![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Insect ecology |
Study of relationships. |
|
|
Metapopulations |
Population that is composed of a separate but interacting set of subpopulations. Common in insects and herbivores. Independent networks. Source and sink |
|
|
Source and sink |
Source- output , sink - recieve |
|
|
Carrying capacity |
K selected individuals mostly. Produce lower numbers over long lifespan. With high parental investment |
|
|
High growth rate |
R selected. Produce high numbers with minimal parenting and short lived lives |
|
|
Most striking aspect of insect communities |
Precieved environment in a much finer grained fasion |
|
|
Insect niches |
Can specify. Many freshwater insects specialize in narrow ranges or temp. Flows. And oxygen |
|
|
niche partitioning by leaf miners on white oak |
up to 19 species of leafminers during a season in NE. 3 to 4 miners can share a leaf. specialists: new vs old leaf, midrib (vein), leaf edge vs middle |
|
|
Exploitation Competition |
Free for all, first come first served. most common type of competition in leaf minors. |
|
|
Interference Competition |
Direct interference; distribution of one species ability to use resources. ex. ants chemical release. usually aggressive and fight/defend |
|
|
examples of interface competition |
1. flour beetles- constant conditioning results in extinction of one species.
2. tiger beetles in AZ, habitat partitioning, tropic partitioning(mandible size) 3. Aphytis wasps- biological control agents, three seperate introductions where each species nearly replaced the other. |
|
|
Gause's Competitive Exclusion Principle |
the idea that 2 complete competitors cannot coexist, or that no 2 species can share the same niche. |
|
|
Competitive displacement in New England Lady beetles |
started with the c-9 lady beetle, then c-7 lady beetle, now Asian lady beetle. |
|
|
HHS theory on insect herbivory (hairston, smith, and slobodkin) |
the world is green (food for herbivores) so there should be something to limit the herbivore numbers. parasitoids, pathogens and predators must play a role. OR plants are good at defending themselves. HHS theory= limiting factors could be trophic level dependent. |
|
|
Economic Injury Level (EIL) |
pest population density when cost of control measures are thought to be equivalent to amount of injury to crop. |
|
|
Economic Threshold (ET) |
point where control measures should be effected to prevent pest population from overshooting. |
|
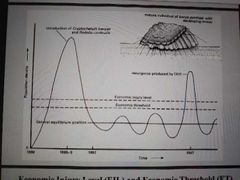
|
Showing the level of control and the threshold |
|
|
important data for integrated pest management system-
|
affect by weather, activities of adjacent farmers, natural enemies, other insects present, genetics of crop, value of crop. |
|
|
agriculture systems as artificial ecosystems
|
highly distributed communities, similar to early successional stages, usually monocultures, reduce natural enemies, well fertilized, crops have natural pest resistance bred out for faster growing and higher yeilds. |
|
|
Integrated pest management (IPM) |
-multi faced approach aimed at lowering pesticide dependency. keep insects from reaching EIL. the key is an integrated approach based on sound knowledge of abiotic and biotic factors. *broad, env friendly, results in positive long term outcomes |
|
|
IPM Arsenal |
Chemical controls: pesticides, insect growth regulators, neuropeptides. -biological control, insectisides, genetic engineering, cultural controls, pheremores.. |
|
|
Chemical Pesticides |
insecticides, herbicides, fungicidesm miticides ect. pros- works fast, immediately available, con- health risks, DDT. - chem pesticides save thousands of lives and increases food production. |
|
|
Disadvantages to pesticides |
pesticide resistance, indirect cost (social, env, health), ground water contamination, poisoning, increased cases of cancer, non target impacts |
|
|
secondary pest |
a pest that would not have become one if the pesticide had not been applied (internal feeders) |
|
|
Insect growth regulators (IGR) |
1. juvenoids: Juvenile hormones effective against insects where adults are pests. (fleas, ants) 2. antijuvenile hormones (premature maturation) 3. chitin synthesis inhibitors (die at molt) 4. ecdysone disruptors/molting hormone 5. neuropeptides (disrupt develop. and rep.) |

