilateral symmetry -twice the number of features -internal and external -asexual repro (binary fission of trophozoites) -mostly parasites -obligate, direct life cycle |
|
|
Phylum Axostylata (6) |
-some have axostyle -no mitochondria -have golgi bodies -prasitic or mutualistic -no cyst formation -multiple organ systems of vertebrates |
|
|
Phylum Retortamonada (6) |
-some have axostyle -no mitochondria -no golgi bodies -parasitic, commensalistic, and mutualistic -cyst formation common -intestinal tracts of vertebrates |
|
|
Phylum Choanoflagellata (4) |
-distinct "choano" collar -Marine and freshwater -colonial and solitary -1 flagella per cell -in middle of circle of collar |

